Support for C++20 Concepts
Concepts are one of the major language features of the C++20 standard. They provide a way to put compile-time constraints on template arguments, helping you ensure the templates meet your expectations.
tip
To learn more about Concepts, watch this talk from CppCon 2019 by Saar Raz, the author of concepts implementation in Clang: C++20 Concepts: A Day in the Life
The compiler you are using should support the C++20 Concepts feature.
Use Clang10 or later. You can check the status of a particular C++20 feature in C++ Support in Clang.
Use GCC 10 or later. The implementation of Concepts in GCC10 fully conforms to C++20.
MSVC supports Concepts since Visual Studio version 16.3. Note that terse syntax (void fn(MyConcept auto mc)) is not supported yet.
Adding #define __cpp_lib_concepts might be required for correct resolve (see the comments to the Microsoft announcement).
CMake project
When creating a new project, select C++20 in the Language standard field of the New Project wizard.
For an existing project, set the
CMAKE_CXX_STANDARDvariable at the beginning of CMakeLists.txt:set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 20)
Makefile project
Set the CXXFLAGS variable in the Makefile:
CXXFLAGS += -std=c++20tip
Concepts support in CLion works the same regardless of the project format: CMake, compilation database, or Makefiles. Make sure to set the language standard to C++20 and use an appropriate compiler.
By default, CLion's code completion is performed by the Clangd-based engine. When working with Concepts, use the default option Only Clangd completion or switch to Clangd completion merged with builtin.
Go to Settings | Languages & Frameworks | C/C++ | Clangd.
In the Code completion section, select either Only Clangd completion or Clangd completion merged with builtin.
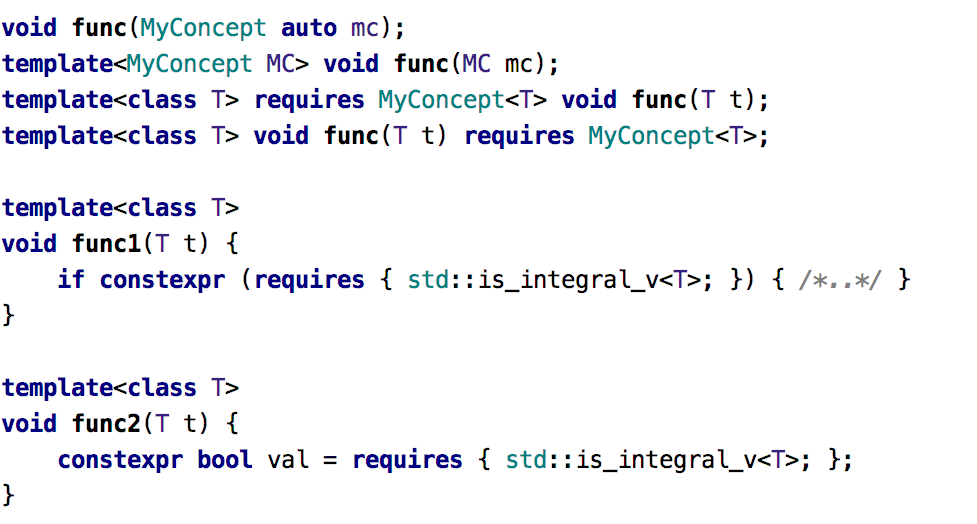
CLion parses and highlights all the standard syntax forms for concept and requires:
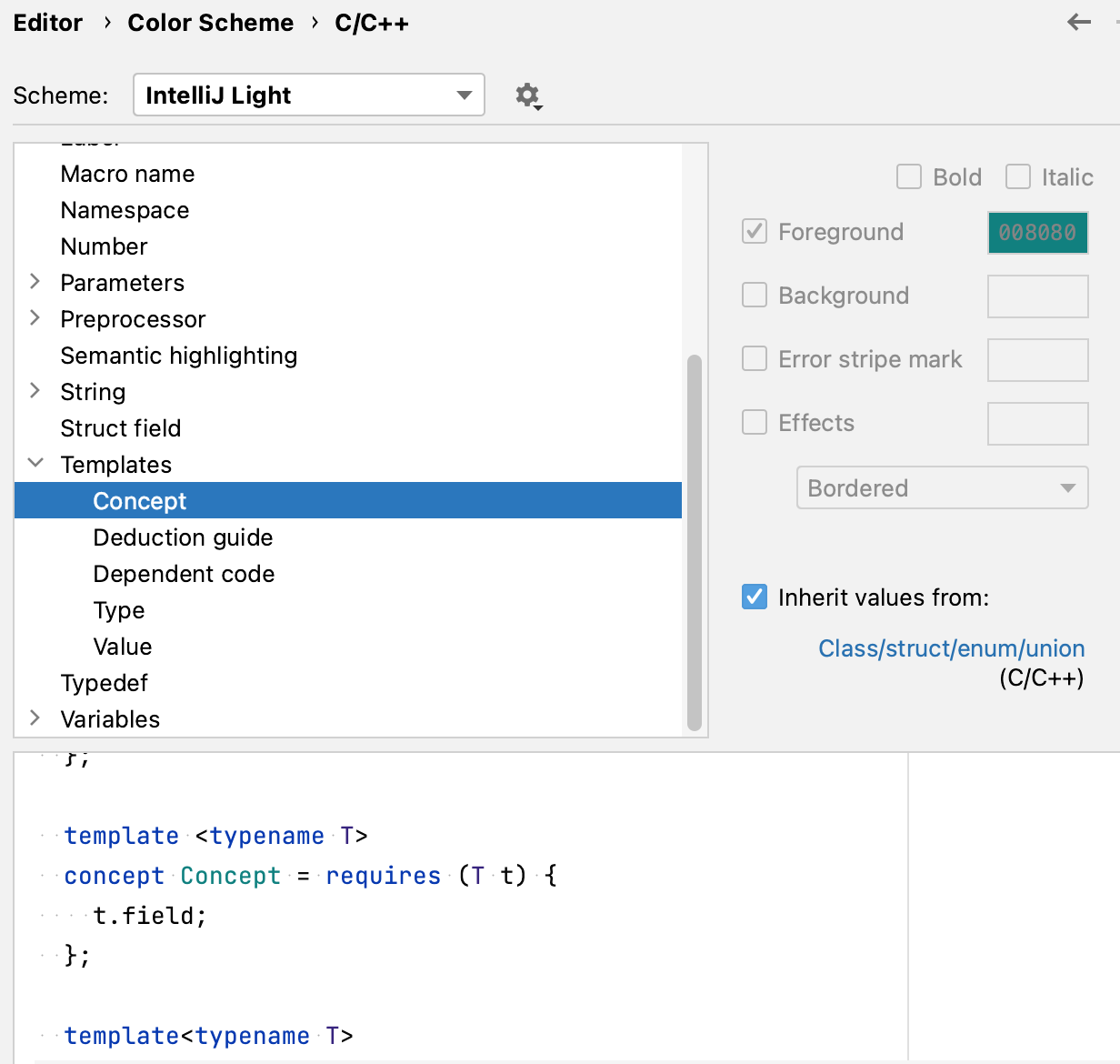
You can tune the highlighting settings for Concepts in Settings | Editor | Color Scheme | C/C++ | Templates | Concept. By default, the scheme is inherited from C/C++ Class/struct/enum/union.
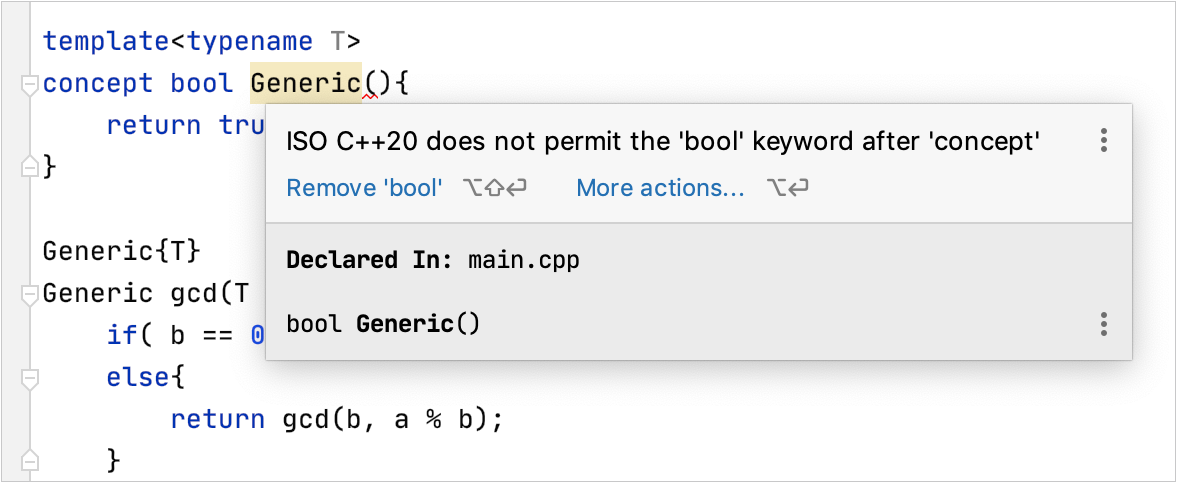
A set of inspections with quick-fixed is available for your code using Concepts.
Among the inspections, some checks come from the compiler:
CLion provides two dedicated inspections for Concepts, Unused concept and Unconstrained variable type. You can configure them in Settings | Editor | Inspections | C/C++:
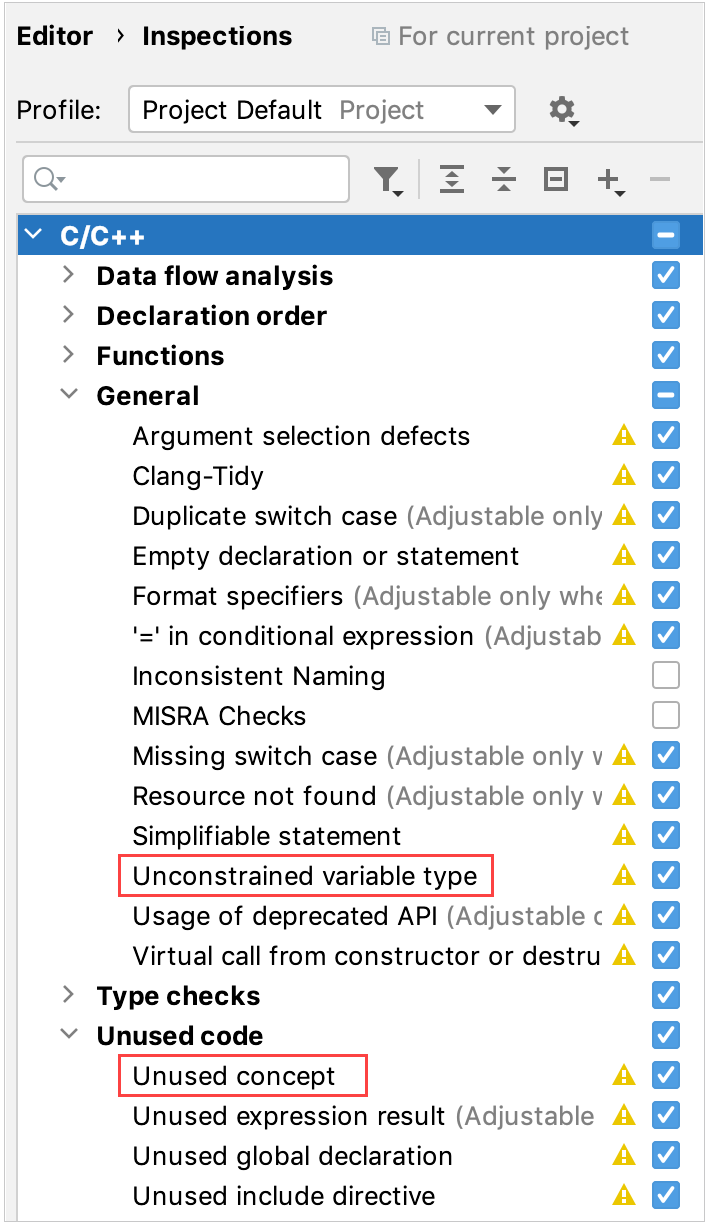
Concepts are also covered by all the relevant Unused code inspections such as Unused include directive.
The Unconstrained variable type inspection suggests constraining local variables declared as auto if the result of a constrained expression or function call is assigned to them. This inspection is disabled by default on Windows.
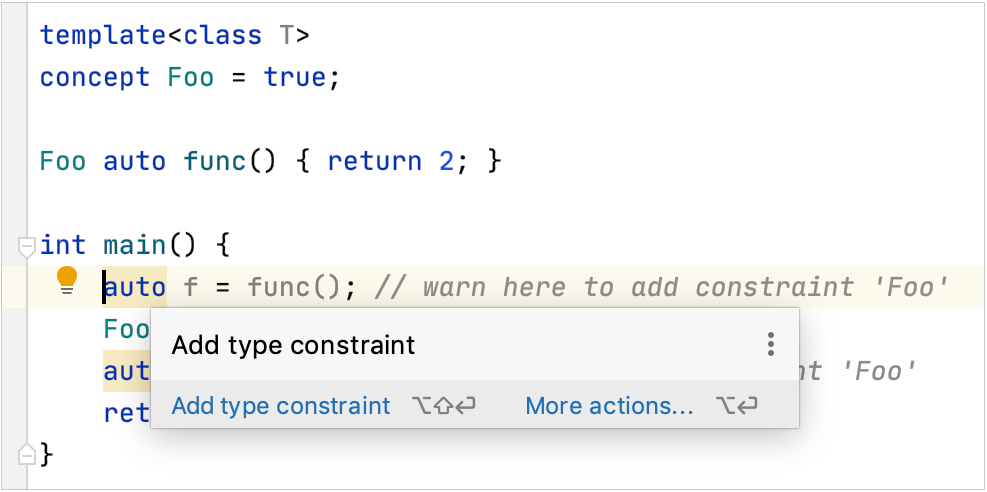
Code completion for Concepts is available in the following cases:
Completion for template type parameters that are constrained:
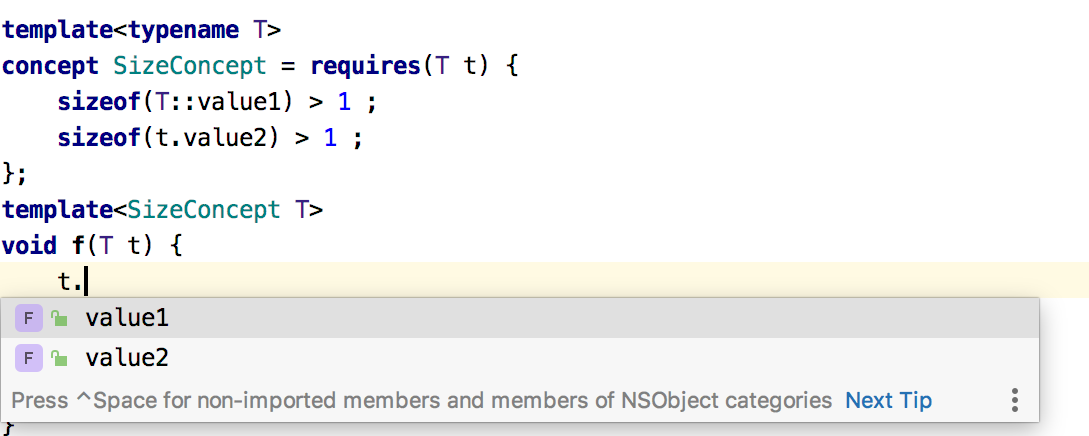
Completion for types constrained by
std::is_base_of<MyBase, T>andstd::is_same<Other, T>.The list of suggestions on
Tinstd::is_base_of<MyBase, T>andstd::is_same<Other, T>includes the options fromMyBaseandOther, respectively: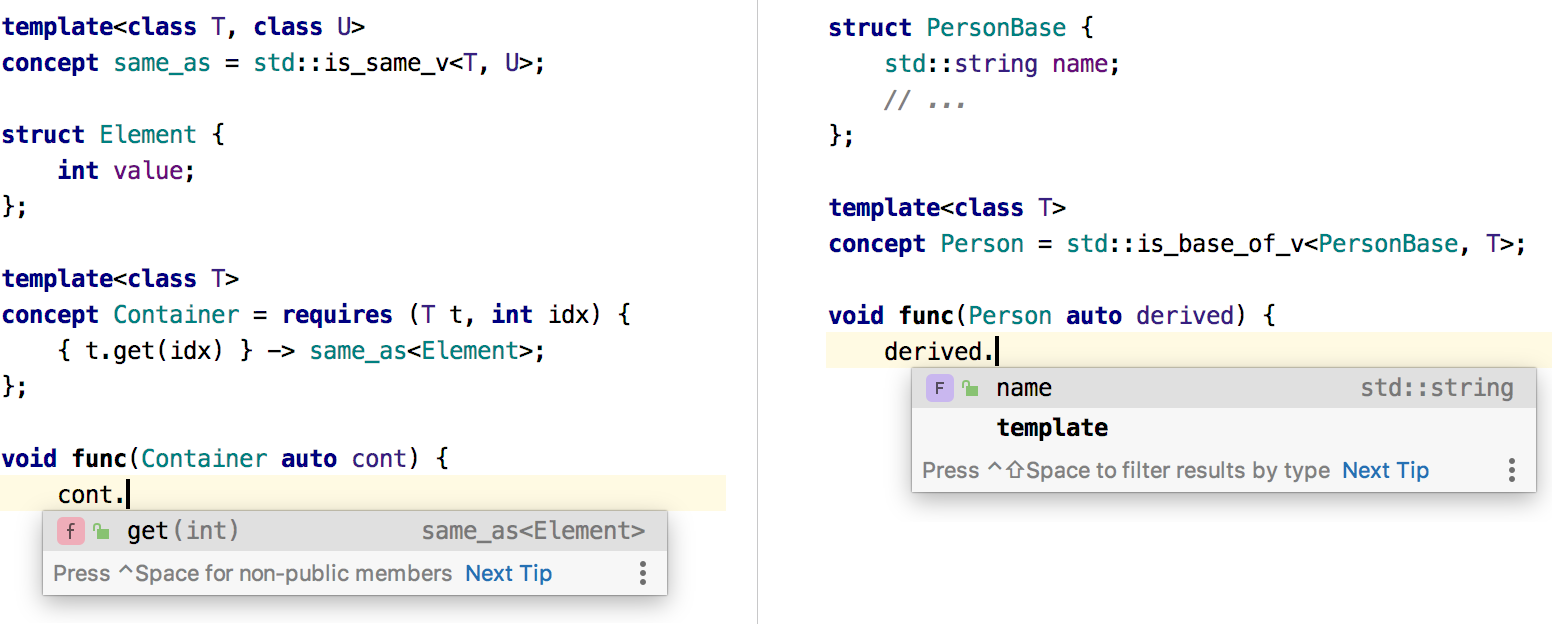
Note that completion for this case works only if
MyBaseandOtherare concrete types (not template types).
Rename refactoring and navigation actions like Go to Definition and Find Usages are also supported for code with Concepts.
Thanks for your feedback!