Legacy type syntax for docstrings
Last modified: 11 January 2023PyCharm supports legacy approach to specifying types in Python using docstrings. In doing so, the supported formats are:
To choose the desired docstring format, use the Python Integrated Tools page of the Settings dialog.
Type syntax in Python docstrings is not defined by any standard. Thus, PyCharm suggests the following notation:
Syntax | Description |
|---|---|
| Class Foo visible in the current scope |
| Class Bar from x.y module |
| Foo or Bar |
| Tuple of Foo and Bar |
| List of Foo elements |
| Dict from Foo to Bar |
| Generic type (T-Z are reserved for generics) |
| Generic type with upper bound Foo |
| Foo parameterized with T |
| Function of Foo and Bar that returns Baz |
| List of dicts from str to datetime (nested arguments) |
Specifying types of local variables
Consider adding information about the expected type of a local variable using :type or @type docstrings:
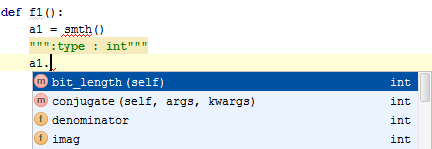
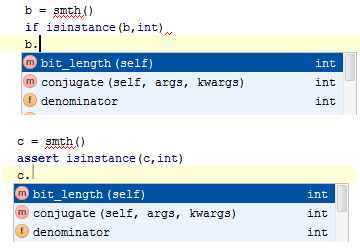
It is also possible to use isinstance to define the expected local variable type:
Specifying types of fields
You can use type hinting to specify the expected type of fields:

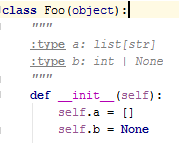
Alternatively, you can specify types of fields in the docstring of a class:
Specifying return types
Use docstrings :rtype or @rtype to specify the expected return type:
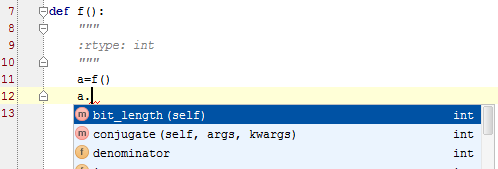
:rtype: collections.Iterable[int] # return type: 'items' is of typegeneratororcollections.Iterable, 'a' is of typeint, see the following code:def my_iter(): global i for i in range(10): yield i items = my_iter() for a in items: print a:rtype: list[int] for my_iter # return type: 'a' is of type
int, see the following code:def my_iter(): for i in range(10): yield i for a in my_iter(): print a
Specifying parameter types
Consider adding information about the expected parameter type. This information is specified using docstrings. You can use different docstrings depending on the selected docstring format, for example, :type, @type, or Args. Use project settings to alter the docstring format (File | Settings | Tools | Python Integrated Tools).


Thanks for your feedback!