Connect to MS SQL server
Prerequisites
Microsoft SQL Server 2019 (Express Edition) – download link from the Microsoft site
Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio 18.8 - download link from the Microsoft site
DataGrip 2019.1 and later – download link from the JetBrains site
This topic gives you an example of how you can configure Microsoft SQL Server and create a connection to it from DataGrip. If you already have Microsoft SQL Server installed and configured, consider jumping to the section that describes a creation of a database connection in DataGrip.
Step 1. Configure the SQL Server Configuration Manager
To open SQL Server Configuration Manager, open the Search dialog on Windows and type SQLServerManager15.msc (for Microsoft SQL Server 2019). Double-click the found result.
If you use other versions of Microsoft SQL Server, change the second digit before .msc or check the following locations:
SQL Server 2019: C:\Windows\SysWOW64\SQLServerManager15.msc
SQL Server 2017: C:\Windows\SysWOW64\SQLServerManager14.msc
SQL Server 2016: C:\Windows\SysWOW64\SQLServerManager13.msc
SQL Server 2014 (12.x): C:\Windows\SysWOW64\SQLServerManager12.msc
SQL Server 2012 (11.x): C:\Windows\SysWOW64\SQLServerManager11.msc

Run the SQL Server Browser
SQL Server Browser listens for incoming requests and provides information about Microsoft SQL Server instances on the computer. For more information about SQL Server Browser, see SQL Server Browser in the Microsoft documentation.
If the SQL Server Browser menu items are disabled, try to enable the SQL Server Agent service.
In the SQL Server Configuration Manager, click SQL Server Services.
In the right pane that lists server services, right-click SQL Server Browser and select Start.

Enable SQL Server Agent
SQL Server Agent is a Microsoft Windows service that executes scheduled administrative tasks. For more information about the service, see SQL Server Agent in the official Microsoft documentation. Ensure that SQL Server Agent is running and starts automatically. After the change, a restart might be required.
Navigate to .
In the Services window, right-click SQL Server Agent(<server_name>) and select Properties. For this tutorial, <server_name> is MSSQLSERVER.
From the Startup type list, select Automatic and click Start.

Enable the TCP/IP connection
In the SQL Server Configuration Manager, expand SQL Server Network Configuration and click Protocols for MSSQLSERVER, where MSSQLSERVER is a name of the Microsoft SQL Server instance.
In the list of protocol names, right-click TCP/IP and select Properties.
On the Protocol tab, from the Enabled list, select Yes.
On the IP Addresses tab, find the interface that your workstation uses and see the connection port. By default, the port is 1433. Verify that other running applications do not use the same port.

Step 2. Configure SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS)
Create a user
In the SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS), navigate to .
Right-click the Logins root folder and select New Login.
On the General page, specify a login name in the Login name field.
Select authentication mode. You can select between the following authentication modes:
Windows authentication: to use your domain login and password.
SQL Server authentication: to use a custom login and password. If you select Enforce password security policy checkbox, the user must change the assigned password before connecting to Microsoft SQL Server with DataGrip. Otherwise, clear the Enforce password security policy checkbox.
Click OK.

Configure user roles
Right-click the created user profile and select Properties.
On the Server Roles page, select the appropriate user role (for example, sysadmin).

Step 3. Connect to Microsoft SQL Server with DataGrip
The following section describes configuration of DataGrip on Windows, macOS, and Linux. Note that the Use Windows domain authentication checkbox is available only on Windows. To configure Windows domain authentication on macOS and Linux, see Connect by using Windows domain authentication.
Windows
Connect by using SQL Server authentication
Navigate to or press Control+Alt+Shift+S.
In the Data Sources and Drivers dialog, click the Add icon (
) and select Microsoft SQL Server.
Click the Driver link and select Microsoft SQL Server (jTds).
Check if there is a Download missing driver files link at the bottom of the data source settings area. As you click this link, DataGrip downloads drivers that are required to interact with a database. The IDE does not include bundled drivers in order to have a smaller size of the installation package and to keep driver versions up-to-date for each IDE version.
You can specify your drivers for the data source if you do not want to download the provided drivers. For more information about creating a database connection with your driver, see Add a user driver to an existing connection.
In Host, Instance, and Port fields, specify your connection details. If the server name (in our case,
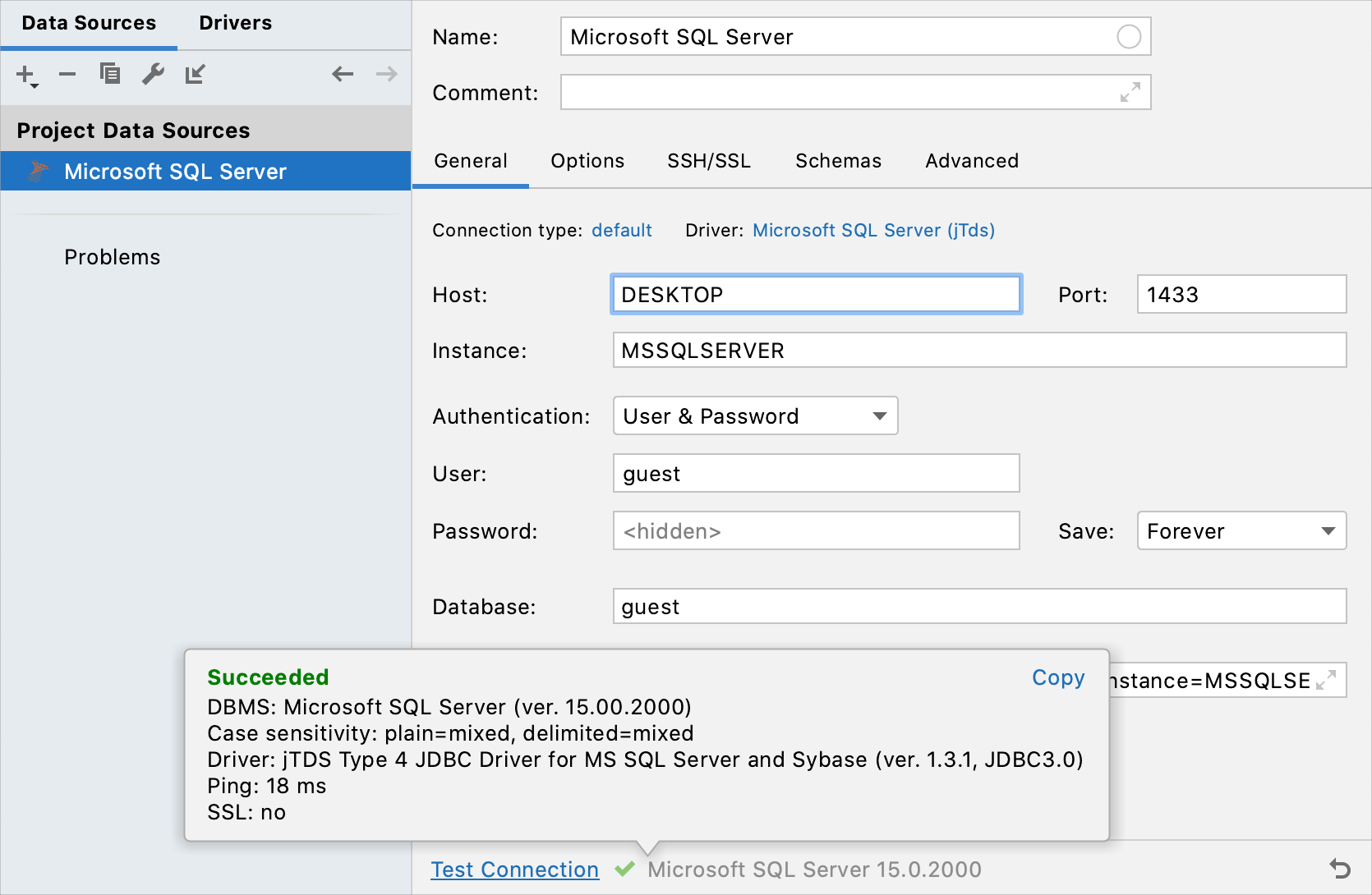
DESKTOP) does not work, replace it with the server IP address.From the Authentication list, select User & Password.
In User and Password fields, specify your credentials.
To ensure that the connection to the data source is successful, click the Test Connection link.
(Optional) If you are connecting to a data source that contains a lot of databases and schemas, in the Schemas tab, select the schemas that you need to work with.
Click OK to create the data source.
Find your new data source in Database Explorer.
To write and run queries, open the default query console by clicking the data source and pressing F4.
To view and edit data, use Data editor.
To learn how to work with database objects in DataGrip, see Database objects.

Connect by using single sign-on for Microsoft SQL Server
If you run DataGrip on Windows in the same domain as the Microsoft SQL Server database, you can use the Single-Sign On (SSO).
Navigate to or press Control+Alt+Shift+S.
In the Data Sources and Drivers dialog, click the Add icon (
) and select Microsoft SQL Server.
Click the Driver link and select Microsoft SQL Server (jTds).
Check if there is a Download missing driver files link at the bottom of the data source settings area. As you click this link, DataGrip downloads drivers that are required to interact with a database. The IDE does not include bundled drivers in order to have a smaller size of the installation package and to keep driver versions up-to-date for each IDE version.
You can specify your drivers for the data source if you do not want to download the provided drivers. For more information about creating a database connection with your driver, see Add a user driver to an existing connection.
In Host, Instance, and Port fields, specify your connection details. If the server name (in our case,
DESKTOP) does not work, replace it with the server IP address.From the Authentication list, select Windows credentials.
To ensure that the connection to the data source is successful, click the Test Connection link.
(Optional) If you are connecting to a data source that contains a lot of databases and schemas, in the Schemas tab, select the schemas that you need to work with.
Click OK to create the data source.
Find your new data source in Database Explorer.
To write and run queries, open the default query console by clicking the data source and pressing F4.
To view and edit data, use Data editor.
To learn how to work with database objects in DataGrip, see Database objects.

Connect by using Windows domain authentication
Navigate to or press Control+Alt+Shift+S.
In the Data Sources and Drivers dialog, click the Add icon (
) and select Microsoft SQL Server.
Click the Driver link and select Microsoft SQL Server (jTds).
Check if there is a Download missing driver files link at the bottom of the data source settings area. As you click this link, DataGrip downloads drivers that are required to interact with a database. The IDE does not include bundled drivers in order to have a smaller size of the installation package and to keep driver versions up-to-date for each IDE version.
You can specify your drivers for the data source if you do not want to download the provided drivers. For more information about creating a database connection with your driver, see Add a user driver to an existing connection.
In Host, Instance, and Port fields, specify your connection details. If the server name (in our case,
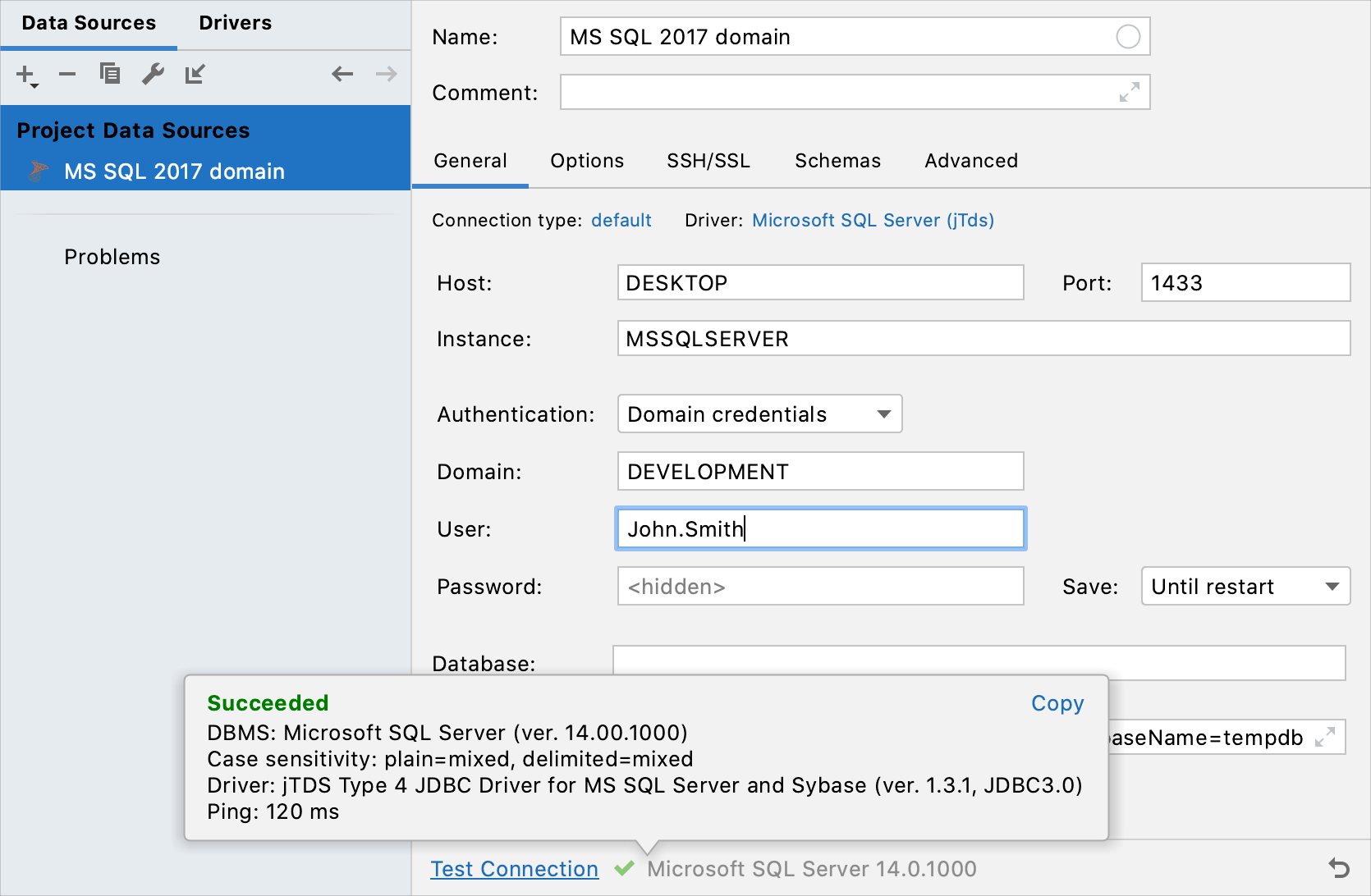
DESKTOP) does not work, replace it with the server IP address.From the Authentication list, select Domain credentials.
In the Domain field, specify the domain (for example,
DEVELOPMENT).In User and Password fields, specify your domain credentials. In the User field, type your domain user without the domain prefix (for example,
John.Smithinstead ofDOMAIN\John.Smith).Alternatively, on the General tab, specify the connection string. Consider the following example of a full connection string:
jdbc:jtds:sqlserver://DESKTOP:1433;domain=DEVELOPMENT;instance=MSSQLSERVER;databaseName=guest;To ensure that the connection to the data source is successful, click the Test Connection link.
(Optional) If you are connecting to a data source that contains a lot of databases and schemas, in the Schemas tab, select the schemas that you need to work with.
Click OK to create the data source.
Find your new data source in Database Explorer.
To write and run queries, open the default query console by clicking the data source and pressing F4.
To view and edit data, use Data editor.
To learn how to work with database objects in DataGrip, see Database objects.

macOS and Linux
Connect by using SQL Server authentication
Navigate to or press Control+Alt+Shift+S.
In the Data Sources and Drivers dialog, click the Add icon (
) and select Microsoft SQL Server.
Click the Driver link and select Microsoft SQL Server (jTds).
Check if there is a Download missing driver files link at the bottom of the data source settings area. As you click this link, DataGrip downloads drivers that are required to interact with a database. The IDE does not include bundled drivers in order to have a smaller size of the installation package and to keep driver versions up-to-date for each IDE version.
You can specify your drivers for the data source if you do not want to download the provided drivers. For more information about creating a database connection with your driver, see Add a user driver to an existing connection.
In Host, Instance, and Port fields, specify your connection details. If the server name (in our case,
DESKTOP) does not work, replace it with the server IP address.From the Authentication list, select User & Password.
In User and Password fields, specify your credentials.
To ensure that the connection to the data source is successful, click the Test Connection link.
(Optional) If you are connecting to a data source that contains a lot of databases and schemas, in the Schemas tab, select the schemas that you need to work with.
Click OK to create the data source.
Find your new data source in Database Explorer.
To write and run queries, open the default query console by clicking the data source and pressing F4.
To view and edit data, use Data editor.
To learn how to work with database objects in DataGrip, see Database objects.
Connect by using Windows domain authentication
Navigate to or press Control+Alt+Shift+S.
In the Data Sources and Drivers dialog, click the Add icon (
) and select Microsoft SQL Server.
Click the Driver link and select Microsoft SQL Server (jTds).
Check if there is a Download missing driver files link at the bottom of the data source settings area. As you click this link, DataGrip downloads drivers that are required to interact with a database. The IDE does not include bundled drivers in order to have a smaller size of the installation package and to keep driver versions up-to-date for each IDE version.
You can specify your drivers for the data source if you do not want to download the provided drivers. For more information about creating a database connection with your driver, see Add a user driver to an existing connection.
In Host, Instance, and Port fields, specify your connection details. If the server name (in our case,
DESKTOP) does not work, replace it with the server IP address.From the Authentication list, select Domain credentials.
In the Domain field, specify the domain (for example,
DEVELOPMENT).In User and Password fields, specify your domain credentials. In the User field, type your domain user without the domain prefix (for example,
John.Smithinstead ofDOMAIN\John.Smith).Alternatively, on the General tab, specify the connection string. Consider the following example of a full connection string:
jdbc:jtds:sqlserver://DESKTOP:1433;domain=DEVELOPMENT;instance=MSSQLSERVER;databaseName=guest;To ensure that the connection to the data source is successful, click the Test Connection link.
(Optional) If you are connecting to a data source that contains a lot of databases and schemas, in the Schemas tab, select the schemas that you need to work with.
Click OK to create the data source.
Find your new data source in Database Explorer.
To write and run queries, open the default query console by clicking the data source and pressing F4.
To view and edit data, use Data editor.
To learn how to work with database objects in DataGrip, see Database objects.