Azure AD 2.0 Auth Module
The Azure AD 2.0 authentication module is a pre-configured OAuth 2.0 auth module that lets users log in to Hub and any connected services with their Azure AD 2.0 credentials.
Custom Tenant Setup
When you follow this setup, logins are restricted to users whose accounts are stored in your Azure AD instance. If you want to accept login requests from any Azure Active Directory (AD) tenant, follow the instructions for a common tenant.
When you create an Azure AD 2.0 module for a custom tenant, you provide the directory ID of the custom tenant when you create the auth module. This automatically adds your Azure Tenant ID to the authorization and token endpoints that are used by the auth module.
To get the directory ID for the custom tenant:
Access the Microsoft Azure Portal and create a directory.
In the sidebar, select Azure Active Directory.
In the Manage section of the Azure Active Directory menu, select Properties.
Copy the value that is stored as the Directory ID.
Now that you have the directory ID for your custom tenant, you can create the Azure AD 2.0 auth module in Hub.
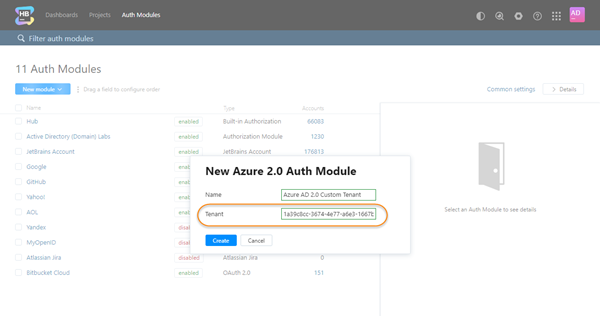
To create the Azure AD 2.0 module:
In the Access Management section of the Administration menu, select .
- From the New Module drop-down list, select Azure AD 2.0.
Paste the directory ID from Microsoft Azure into the Tenant input field.
- Click the Create button in the dialog.
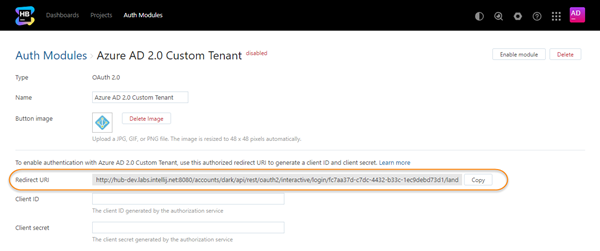
If the feature is supported by your browser, use the Copy button to copy the redirect URI to your clipboard.
The next step is to register the authorized redirect URI for Hub in Microsoft Azure. This gives you access to the client ID and secret that you need to enable the Azure AD 2.0 authentication module.
Start from your Microsoft Azure Portal and switch back to Hub when instructed.
To get a Client ID and Secret for use with Azure AD 2.0:
In the Manage section of the Azure Active Directory menu, select App registrations.
- Click the New application registration button in the header.
Enter a name for the application in the Name field.
For the Application type, leave the Web app / API selection.
For the Sign-on URL, enter the base URL of your Hub installation.
Click the Create button.
Copy the Application ID and paste it into the Client ID input field in the Hub auth module.
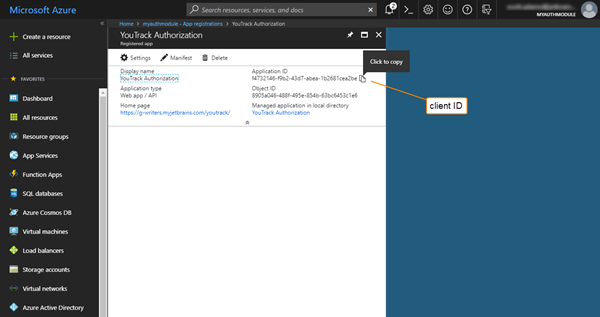
Click the Settings button in the toolbar, then select Keys in the API Access section of the Settings blade.
- Generate a password in the Keys blade:
In the Description field, enter an arbitrary value.
Select a duration from the Expires drop-down list.
Click the Save button in the header.
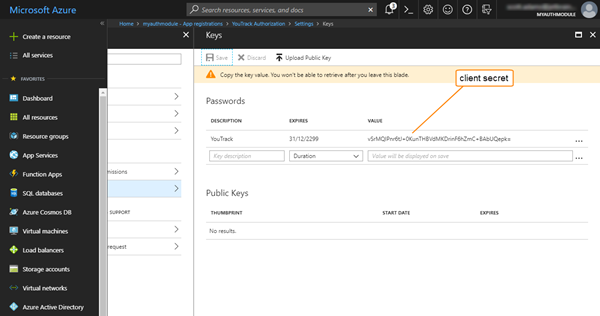
Copy the key value, close the Keys blade, then switch back to Hub.
Paste the key into the Client secret input field in the Hub auth module, then click the Save button.
Copy the Redirect URI from the Hub auth module, then switch back to the Microsoft Azure Portal.
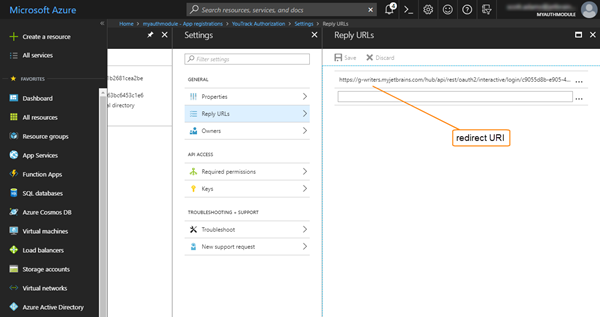
In the General section of the Settings blade, select Reply URLs.
Delete the base URL for your Hub installation.
Paste the redirect URI from Hub into the input field on the Reply URLs blade, then click the Save button in the header.
Switch back to Hub and configure the optional settings for the authentication module. For more information, see Additional Settings.
- Click the Enable module button in the header.
The Azure AD 2.0 authentication module is enabled.
The icon stored in the Button image setting is added to the login dialog window. Users can click this icon to log in to Hub with their Microsoft accounts.
Common Tenant Setup
An Azure AD 2.0 module that uses the endpoint for common tenants follows the standard setup for an OAuth 2.0 auth module. This setup accepts login requests from any Azure Active Directory (AD) tenant, including users who are not members of your organization. If you want to restrict logins to users who are registered in your company's Azure AD instance, follow the instructions for a custom tenant.
Your first step is to create an auth module and generate a redirect URI in Hub.
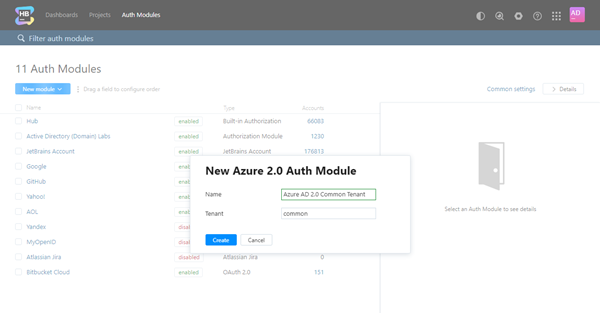
To generate a redirect URI in Hub:
In the Access Management section of the Administration menu, select Auth Modules.
- From the New module drop-down list, select Azure AD 2.0.
- Click the Create button in the dialog.
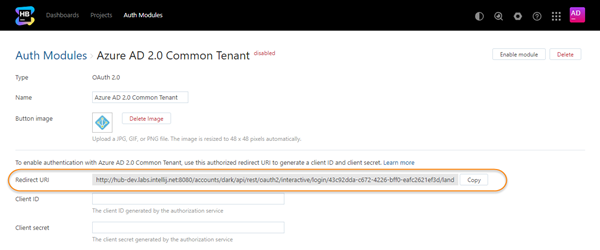
If the feature is supported by your browser, use the Copy button to copy the redirect URI to your clipboard.
Make sure to update the Redirect URI in the authorization service when you change the base URL of your Hub installation. For example, after migrating data to another Hub service or changing proxy settings.
The next step is to register the authorized redirect URI for Hub in the Microsoft Application Registration Portal. This gives you access to the client ID and secret that you need to enable the Azure AD 2.0 authentication module.
To get a Client ID and Secret for use with Azure AD 2.0:
Access the Microsoft Application Console. You can also access this page from the current version of the Microsoft Azure Portal (select App registrations in the Manage section of the Azure Active Directory menu, then click the Microsoft Application Console link).
On the My applications page, click the Add an app button.
Enter a name and click the Create button.
In the Platforms section, click the Add Platform button and select the Web option.
Paste the redirect URI from Hub into the Redirect URIs input field, then click the Save button.
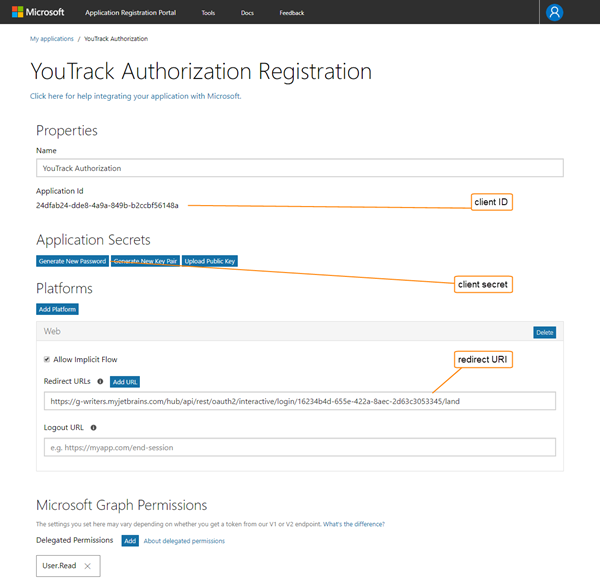
Use the value that is stored as the Application Id for the Client ID setting in Hub.
Use the Generate New Password option to generate a value for the Client secret setting in Hub.
Now that you have the values that are required to connect with the authorization service, you can enable the Azure AD 2.0 auth module.
Copy the Application Id from the Microsoft Application Registration Portal and paste it into the Client ID input field in Hub.
Click the Generate New Password button in the Application Secrets section of the Microsoft Application Registration Portal, copy the value, then paste it into the Client secret input field in Hub.
Configure the optional settings for the authentication module. For more information, see Additional Settings.
Click the Save button to apply the settings.
- Click the Enable module button.
The Azure AD 2.0 authentication module is enabled.
The icon stored in the Button image setting is added to the login dialog window. Users can click this icon to log in to Hub with their Microsoft accounts.
Settings
The first section of the settings page displays the general settings for the authentication module. Here, you also find the redirect URI that you use to register Hub in the authorization service and the input fields that store the Client ID and Client Secret that are generated in the authorization service.
Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Type | Displays the type of authorization service that is enabled for third-party authentication in Hub. |
Name | Stores the name of the authentication module. Use this setting to distinguish this module from other authentication modules in the Auth Modules list. |
Button image | Displays the image used for the button that a user clicks to log in to Hub with a their account in the connected authorization service. You can upload a JPG, GIF or PNG file. The image is resized to 48 x 48 pixels automatically. |
Redirect URI | Displays the authorized redirect URI that is used to register the connection to Hub in the authorization service. |
Client ID | Stores the identifier that the authorization service uses to validate a login request. You generate this value in the authorization service when you configure the authorization settings for a web application and enter an authorized redirect URI. |
Client Secret | Stores the secret or password used to validate the client ID. You generate this value in the authorization service together with the client ID. |
Authorization Service Endpoints
The settings in this section of the page store the OAuth 2.0 endpoints used by Azure AD 2.0.
For pre-configured OAuth 2.0 modules, the values that are used by the selected authorization service are set automatically.
Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Authorization | Stores the endpoint that Hub uses to obtain authorization from the resource owner via user-agent redirection. |
Token | Stores the endpoint that Hub uses to exchange an authorization grant for an access token. |
User data | Stores the endpoint used to locate profile data for the authenticated user. |
The endpoint used to locate the email address of the authenticated user Use only when the email address is not stored in the user profile | |
Default email verification state | Determines which state should be set for an email address in Hub, when the authentication service does not return the verification status for an email address. |
Field Mapping
When a user profile response object is returned by Azure AD 2.0, values from the specified field paths are copied to the user profile in Hub. Use the following settings to define the endpoint that locates profile data for the authenticated user and map fields that are stored in the authorization service to user accounts in Hub.
For the Azure AD 2.0 module, the values are set automatically.
Use a sequence of path segments separated by slashes (/) to specify a path to a field inside a nested object.
Additional settings let you define the request scope, and choose how to authenticate with the service.
Field | Description |
|---|---|
User ID | Maps to the field that stores the value to copy to the User ID property in Hub. |
Maps to the field that stores the value to copy to the Email field in the Hub profile. | |
Verified email | Maps to the field that stores the value to copy to the verified email property in Hub. |
Full name | Maps to the field that stores the value to copy to the Full name field in the Hub profile. |
Avatar | Maps to the field that stores the image to use as the Avatar in the Hub profile. |
Image URL pattern | Generates an image URL for avatars that are referenced by an ID. Use the <picture-id> placeholder to reference the field that stores the avatar. |
Scope | Sets the scope for the access request. Enter a list of scopes, separated by spaces. |
Authentication | Determines how credentials are passed to the authorization service. |
Additional Settings
The following options are located at the bottom of the page. Use these settings to manage Hub account creation and group membership, and to reduce the loss of processing resources consumed by idle connections.
Option | Description |
|---|---|
User creation | Enables creation of Hub accounts for unregistered users who log in with an account that is stored in the connected authorization service. Hub uses the email address to determine whether the user has an existing account. |
Auto-join groups | Adds users to a group when they log in with an account that is stored in the connected authorization service. You can select one or more groups. New users that auto-join a group inherit all of the permissions assigned to this group. |
Connection timeout | Sets the period of time to wait to establish a connection to the authorization service. The default setting is 5000 milliseconds (5 seconds). |
Read timeout | Sets the period of time to wait to read and retrieve user profile data from the authorization service. The default setting is 5000 milliseconds (5 seconds). |
Audit | Links to the Audit Events page in Hub. There, you can view a list of changes that were applied to this authentication module. |