Accessibility
IntelliJ IDEA lets you enable various accessibility features to accommodate your needs. You can use a screen reader or adjust font size, colors, and the behavior of certain UI elements to make the process of working with IntelliJ IDEA easier.
IntelliJ IDEA fully supports screen readers on both Windows and macOS.
Download and enable your preferred screen reader:
WindowsmacOSNVDA: use the NVDA 2019.3 or later version for compatibility with 64-bit Java applications, such as IntelliJ IDEA.
Download, install, and enable NVDA.
JAWS: use the JAWS 12.0.1158 64-bit or later version for compatibility with 64-bit Java applications, such as IntelliJ IDEA.
Download the version you need and restart your computer to enable the JAWS screen reader.
Enable the VoiceOver screen reader since it is already built into the system.
IntelliJ IDEA automatically shows a prompt suggesting enabling the screen reader support if its installation was detected.
In the dialog that opens, click Enable when you first launch IntelliJ IDEA.
The screen reader support can also be activated later or manually for already installed and configured versions of IntelliJ IDEA.
Download and install IntelliJ IDEA.
note
For Windows and macOS, when IntelliJ IDEA detects a screen reader on the first launch, it displays a dialog where you can enable a screen reader for IntelliJ IDEA.
To enable screen reader support before the initial launch of IntelliJ IDEA, do the following:
Open the configuration directory that contains personal settings, such as, keymaps, color schemes, and so on.
Create a file called idea.properties.
Add the
ide.support.screenreaders.enabled=trueproperty to the file you have created.
Launch IntelliJ IDEA. The Support screen readers option located in Settings | Appearance & Behavior | Appearance will be enabled.
note
When the Support screen readers option is enabled, IntelliJ IDEA disables tooltips for icons in the main toolbar, switches controls to a keyboard, and adapts some controls for screen readers.
You can customize the IDE depending on your accessibility needs.
You can adjust IDE and editor colors if you have red-green color vision deficiency. In this case, code notifications such as errors that are usually highlighted in red or strings that are usually green, will be displayed with neutral colors. The color of the progress bar in the test runner will also get adjusted, so it can be easily recognized.
Press to open settings and then select Appearance & Behavior | Appearance.
Select Adjust colors for red-green vision deficiency and save your changes.
Check the following example with the Before image that has String highlighted in green color and Errors highlighted in red and the After image where the colors are adjusted:
BeforeAfter

You can make scrollbars in the editor more visible.
Press to open settings and then select Appearance & Behavior | Appearance.
From the options on the right, under the Accessibility section, select Use contrast scrollbars.
note
To configure the editor vertical scrollbar color and opacity, use the color scheme settings.
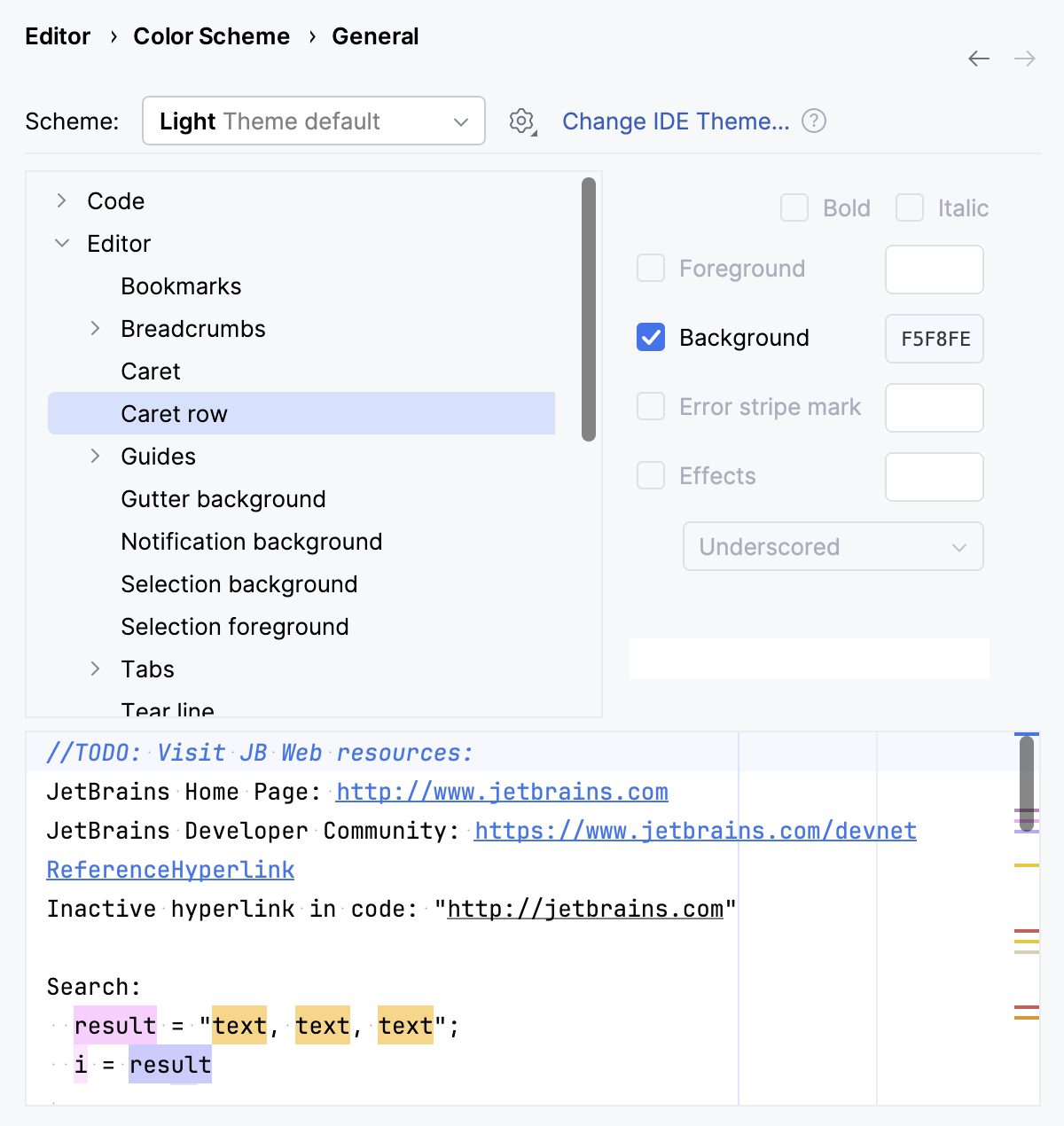
You can adjust colors for code elements, errors, elements of the editor, and tool windows. You can also configure a color for the vertical scrollbar in the editor.
Press to open settings and then select Editor | Color Scheme | General.
From the list on the right, select an element for which you want to adjust the color. For example, you can select Code and adjust colors for injected language fragments or matched braces, and so on. Click OK to save the changes.
You can also adjust colors for the debugger, consoles and other parts of the IDE: select the appropriate node in the list of options located in Settings | Editor | Color Scheme.
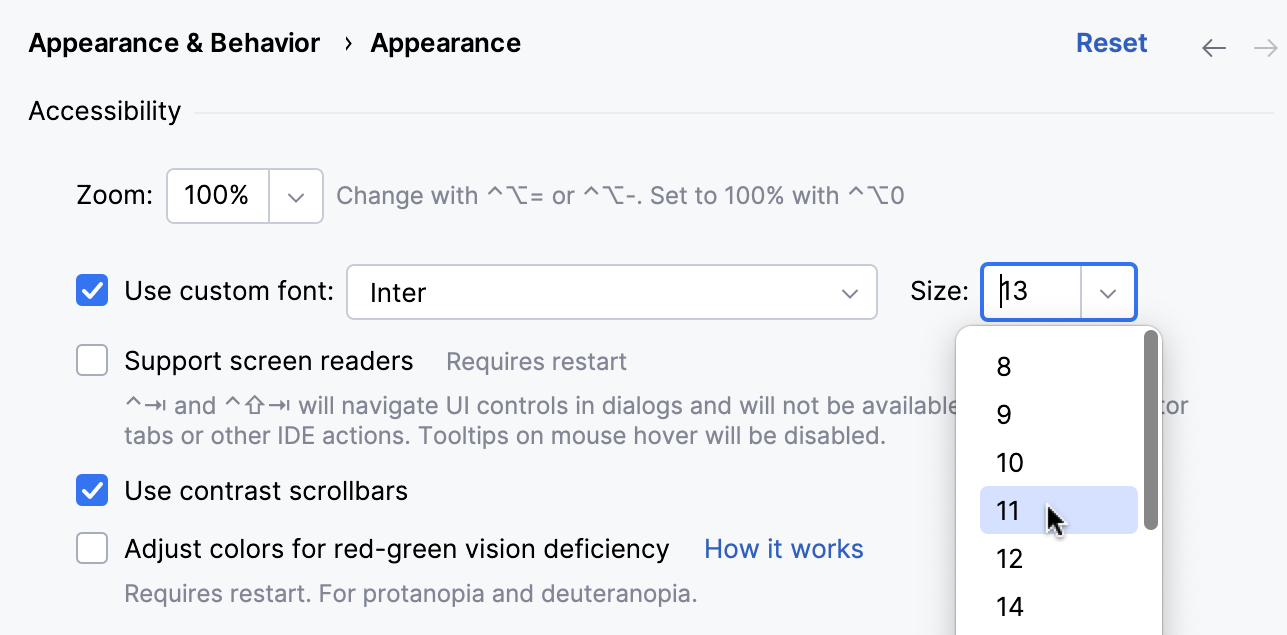
You can override the default fonts of the UI elements.
Press to open settings and then select Appearance & Behavior | Appearance.
From the options on the right, from the Use custom font list, select a font and specify the font size in the Size field.
Click OK to save the changes.
As a result, the size of icons and texts in the UI will be adjusted.
You can resize the actual tool windows vertically or horizontally using shortcuts.
To resize vertically up or down, press or .
To resize horizontally left or right, press or .
You can change the font and the size of the text in the editor.
Press to open settings and then select Editor | General.
From the options on the right, select the Change font size (Zoom) with Ctrl+Mouse Wheel option to quickly change the text size (turning the mouse wheel) while you are working in the editor.
If you need to specify the exact font size, select Editor | Font.
From the options on the right, specify the font, its size, line spacing, and other available options. Click OK to save changes.
You can set the zoom level for the entire IDE, making it smaller or larger than the default scale, depending on your needs.
Go to View | Appearance and select Zoom IDE.
To preview different zoom levels, hover over the options in the popup.

Click the preferred zoom level to apply the changes.
Press to open settings and then select Appearance & Behavior | Appearance.
In the Accessibility section, click the Zoom field and enter your value.
 Gif
GifClick OK to apply the changes.
You can configure custom shortcuts to actions that you frequently use.
Press to open settings and then select Keymap.
From the list of options on the right, such as menus, actions, and tools, select the action you need.
Right-click the selected item and from the context menu, select the action you want to perform, for example, Add Keyboard Shortcut, Add Mouse Shortcut, or Add Abbreviation.

In the dialog that opens, specify a shortcut. If necessary, select the Second stroke option and specify an additional key for the shortcut. To save the changes, click OK with the mouse (if you press , IntelliJ IDEA will consider it a shortcut).
note
You can ignore conflicts and assign a shortcut to several actions. However, it is strongly recommended that you avoid binding two actions with the same shortcut, because the priority of these actions is not defined.
You can configure the behavior of smart keys.
Press to open settings and then select Editor | General | Smart keys.
From the options on the right, select or clear the smart keys options. For example, you can clear the Insert paired brackets or the Insert paired quotes option that automatically inserts a closing bracket or a quote since it might not be useful when you use a screen reader. Click OK to save changes.
You can disable automatic code completion to avoid auto-inserting code elements when you work in the editor with a screen reader.
Press to open settings and then select Editor | General | Code completion.
Clear the Type-Matching Completion option. If necessary, clear Basic Completion to disable basic completion as well.
You can control the code folding behavior and specify what should or should not be folded.
Press to open settings and then select Editor | General | Code folding.
From the options on the right, select what should be collapsed by default.
You can configure spaces, tabs, and indents.
Press to open settings and then select Editor | Code Style | [Language].
From the options on the right, click Tabs and Indents to configure tabs or Spaces to configure where and how to use spaces.
Click OK to save the changes.
You can configure a screen reader to read line numbers, VCS annotations, debugger, and other icons that are located in the left gutter of your editor.
note
Make sure that the Support screen readers option is selected in Settings | Appearance & Behavior | Appearance.
Open your file in the editor.
Press to focus on the gutter. IntelliJ IDEA starts reading from the line where your caret is currently located.
Use the Up and Down arrow keys to move between lines. If you need to move to the next or previous gutter element in the line, use the Right and Left arrow keys respectively.
While the focus is in the gutter, the screen reader can read the gutter icon tooltip if it is available.
To access a tooltip, press the double shortcut . To browse through the tooltip's content (symbol by symbol), use the Right and Left arrow keys.
Press to switch the focus back to the editor.
You can set a high-contrast interface theme to work in IntelliJ IDEA. The interface theme defines the appearance of windows, dialogs, and controls.
Press to open settings and then select Appearance & Behavior | Appearance.
In the UI Options area, from the Theme list, select High Contrast, and click OK to apply changes.
You can set a high-contrast color scheme for your editor. IntelliJ IDEA uses color schemes to help you define the preferred colors and fonts in the editor.
Press to open settings and then select Editor | Color Scheme.
On the Color Scheme page, from the Scheme list, select High Contrast.
Click OK to apply your changes.
You can check Editor basics, IntelliJ IDEA keyboard shortcuts, and User interface to familiarize yourself with other useful shortcuts.