Manage Jupyter notebook servers
This is a Professional feature: download PyCharm Professional to try.
In PyCharm, you can execute code cells using:
Managed server– a Jupyter server that is automatically launched by PyCharm for the current project. It will be terminated when you close PyCharm.
Configured server– any Jupyter server that you connect to by specifying its URL and token.
Launch a local Jupyter server
To run a Jupyter server just execute any code cell. When you initiate cell execution, PyCharm launches the Jupyter server on the local host using any available port (by default, it is the 8888 port). You can switch to the Jupyter Server tool window to preview server's configuration details.
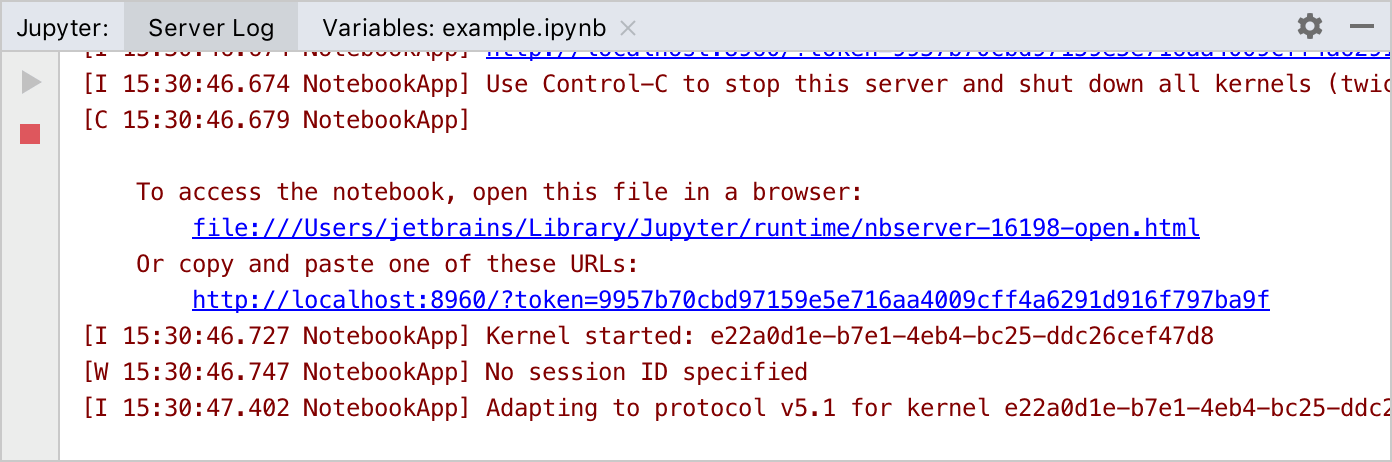
Once the server is launched, it is shown as a managed server in the list of the servers in the Jupyter toolbar. You can also see the automatically created server kernel in the list of kernels. This kernel is based on the PyCharm Python interpreter.

Stop the Jupyter server
To stop any running server, switch to the Jupyter Server tool window and click the
icon or select the corresponding command in the Jupyter Quick List. Preview the status in the Server Log window.

Once you have shut down the server, the current session is terminated. When you start the server next time using the icon or the Jupyter Quick List, execution results for all previous sessions and all notebooks will be lost.
Restart the kernel
You might want to refresh your calculations without shutting down the entire server and affecting any other notebooks. To restart the currently running kernel, click
on the Jupyter notebook toolbar and preview the status in the Server Log window.

You can execute your notebook code cells on a specific Jupyter servers.
Configure the Jupyter server
When you launch any managed server, by default it uses the current Python interpreter and the automatically selected port. However, you can select any other interpreter available in your PyCharm instance and specify an alternative port. You can also connect to any configured server if you know its URL and token.
note
The Jupyter server connection settings are user-specific.
To open the server settings, select Configure Jupyter Server in the list of the Jupyter servers.

Configure the server options:
To customize the default Jupyter server, in the Jupyter Server dialog, select Managed Server and from the Python interpreter list select any local Python interpreter.

To change the automatically detected port, type its number in the Port field.


To connect to any running Jupyter server, in the Jupyter Server dialog, select Configured Server and specify server's path including an URL and a token.

Once done with configuring, click Apply and OK.
Then to explicitly switch to the configured server, select Switch to current Jupyter Server from the list of the servers in the Jupyter toolbar.

Execute any code cell to run the managed server or to connect to the running configured server.
If you see the following warning, the kernel of the newly configured server doesn't match your current Python interpreter. For example, it might have a different set of the installed packages.

You can register your Python interpreter as a kernel on the configured server by clicking the corresponding link. After that you can see it in the list of the kernels for the configured server.
