Perform tests
Run the selected test or test folder: Ctrl+Shift+F10
Stop the current test session: Ctrl+F2
Run a single test
If your tests don't require any specific actions before start and you don't want to configure additional options, you can run them by using the following options:
Place the caret at the test class to run all tests in that class, or at the test method, and press Ctrl+Shift+F10. Alternatively, click the gutter icon next to the test class or test method.
The gutter icon changes depending on the state of your test:
The
gutter icon marks new tests.
The
gutter icon marks successful tests.
The
gutter icon marks failed tests.

To run all tests in a folder, select this folder in the Project tool window and press Ctrl+Shift+F10 or select Run Tests in 'folder' from the context menu .
Run tests via a run/debug configuration
When you run a test, PhpStorm creates a temporary run configuration. You can save temporary run configurations, change their settings, share them with other members of your team. For more information, refer to Run/debug configurations.
Create a new run configuration or save a temporary one.
From the list on the main toolbar, select the configuration you want to run.
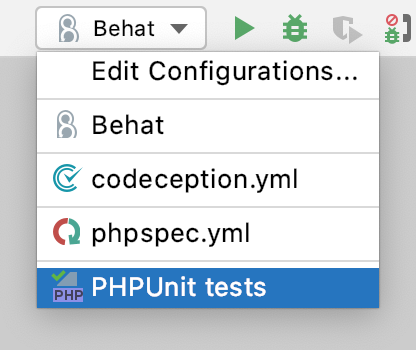
Click
or press Shift+F10.
Create a test configuration
Open the Run/Debug Configuration dialog by doing one of the following:
From the list on the main toolbar, select Run | Edit Configurations.
From the main menu, select Run | Edit Configurations.
Press Alt+Shift+F10 and select Edit Configuration from the context menu.
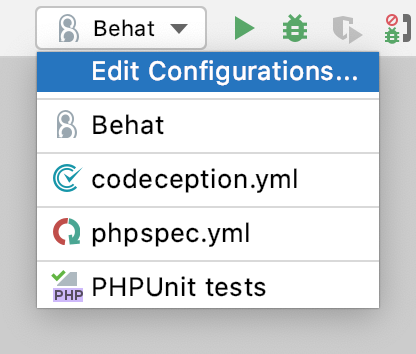
Click
on the toolbar and select the desired configuration type:
Codeception for running Codeception tests. See Codeception and Codeception.
PHPSpec for running PHPSpec specifications. See PHPSpec and PHPSpec.
Jest. See Jest and Run/Debug Configuration: Jest.
Karma. See Karma and Run/Debug Configuration: Karma.
Mocha. See Mocha and Run/Debug Configuration: Mocha.
NodeUnit for testing Node.js. See Testing Node.js and Run/Debug Configuration: NodeUnit.
note
Since May 2018, Nodeunit is deprecated. See the Nodeunit official website for details.
DartUnit for testing Dart, see Run/Debug Configuration: Dart Test.
In the dialog that opens, specify the test scope, configuration parameters, and activities to perform before test execution. Apply the changes and close the dialog.
Create a test configuration for a specific target
In the Project tool window, right-click the desired test directory, individual file, or class.
From the context menu of the selection, choose Create Run configuration.
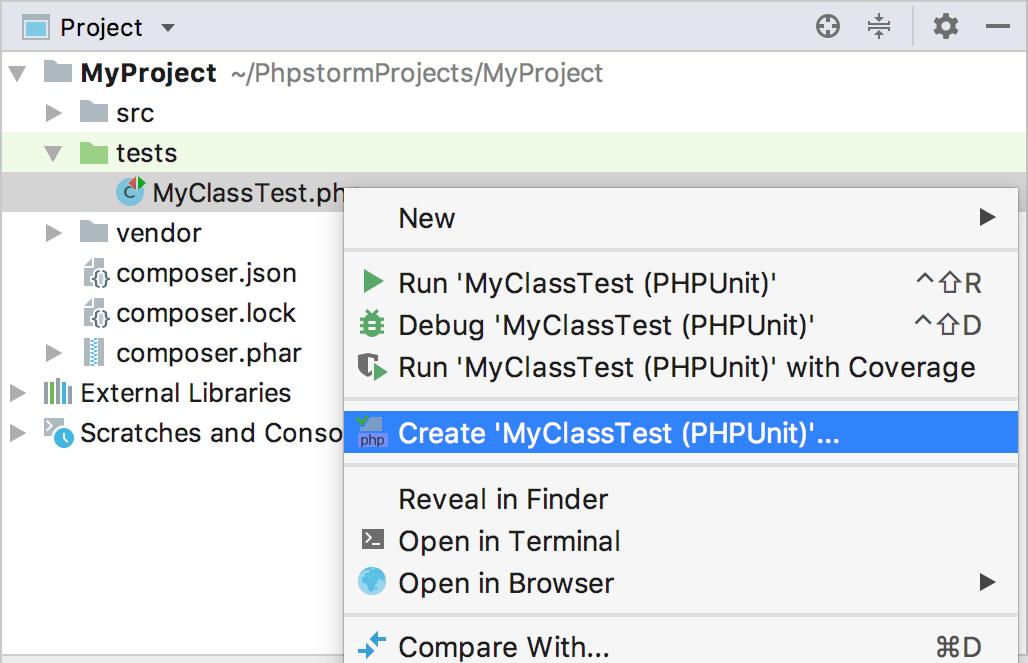
In the Run/Debug Configuration dialog that opens, specify the configuration parameters and activities to perform before test execution. Apply the changes and close the dialog.
tip
Enable the Pin Tab
option on the Run toolbar to open the results of each test run in a separate tab.
After PhpStorm finishes running your tests, it shows the results in the Run tool window on the Test Runner tab. For more information on how to analyze test results, refer to Explore test results.

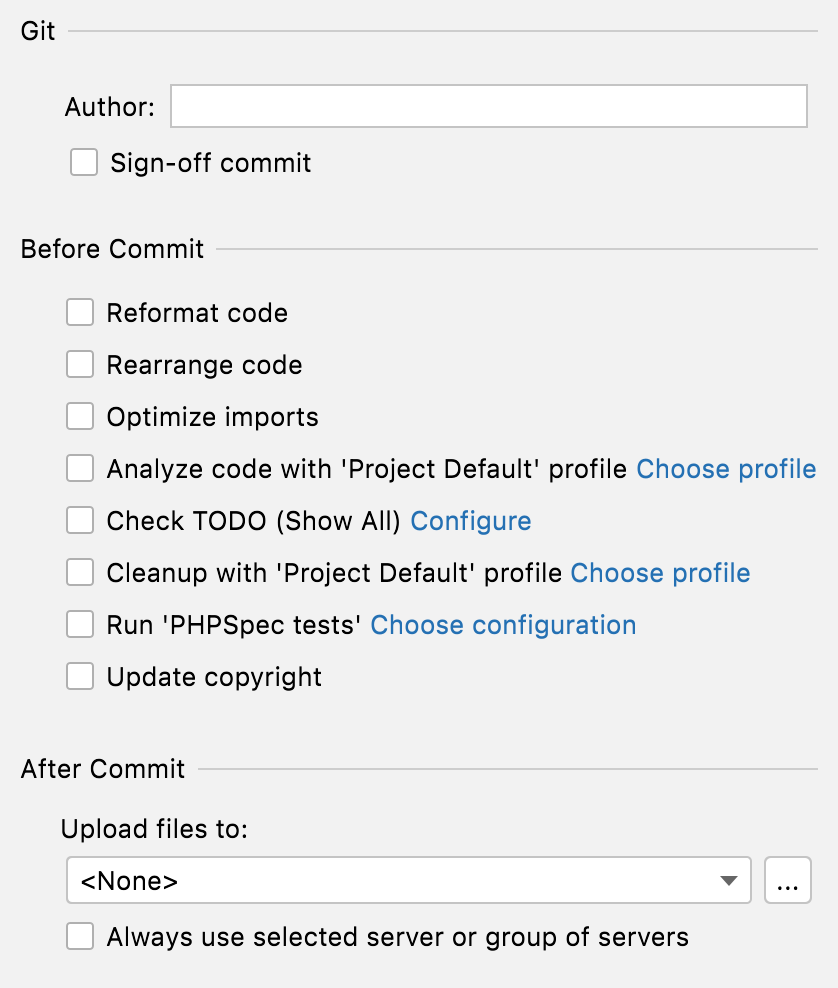
Run tests before commit
When you want to check that your changes wouldn't break the code before committing them, you can do that by running tests as a pre-commit check.
note
This feature is only available for Git and Mercurial.
Set up test configuration
After you have set up the test configuration, the specified tests will run every time you make a commit.
Stop tests
Use the following options on the Run toolbar of the Test Runner tab:
Click
or press Ctrl+F2 to terminate the process immediately.
Rerun tests
Rerun a single test
Right-click a test on the Test Runner tab of the Run tool window and select Run 'test name'.
Rerun all tests in a session
Click
on the Run toolbar or press Ctrl+F5 to rerun all tests in a session.
Rerun failed tests
Click
on the Run toolbar to rerun only failed tests.
Rerun tests automatically
In PhpStorm, you can enable the autotest-like runner: any test in the current run configuration restarts automatically after you change the related source code.
Click
Toggle auto-test on the Run toolbar to enable the autotest-like runner.
Debug failed tests
If you don't know why a test fails, you can debug it.
In the editor, click the gutter on the line where you want to set a breakpoint.
There are different types of breakpoints that you can use depending on where you want to suspend the program. For more information, refer to Breakpoints.
Right-click the
gutter icon next to the failed test and select Debug 'test name'.
The test that has failed will be rerun in the debug mode. After that, the test will be suspended, allowing you to examine its current state.
You can step through the test to analyze its execution in detail.
Thanks for your feedback!