Maven dependencies
IntelliJ IDEA lets you manage Maven dependencies in your project. You can add, import Maven dependencies, view them in the diagram, and also analyze them.
Add a Maven dependency
IntelliJ IDEA lets you add a Maven dependency to your project. We recommend that you specify the dependency inside your POM. Dependencies that you set up manually inside IntelliJ IDEA module settings will be discarded on the next Maven project reload.
Open your POM in the editor.
Press Alt+Insert to open the Generate context menu.
From the context menu, select Dependency.
In the Maven Artifact Search tool window, in the search field, start typing the name of your dependency. In the list of results select the one you need and click Add.
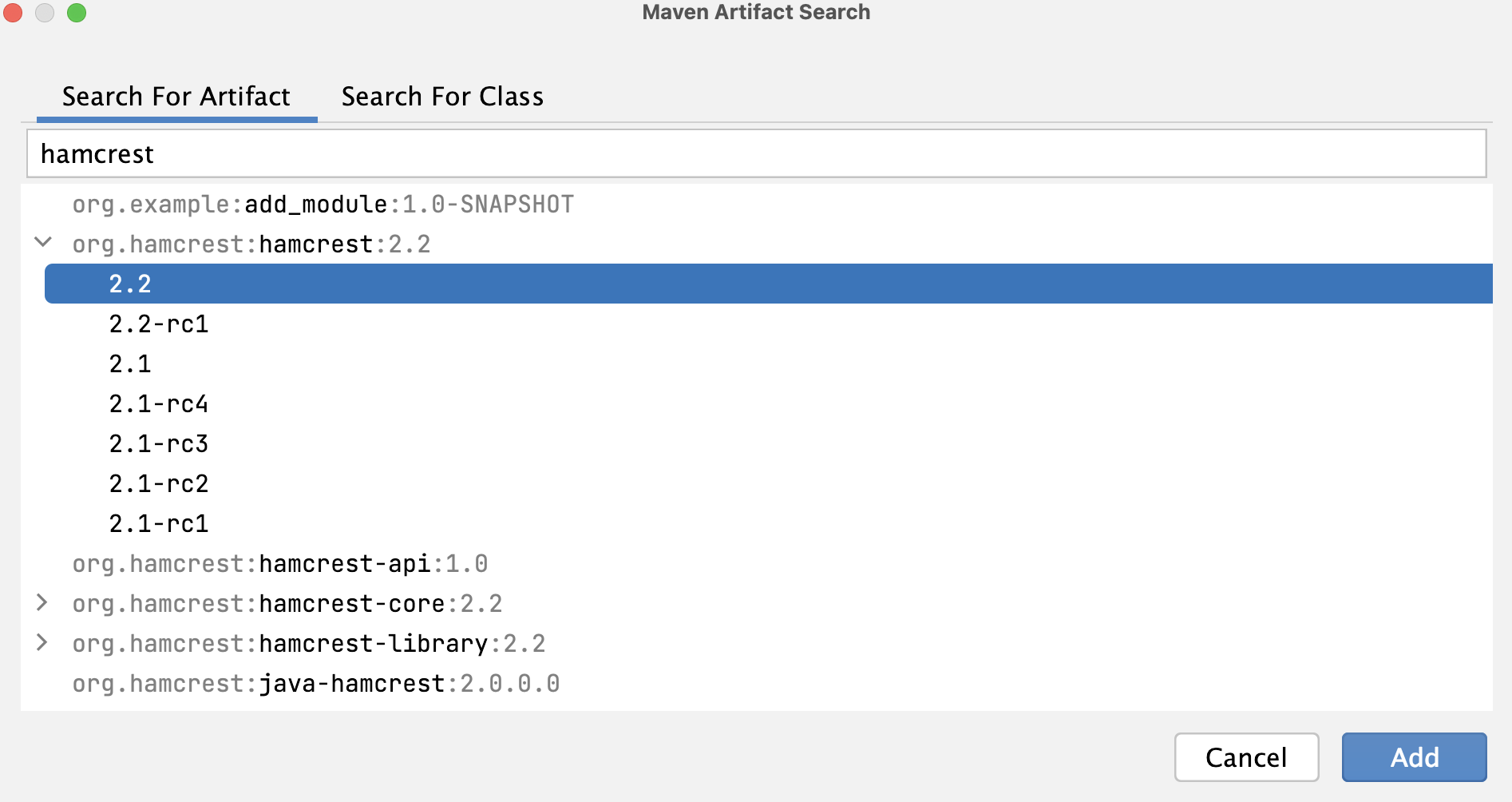
IntelliJ IDEA adds the dependency to your pom.xml.
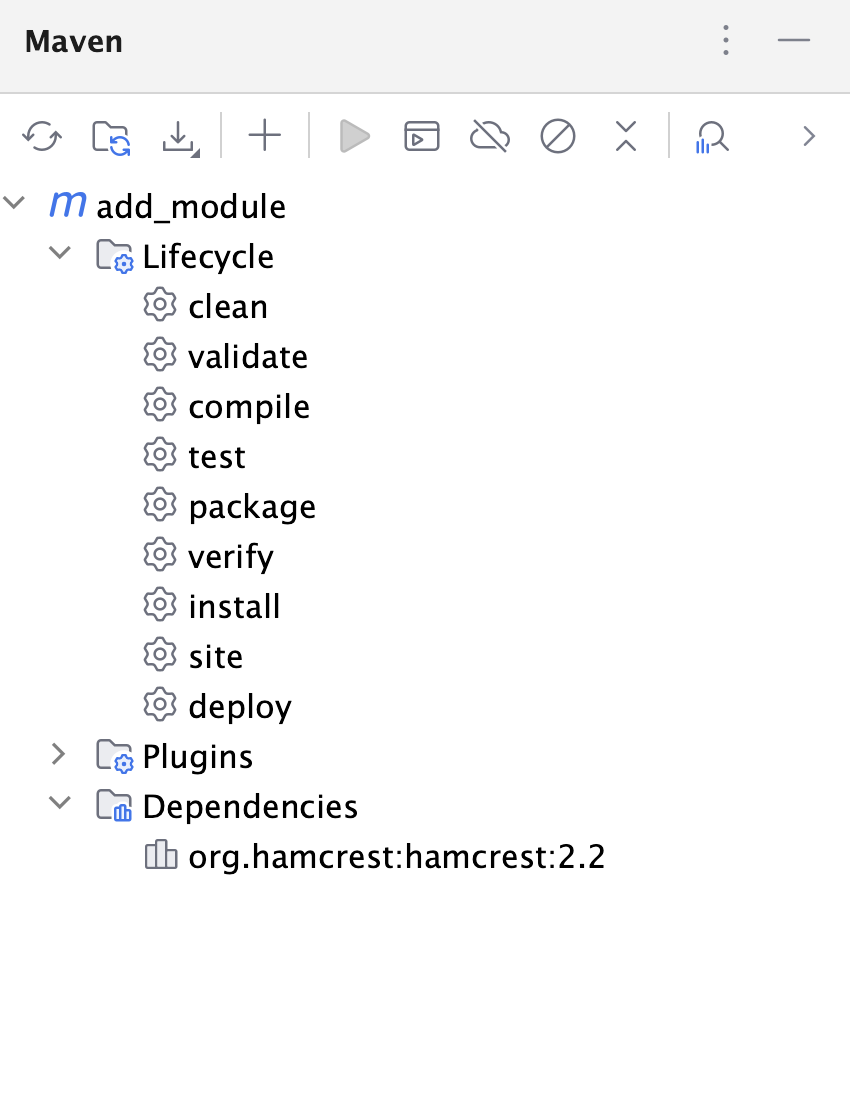
IntelliJ IDEA also adds the dependency to the Dependencies node in the Maven tool window and to the External Libraries in the Project tool window.
If the added dependency has its own transitive dependencies, IntelliJ IDEA displays them in both tool windows.
Enable annotation processors
Open your POM file.
Specify the
annotationProcessorsandannotationProcessorPathsoptions.For example, check the following code:
<build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId> <version>3.5.1</version> <configuration> <annotationProcessorPaths> <path> <groupId>org.sample</groupId> <artifactId>sample-annotation-processor</artifactId> <version>1.2.3</version> </path> </annotationProcessorPaths> </configuration> </plugin> </plugins> </build>For more information, refer to Maven.
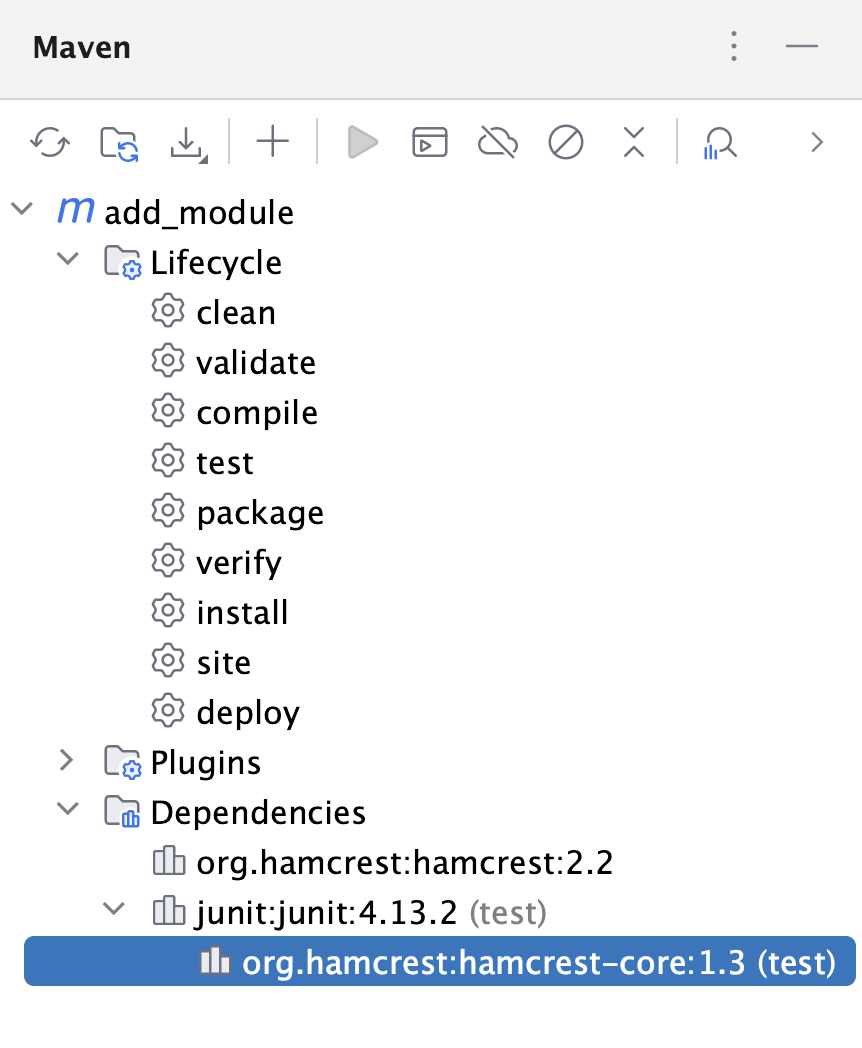
Re-import your project. IntelliJ IDEA creates an annotation processors profile, enables the annotation processing and adds the appropriate path to the Annotation Processor settings located in .
Centralize dependency information
In a multi-module Maven project, the dependency in the parent POM will be inherited by all subprojects. You can use dependencyManagement to consolidate and centralize the management of the dependencies' versions.
Open your POM in the editor.
Press Alt+Insert to open the Generate context menu.
From the context menu, select the Managed Dependency option that will show you the list of the dependencies that are defined in the
dependencyManagementsection of your parent POM in a multi-module project. IntelliJ IDEA also shows the list of dependencies from the BOM files.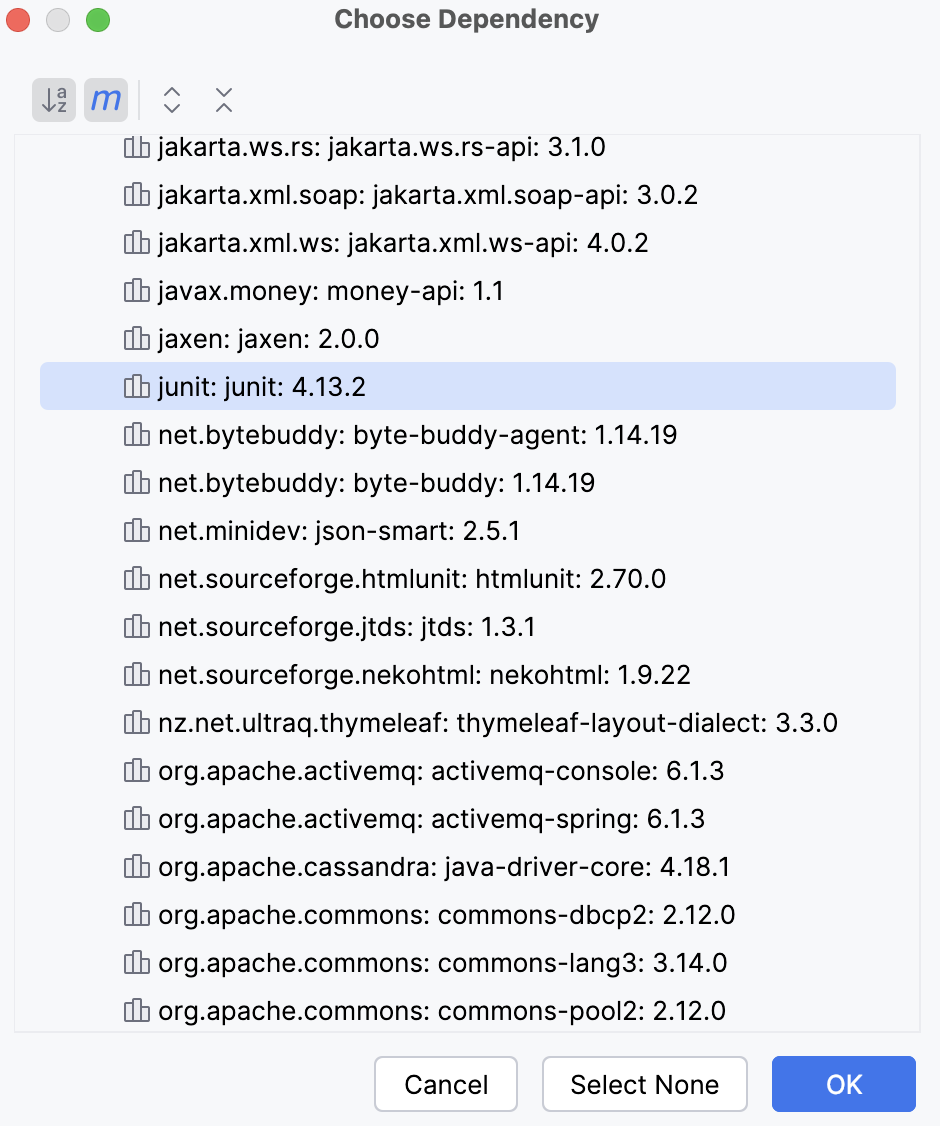
Select the required dependency and click OK. The dependency is added to the POM. You do not need to specify the version on the dependency it will be taken from the
DependencyManagement.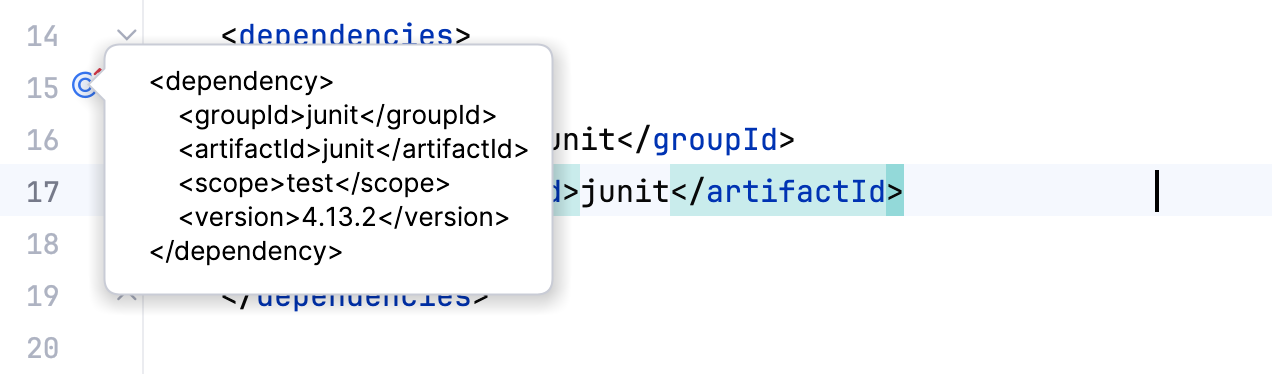
However, if you want to overwrite the defined version, you need to include
versionwhen you add the managed dependency to the POM.
Add a scope for the Maven dependency
You can add a scope for your dependency using POM. In this case IntelliJ IDEA will execute the dependency at the specified phase.
In your POM, in the dependency description add
scopeand using the code completion, add the name of the scope.<dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.13.2</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency>Import your changes. The name of the scope is displayed in the Maven tool window. In the Project Structure dialog, on the Modules page you can see that the scope of the dependency is also displayed.
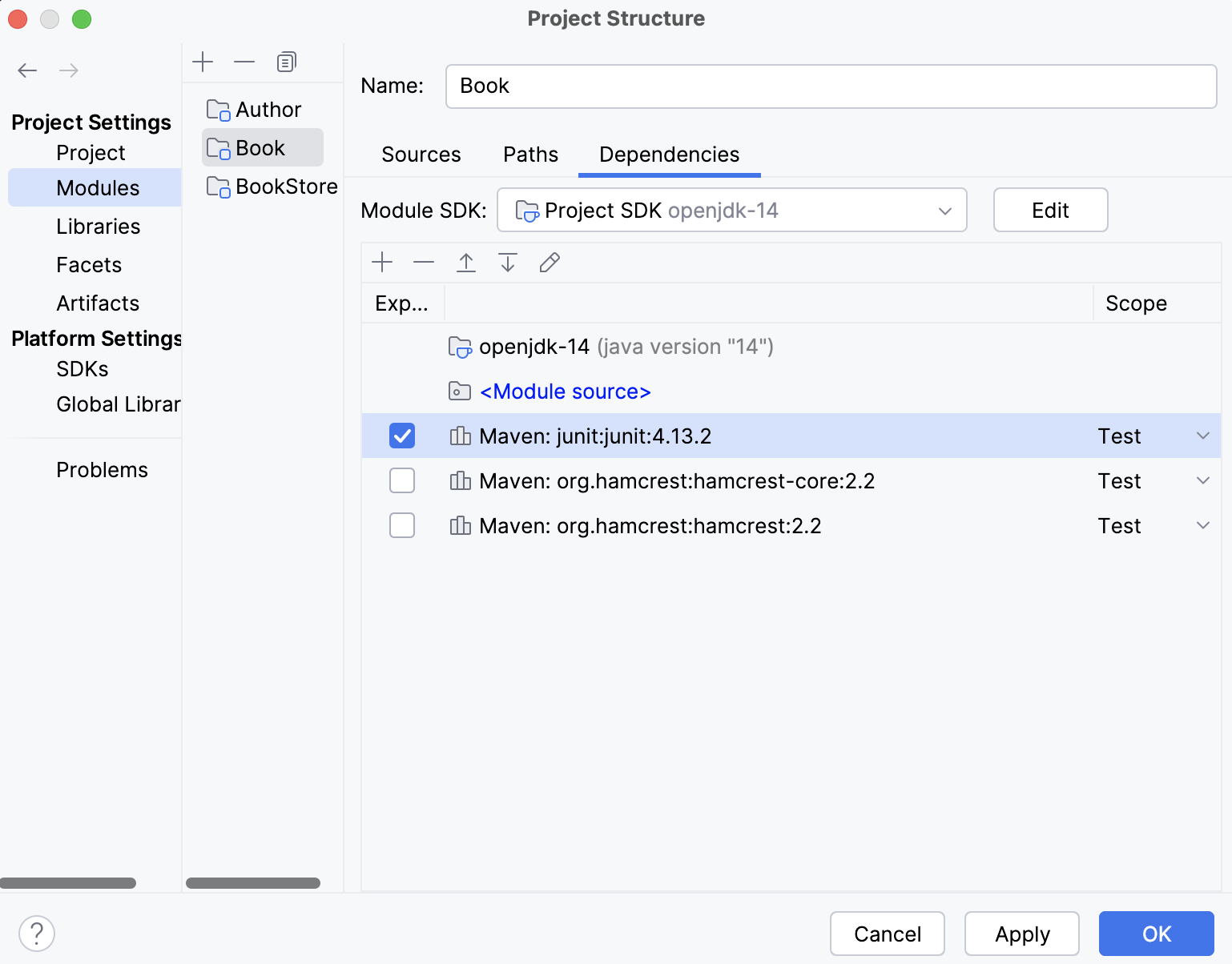
Note that changing dependency's scope in the Project Structure dialog will not affect the pom.xml file.
You can also add a custom jar file as a dependency using the Maven scope system when you define your dependency. However, note that this dependency will only be available on your machine, and you can use it only for the local deployment.
Work with Maven transitive dependencies
You can view transitive dependencies that were pulled in with the added or imported Maven dependency. You can check their versions, change them, or exclude those dependencies altogether.
The Maven tool window displays the direct dependency and all its transitive dependencies that were pulled in.
View the transitive dependency
In your project's POM, press Ctrl and hover over the dependency.
Click the dependency to open the dependency's POM.
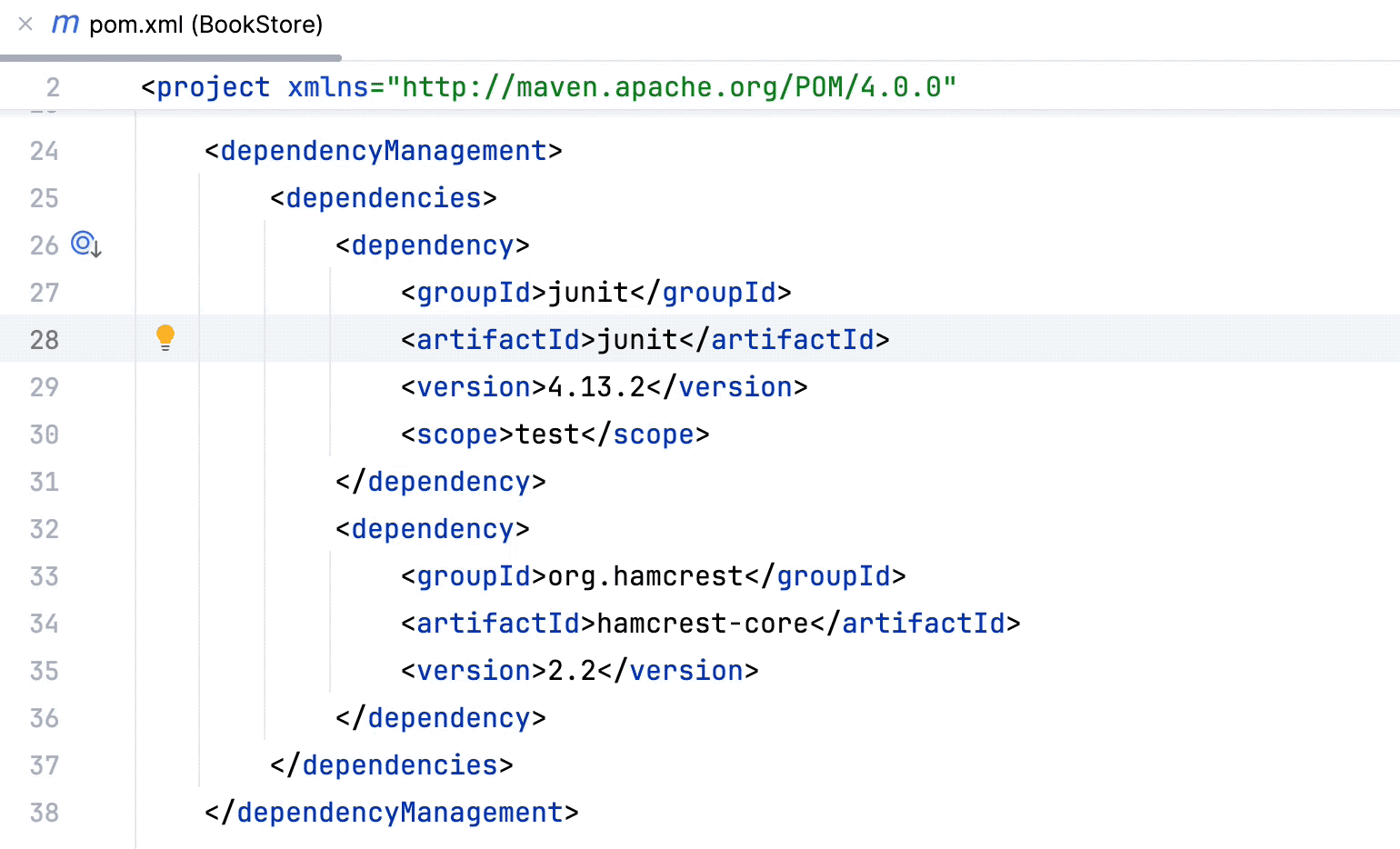
In the dependency POM, view the active dependency, its transitive dependencies and their versions.
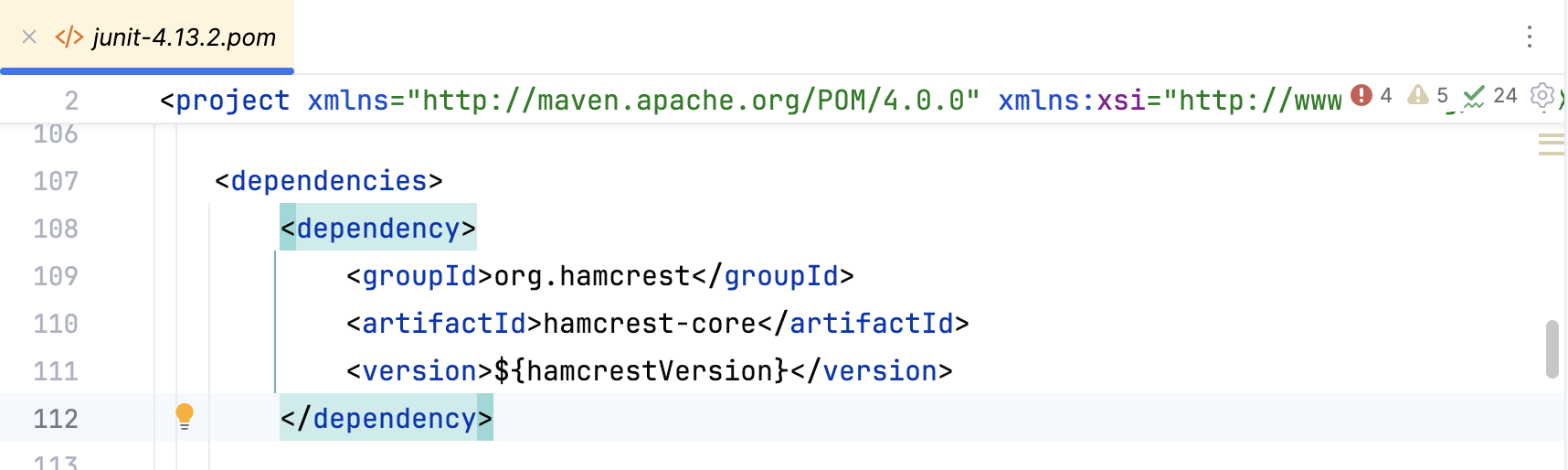
You can check the origin from which the dependency was pulled in.
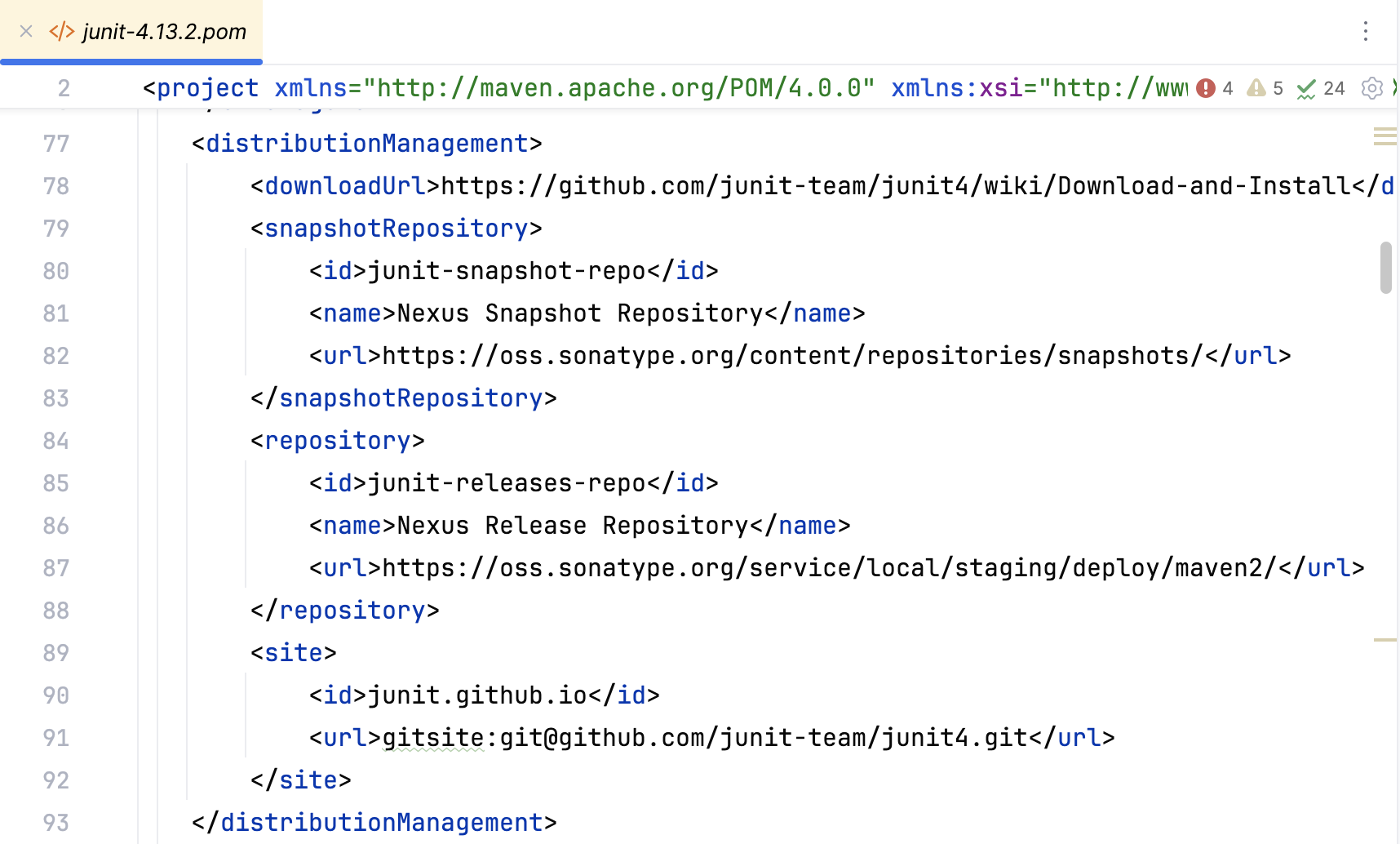
Exclude the transitive dependency
You can exclude a transitive dependency if you want.
Open the dependency POM and find the transitive dependency you want to exclude. Copy
groupIdandartifactId.In your project POM, underneath your active dependency, enter
exclusionsand using code completion paste the copied info of the dependency you want to exclude.<dependencyManagement> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.13.2</version> <scope>test</scope> <exclusions> <exclusion> <groupId>org.hamcrest</groupId> <artifactId>hamcrest-core</artifactId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency> </dependencies> </dependencyManagement>The dependency is also excluded from the Project and Maven tool windows.
Import Maven dependencies
You can import dependencies to your Maven project. When IntelliJ IDEA imports the added dependency, it parses the dependency and updates your project.
In the pom.xml file, add a dependency you need. When you change the pom.xml, IntelliJ IDEA displays a notification suggesting to load the changes. Click
in the editor to import the dependency and update your project.
In the Maven tool window, press
. In this case, you manually trigger the re-importing process of all projects and their dependencies.
View Maven dependencies as a diagram
IntelliJ IDEA lets you view and work with Maven dependencies in a diagram format.
Generate a diagram
In the Maven tool window, on the toolbar, click
or select the appropriate option from the context menu.
In the diagram window, IntelliJ IDEA displays the sub-project and all its dependencies, including the transitive ones.
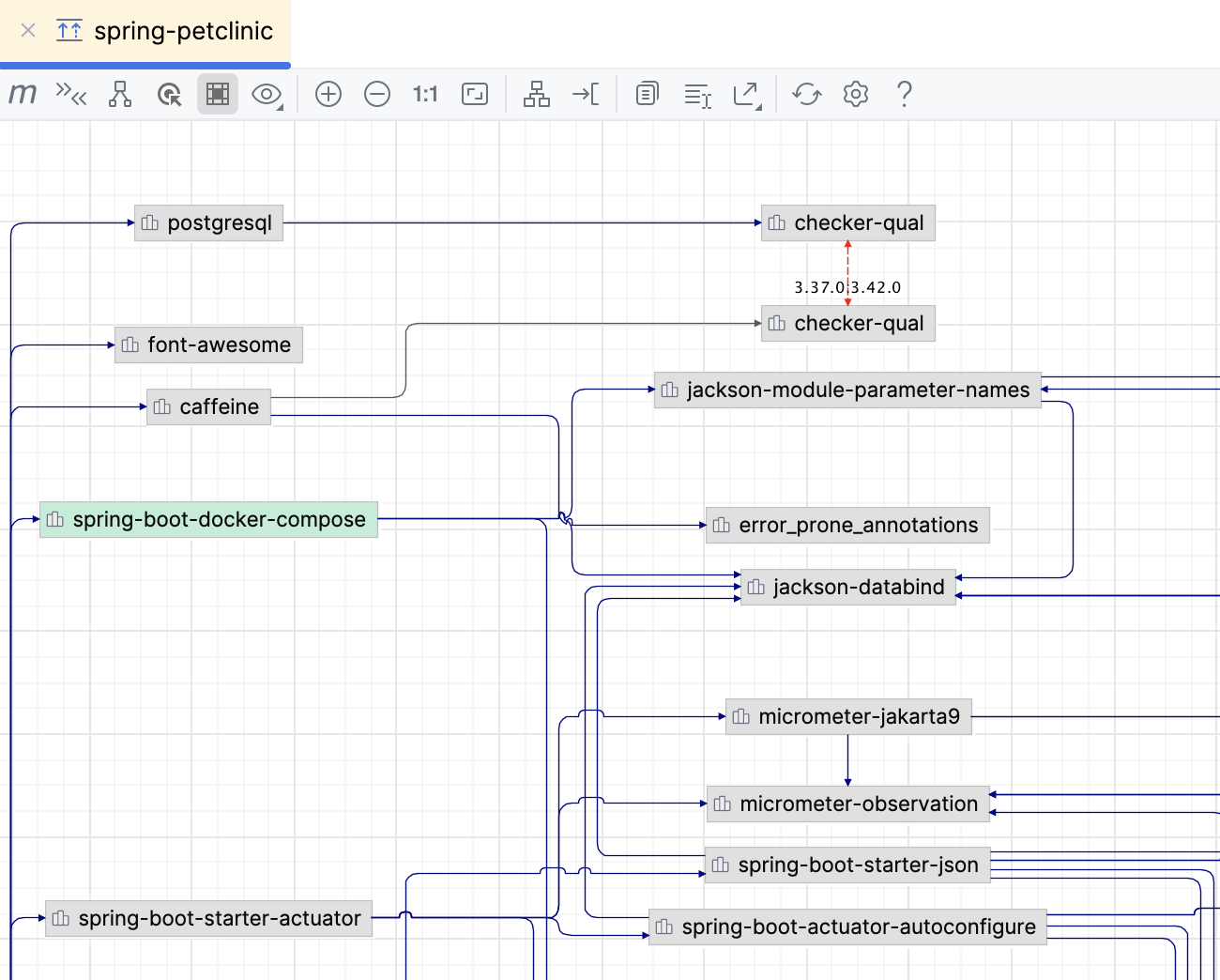
You can perform different actions while in the diagram window.
Change the visibility level
You can change the visibility level and, for example, view dependencies that have a specific scope (compile, test, and so on).
In the diagram window, select the subproject and click
 .
.From the list, select the dependency scope you want to see. IntelliJ IDEA displays only the specified dependency scope.
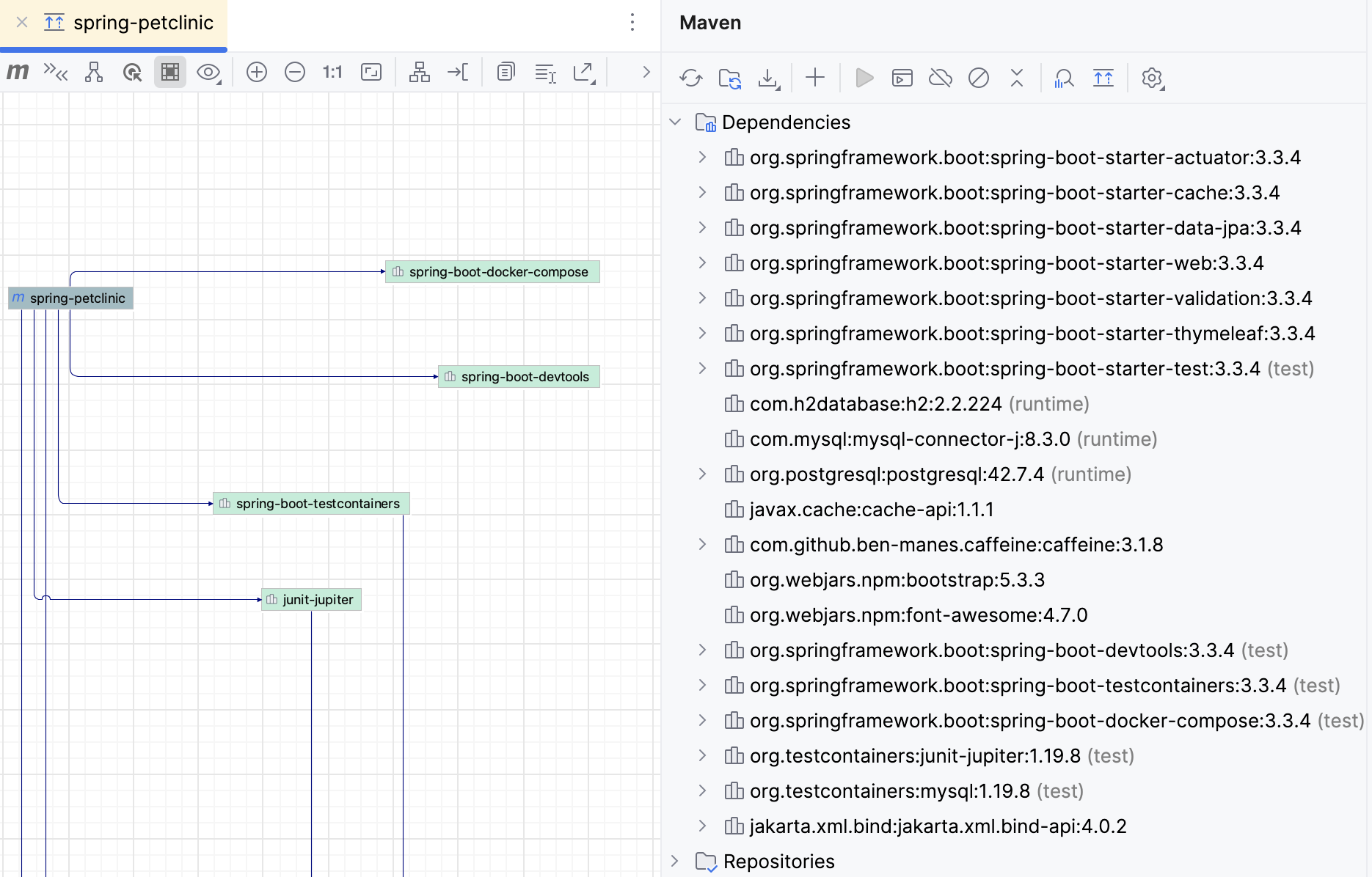
Navigate to POM
You can navigate to POM from the diagram window.
Select the required node and press F4, or choose on its context menu. The corresponding file opens in the editor.
You can check conflicts and duplicates by clicking icon in the diagram window.
Check conflicts and duplicates
In the diagram window, click
icon.
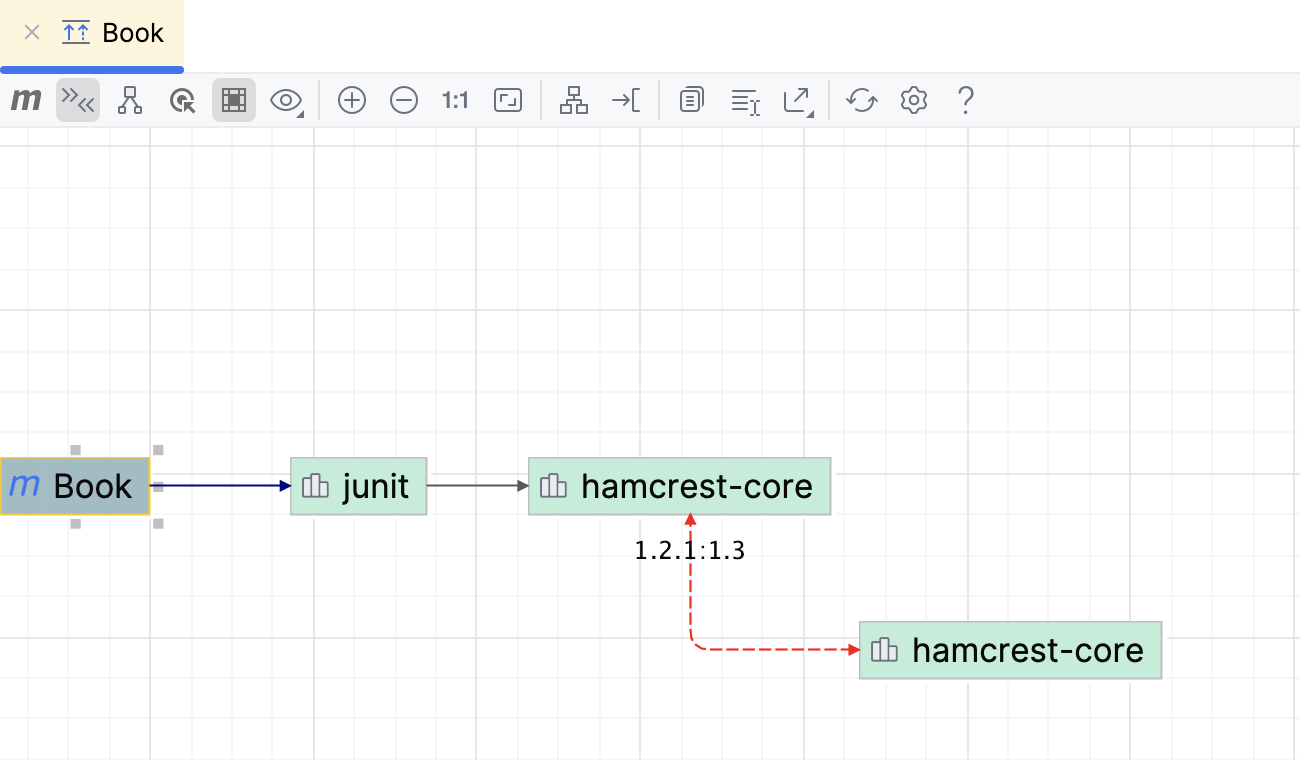
The red arrow points to dependencies that contain duplicates or errors. IntelliJ IDEA also displays dependencies' versions to help you resolve the conflicts. Double-click the dependency to open its POM.
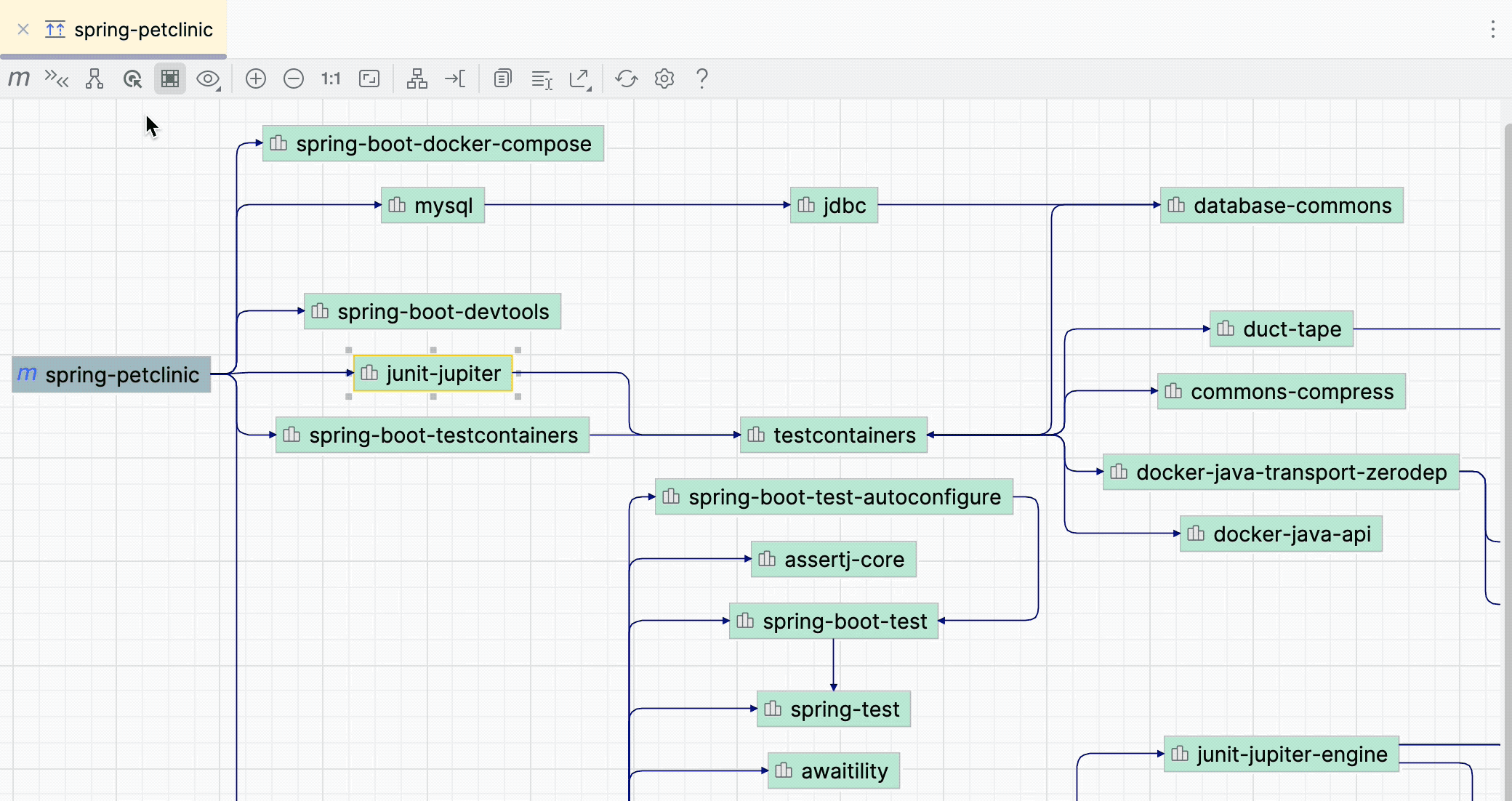
Show path from the selection to the root
You can select dependencies and see how they are included in the project.
In the diagram window, select a dependency for which you want to see a connection to a project. If you want to select several dependencies at once, hold down Shift and make the selection.
Click
.
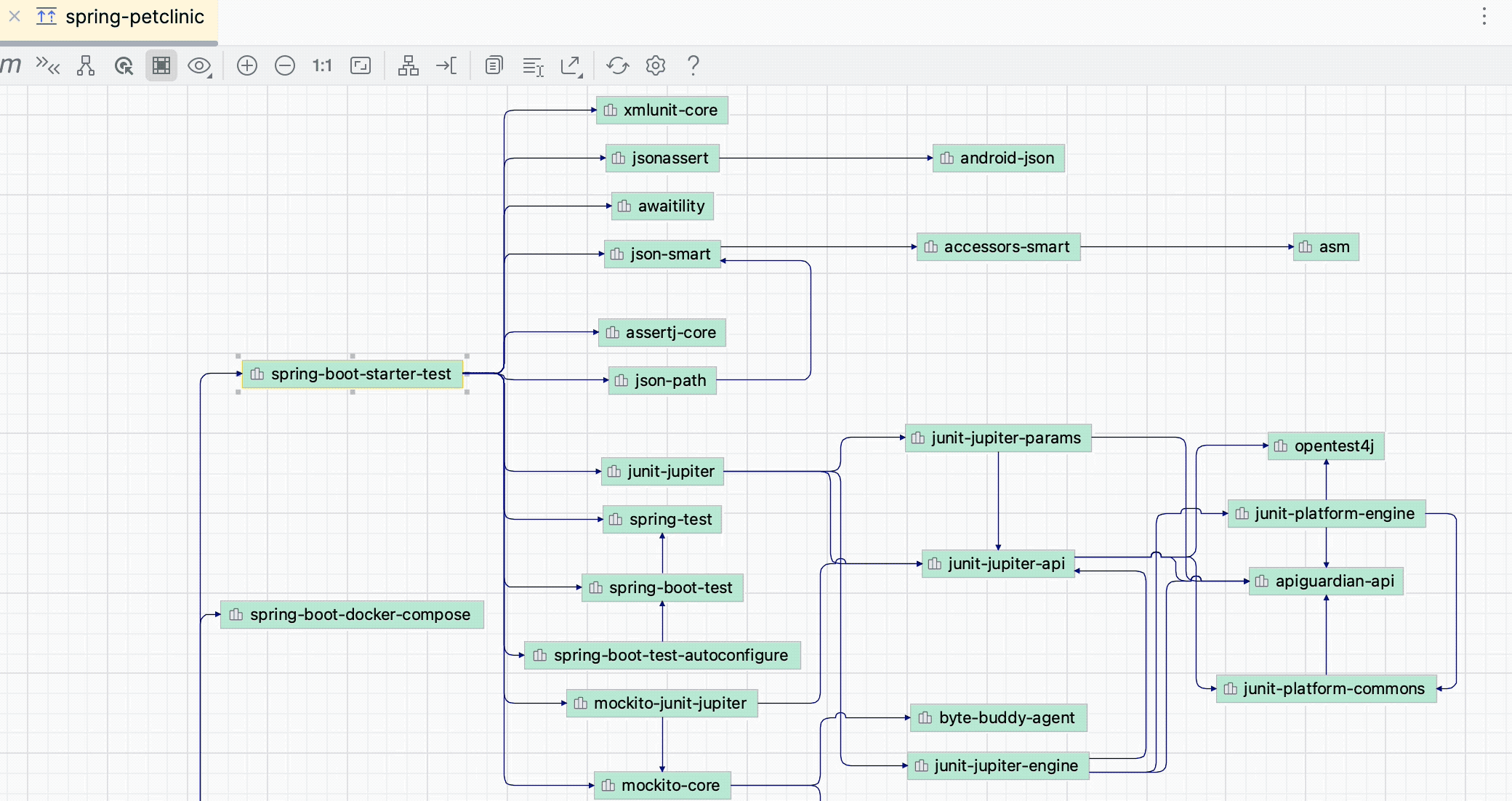
Show neighbors of the selected node
You can select dependencies and see what other dependencies are connected to the selected nodes. It might be helpful if you have a large diagram and want to focus on a part of it.
In the diagram window, select a dependency you need. If you want to select several dependencies at once, hold down Shift and make the selection.
Click
.
Dependency analyzer
Maven dependency analyzer lets you quickly see and analyze resolved dependencies, the unresolved ones, dependencies with conflicts, and transitive dependencies in your project and subprojects.
Analyze dependencies
On the toolbar in the Maven tool window, click
.
Alternatively, in the Maven tool window, right-click the necessary dependency and select Analyze Dependencies from the context menu. You can also right-click a module in the Project view and use the same action.
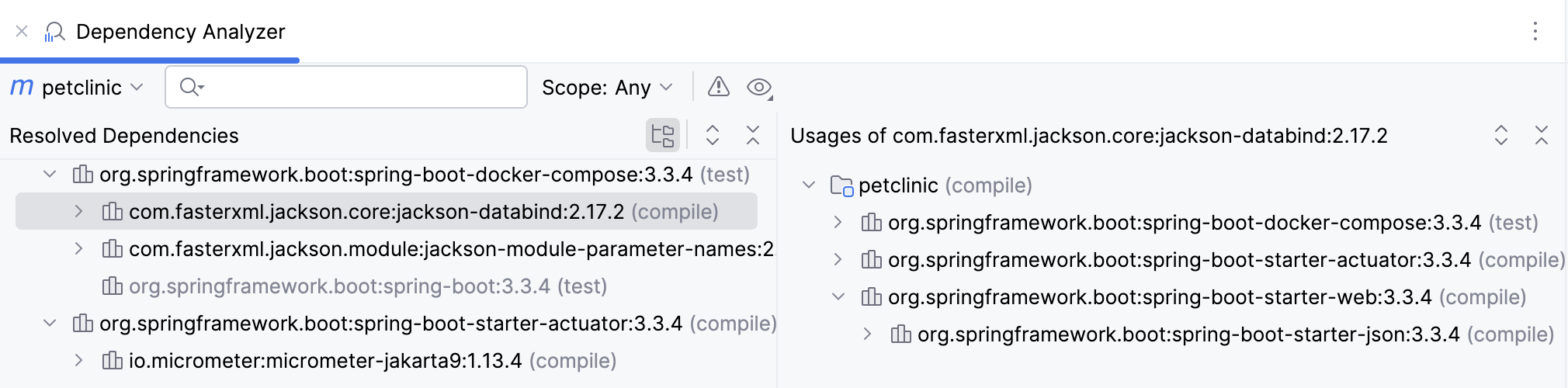
In the Dependency Analyzer window, you can narrow down your analysis scope, check only the conflicted dependencies, or check usages.
If you want to see the required dependency in the
pom.xmlfile, right-click the dependency and select Go to Maven Dependency. If you click Open Maven Config on the specific dependency, IntelliJ IDEA will open the dependency's POM file.If the duplicate dependency is found, it will be greyed out.
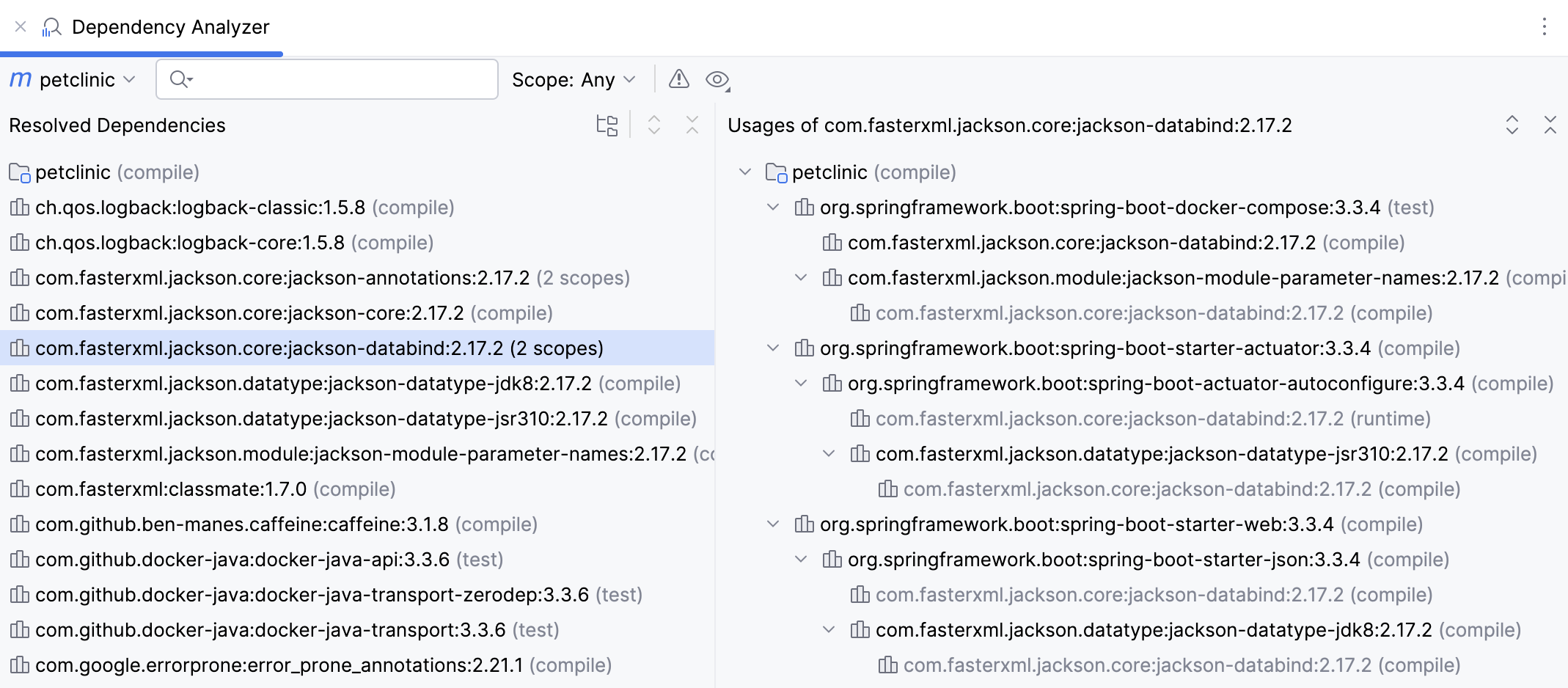
For more information about available options and icons in the Dependency Analyzer window, refer to the reference section.
Dependency analyzer tool window reference
Item | Description |
|---|---|
Scope | You can see scopes in which every dependency is used in the project. To narrow down the list of the dependencies based on their scope, select the appropriate option from the list of scopes. 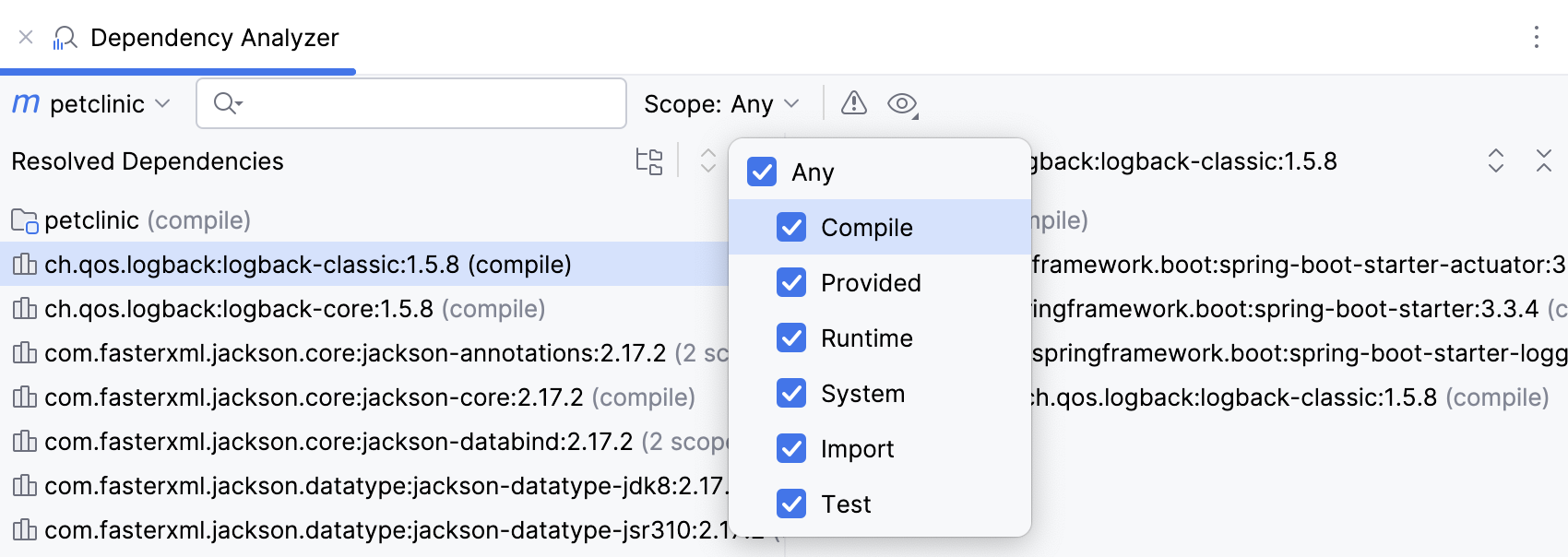 |
Show Conflicts Only | Click 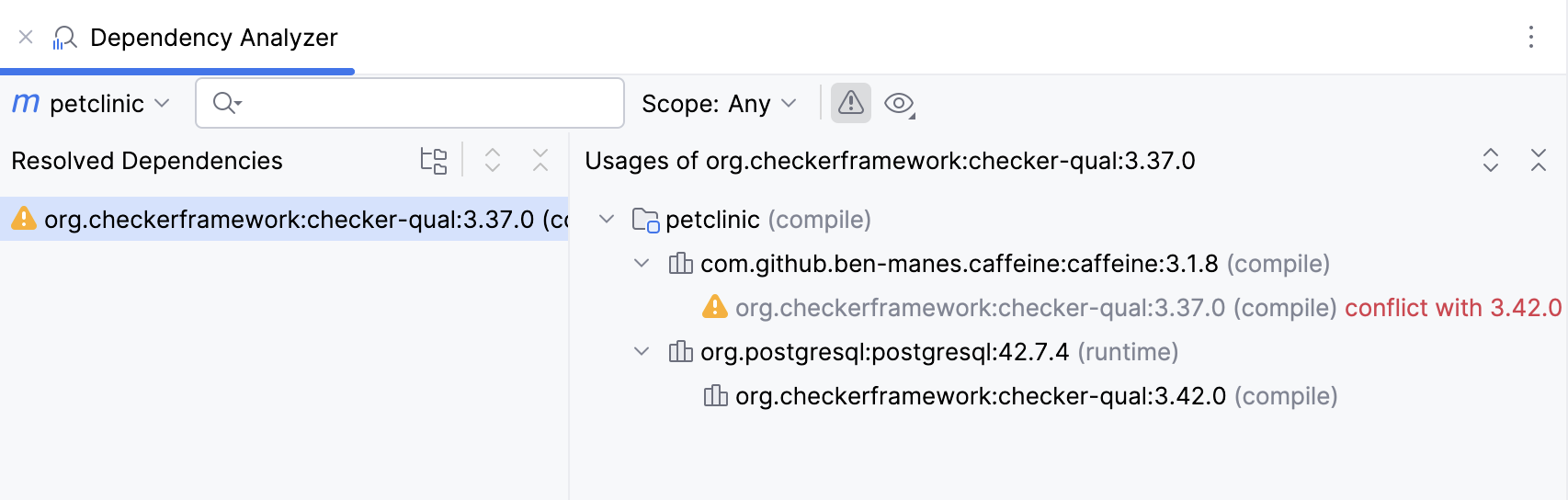 |
Show GroupId | Click |
Show as Tree | Toggle The tree view will help you quickly check the transitive dependencies. |
Expand / Collapse | Use |