Support for C++20 Modules
Modules were introduced in the C++20 standard. They work as alternative to some use cases of header files and help share declarations and definitions across translation units.
tip
For now, CLion does not consider .cpp files to be modules, so it's recommended that you use other extensions (for example, .cppm).
CLion collects information from .ixx, .cppm, and .mxx files, parses export module {name} statements and creates mappings between {name} and module filenames. Then, the mappings are passed to the Clangd engine and used to provide code assistance and highlighting.
If you update the module’s code or rename the module, CLion will automatically parse the changes. The information collected from modules is preserved between the IDE restarts.
CLion's support for modules has been tested in the following environments:
CMake, Ninja generator, Visual Studio C++ toolchain.
CMake, Visual Studio generator, Visual Studio C++ toolchain.
CMake, Clang toolchain with compiler flags.
tip
For details on project configuration, see CMake generators, MSVC, Compilers, and Quick CMake tutorial.
CLion highlights module keywords (
import,export, andmodule):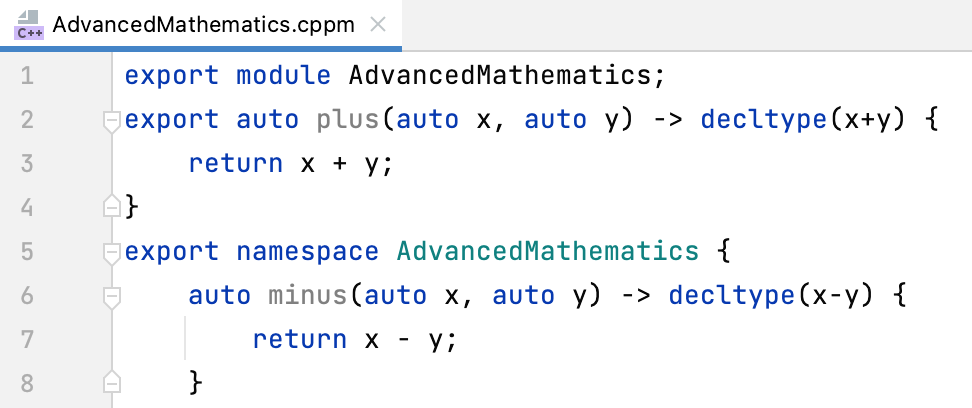
Completion works for symbols from modules:
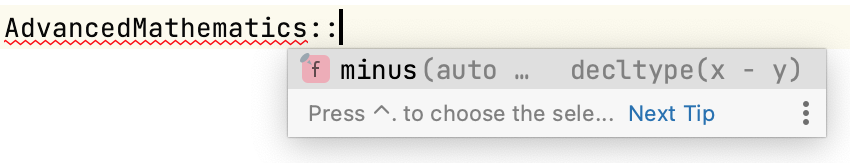
You can navigate between declarations and definitions of symbols from modules using Ctrl0B:
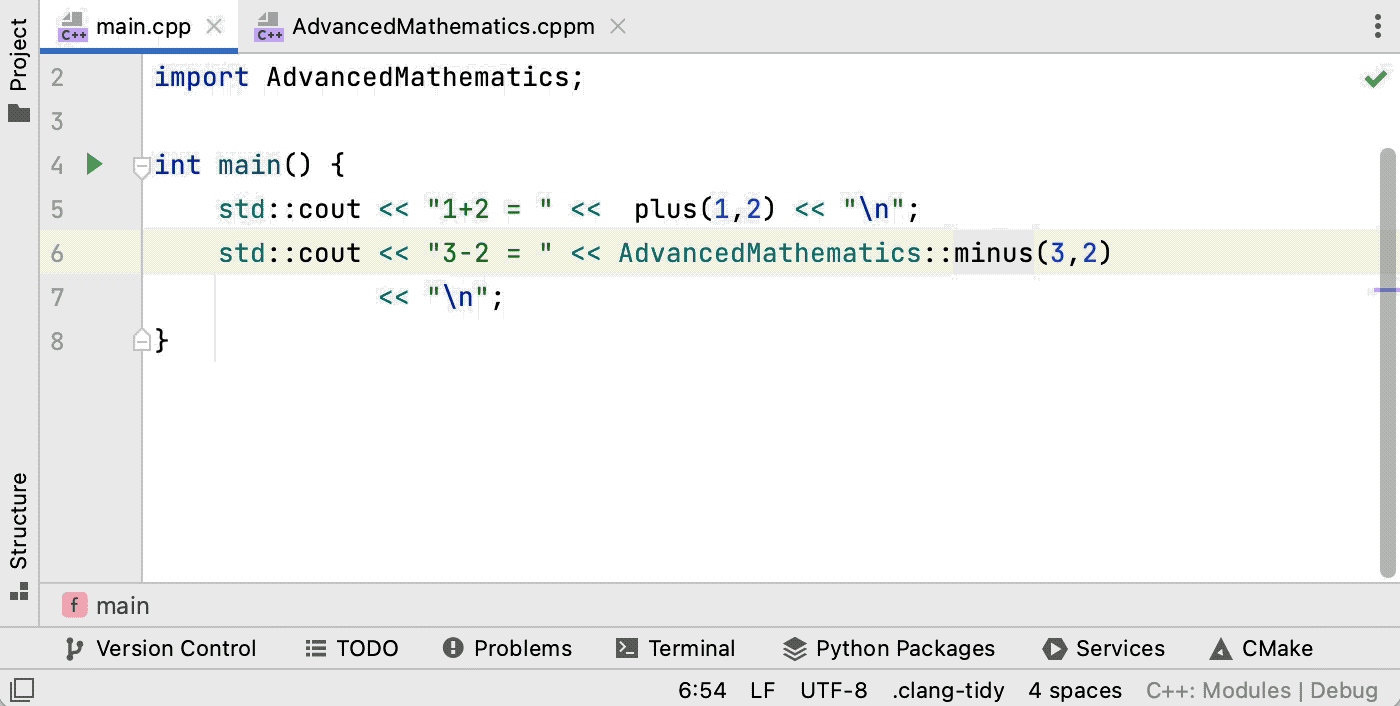 Gif
GifFind Usages and refactorings are available inside modules.
There are also early versions of the Rename, Change Signature, and Extract refactorings that work across module boundaries (for now, they only work for files opened in CLion).
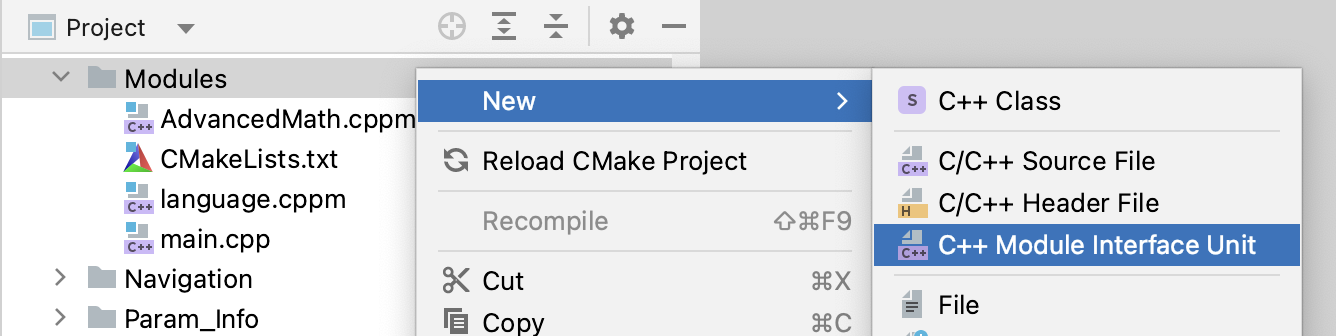
In CLion, you can add new modules to your project automatically.
In the project tree, right-click the folder where you want to add a module and select New | C++ Module Interface Unit:
Specify the module name, its type (extension), and whether you want CLion to add the newly created module to an existing CMake target:
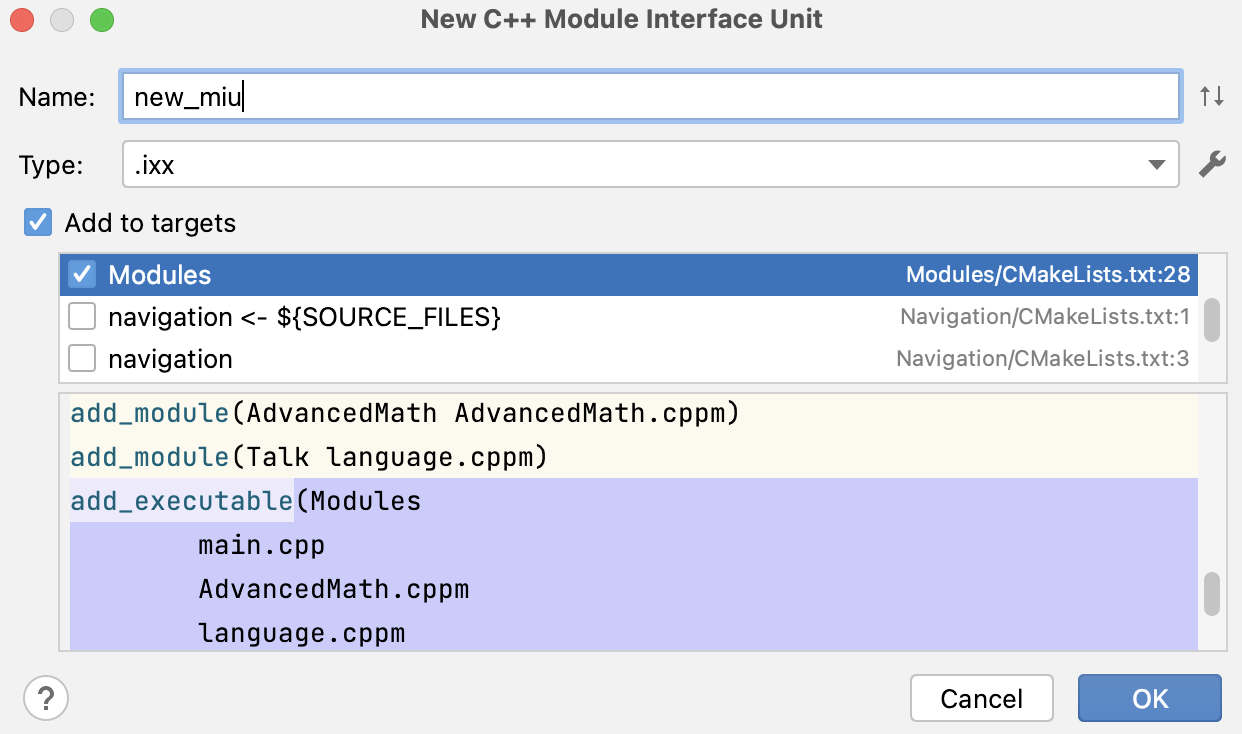
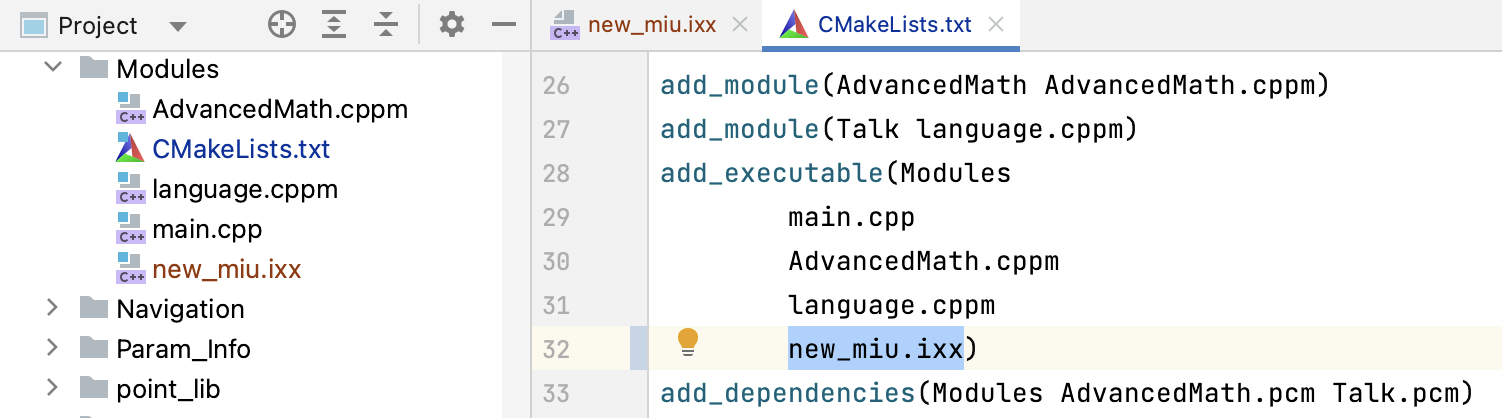
A new module will be created in your project tree and added to the CMakeLists.txt script if you chose that option:
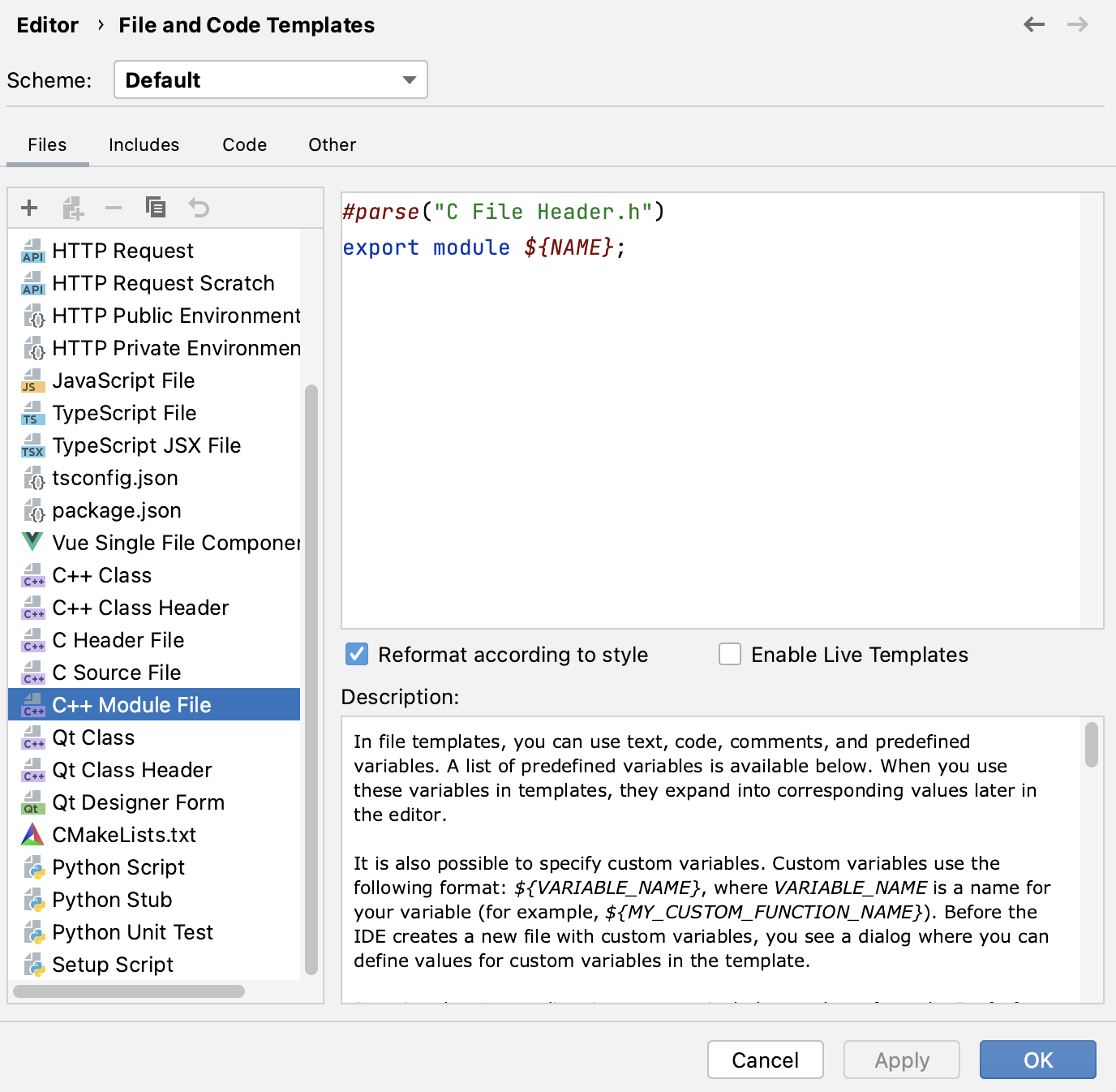
You can edit the template that CLion uses when creating module files in Settings | Editor | File and Code Templates:
Thanks for your feedback!