Use prompts to explain, refactor, and suggest changes to your code
Use pre-written prompts to explain code, refactor, and find problems in your code. PyCharm provides project-specific context, such as the languages and technologies used in your project.
You can also define your own custom prompts and add them to the AI Actions menu.
Explain code
Select a code fragment and right-click it to open the context menu.
Alternatively, select a code fragment and press Alt+Enter.
Select AI Actions and then Explain Code.
The AI Assistant tool window will open to provide you with an explanation.
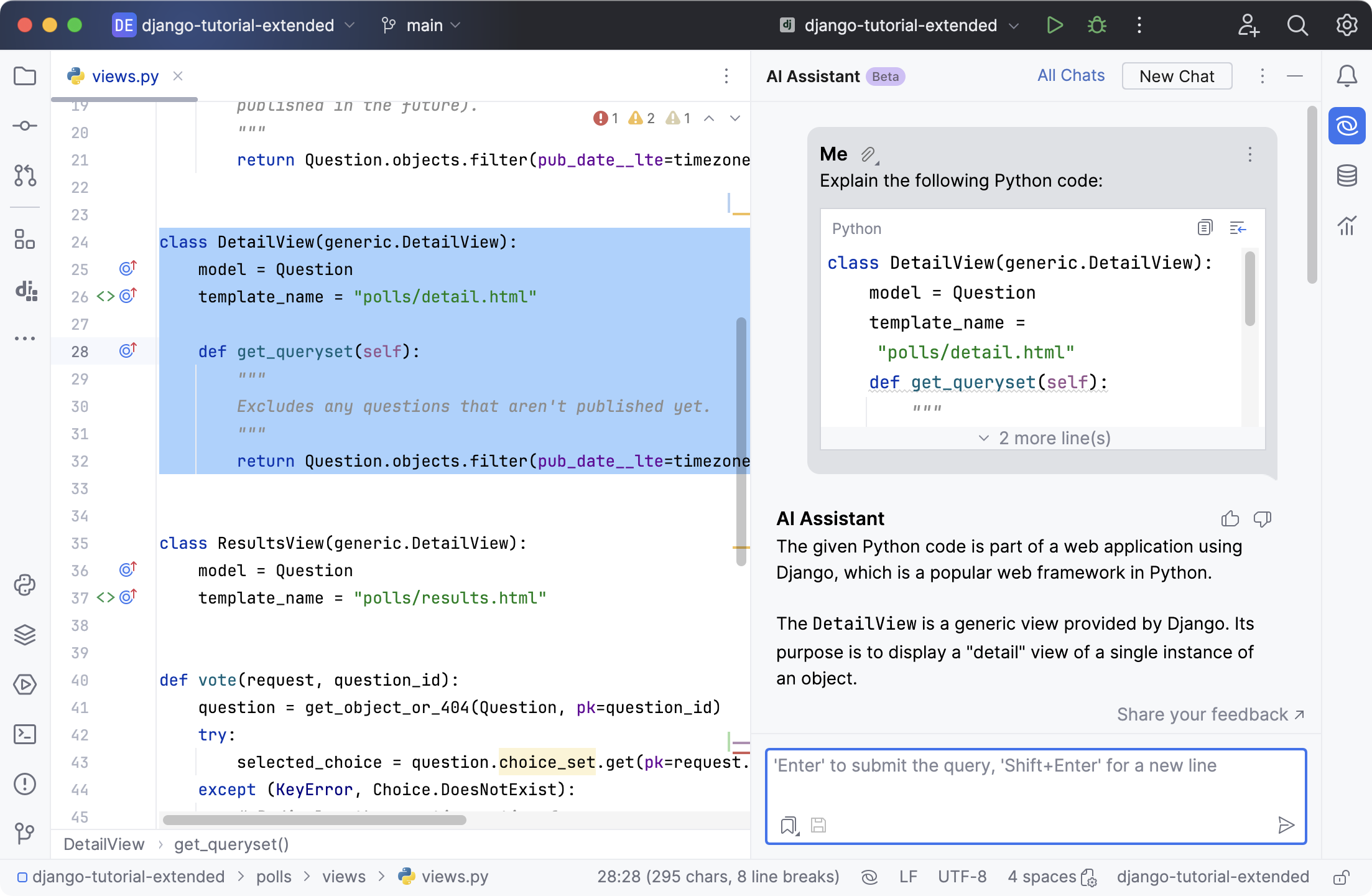
Click
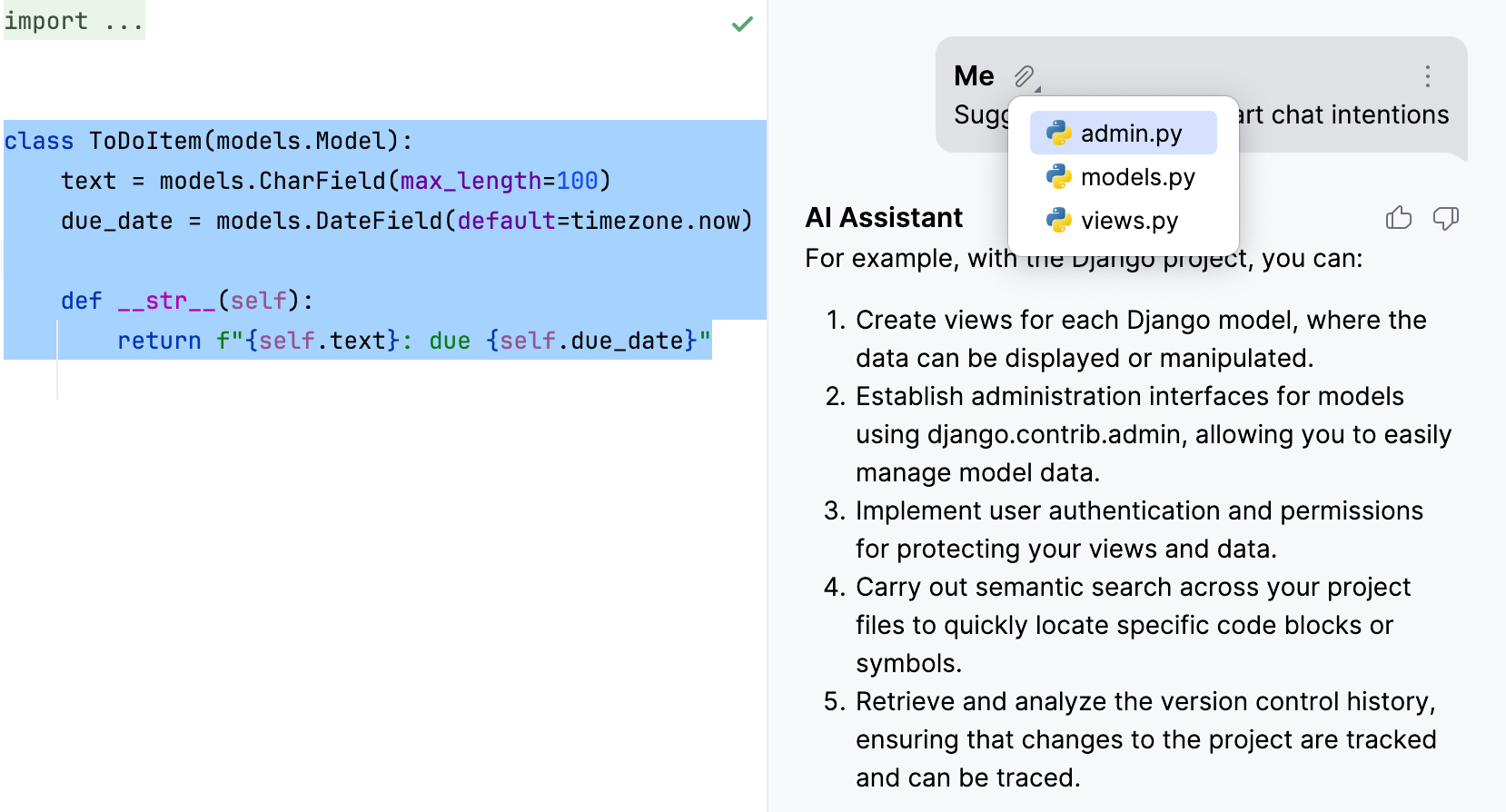
Attached elements to see the list of files that provided the necessary context for generating the answer.
Explain DataFrame
Click
Explain DataFrame in the upper-right corner of the output cell.
The AI Assistant tool window will open to provide a detailed description of the DataFrame.

Explain Jupyter cell
Open Jupyter notebook and do one of the following:
Right-click cell to open the context menu.
Press Alt+Enter.
Select AI Actions and then Explain Code.
Select Jupyter Cell or Whole Jupyter File.
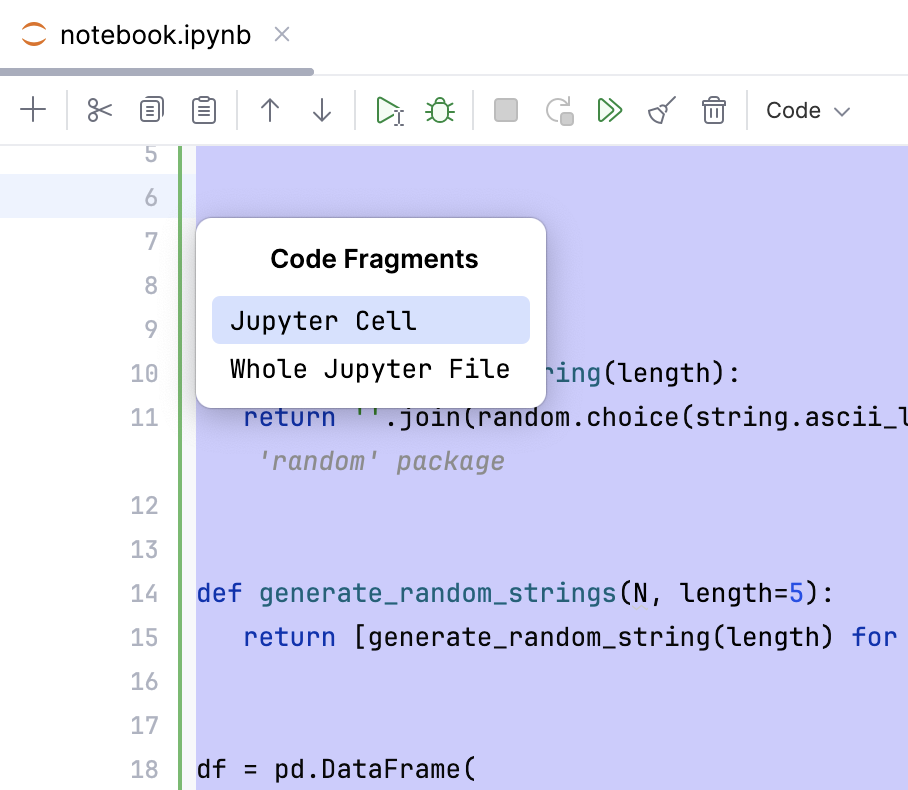
The AI Assistant tool window will open to provide a detailed description of the Jupyter file or selected cell.
Suggest refactoring
Select a code fragment and right-click it to open the context menu.
Alternatively, select a code fragment and press Alt+Enter.
Select AI Actions and then Suggest Refactoring.
The AI chat will open to offer you refactoring suggestions.
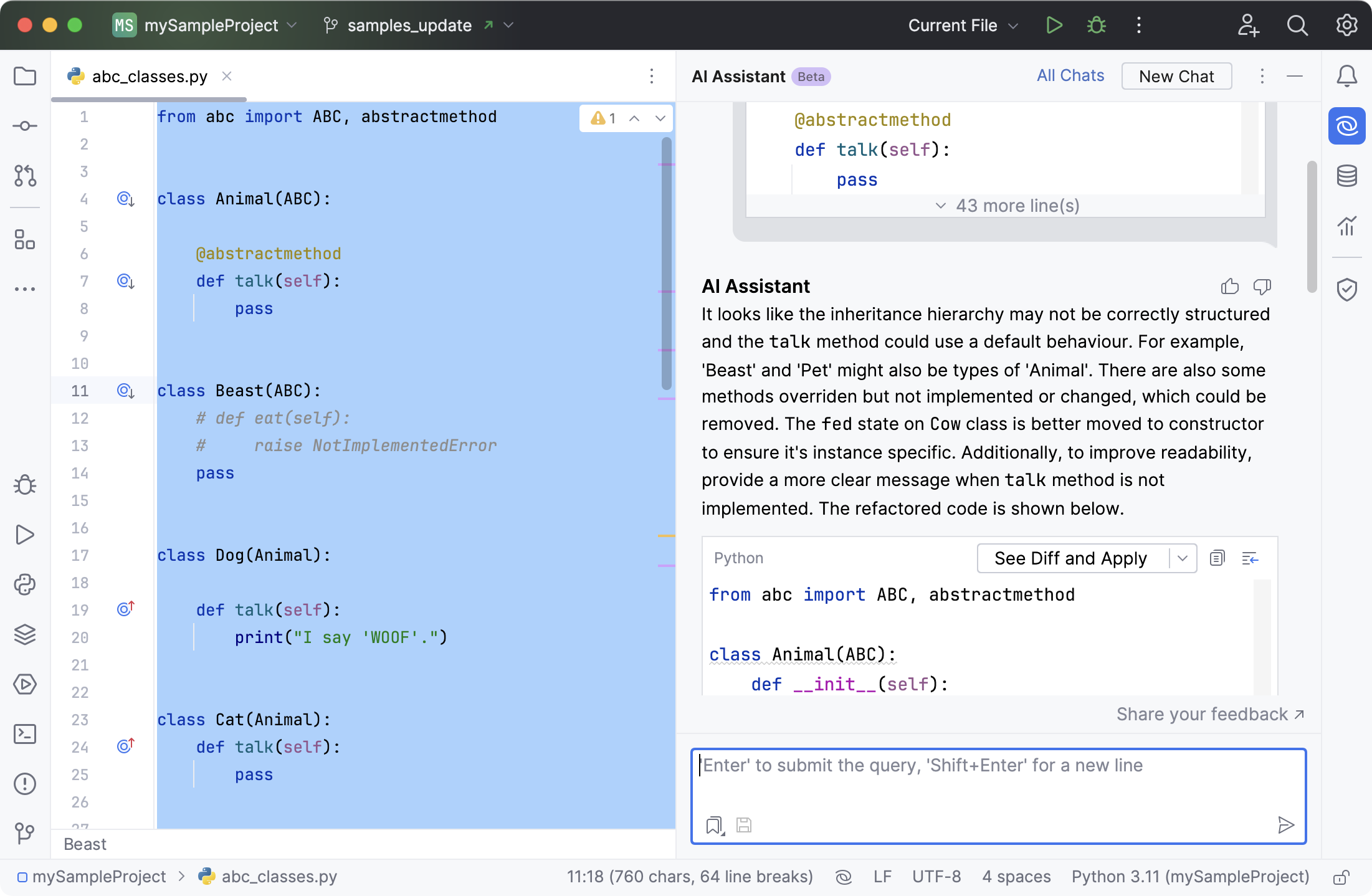
In the field with the refactored code, click See Diff and Apply to open the diff viewer. To skip the diff viewing step, expand the list next to See Diff and Apply and select Apply Immediately.
In the diff viewer, use Unified or Two-Side view to review the suggested changes.
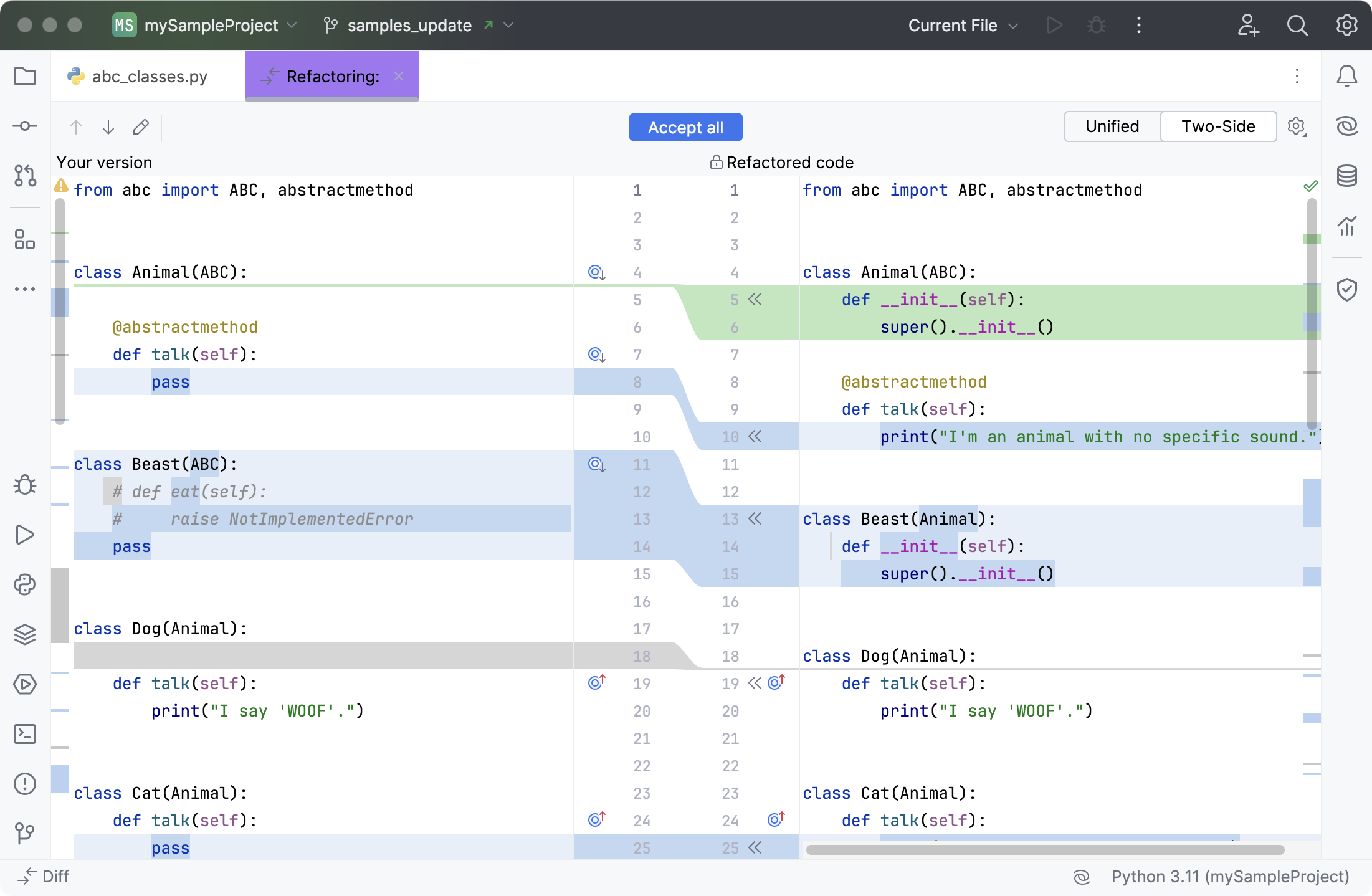
If you like the result, click
Accept in the gutter to move the selected AI-generated code snippets to the source file, or click Accept all to fully replace the originally selected code fragment. Otherwise, close the diff viewer to skip the suggested refactoring.
Find problems
Select a code fragment and right-click it to open the context menu.
Alternatively, select a code fragment and press Alt+Enter.
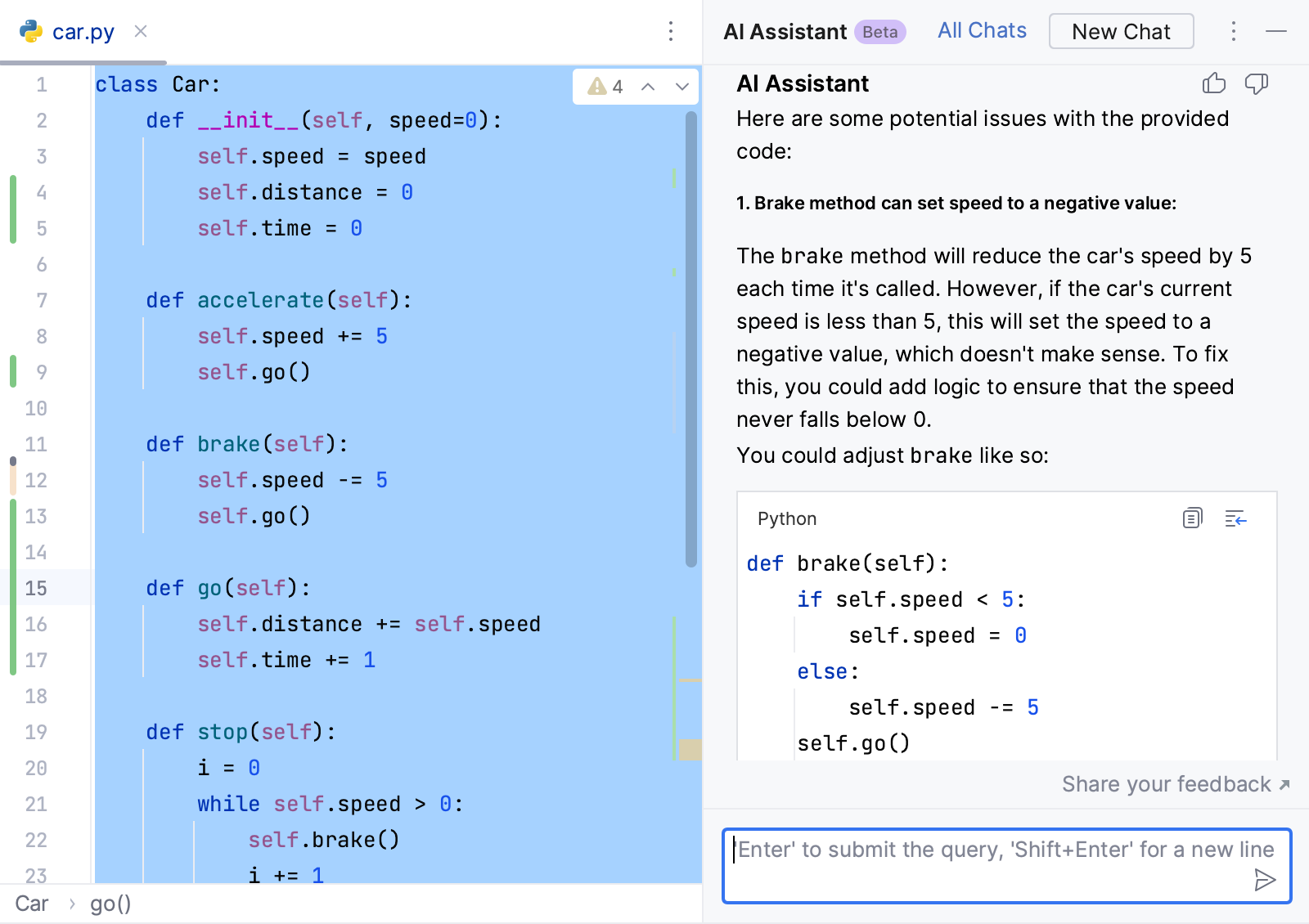
Select AI Actions and then Find Problems.
The AI chat will open to show the potential issues you may want to look into.
Explain runtime error
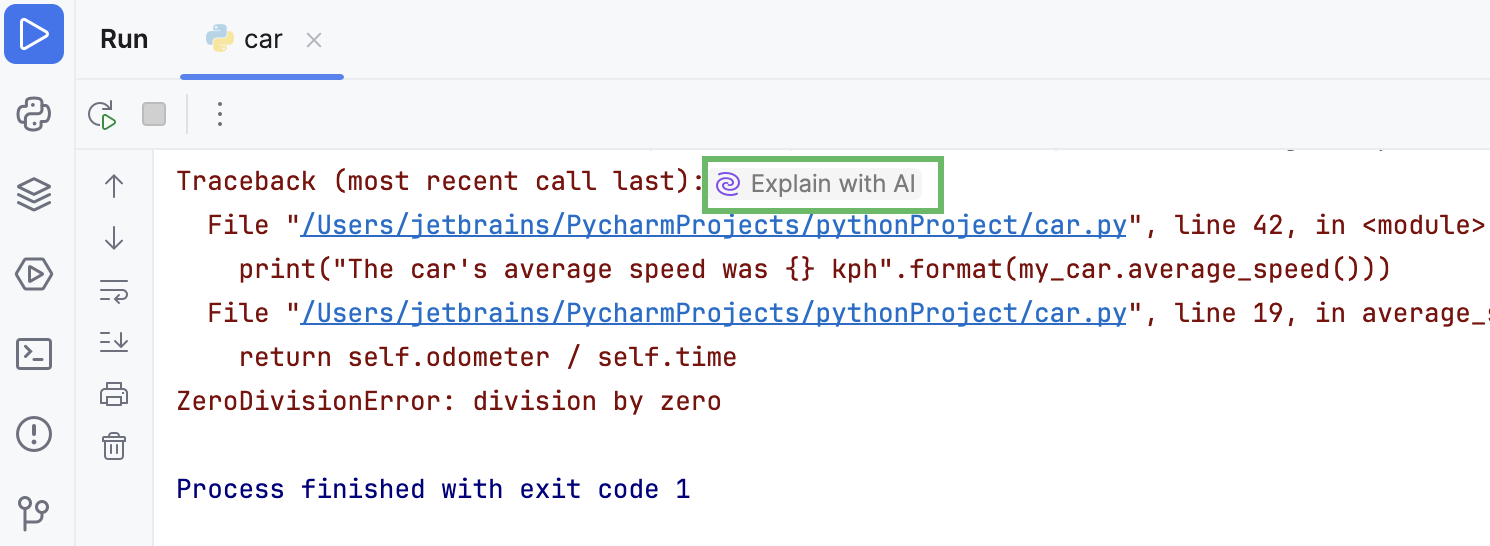
For Python runtime errors shown in the console, PyCharm shows inlay hints, allowing you to get AI explanations for those errors.
Click Explain with AI in the console.
The AI Assistant tool window will open to give you an explanation of the error and suggest a fix.
If you want to use the suggested fix, click
in the field with the refactored code to put the AI-generated code into the editor.
Suggest Django intentions
Select a code fragment and right-click it to open the context menu.
Alternatively, select a code fragment and press Alt+Enter.
Select AI Actions and choose the Django intention.
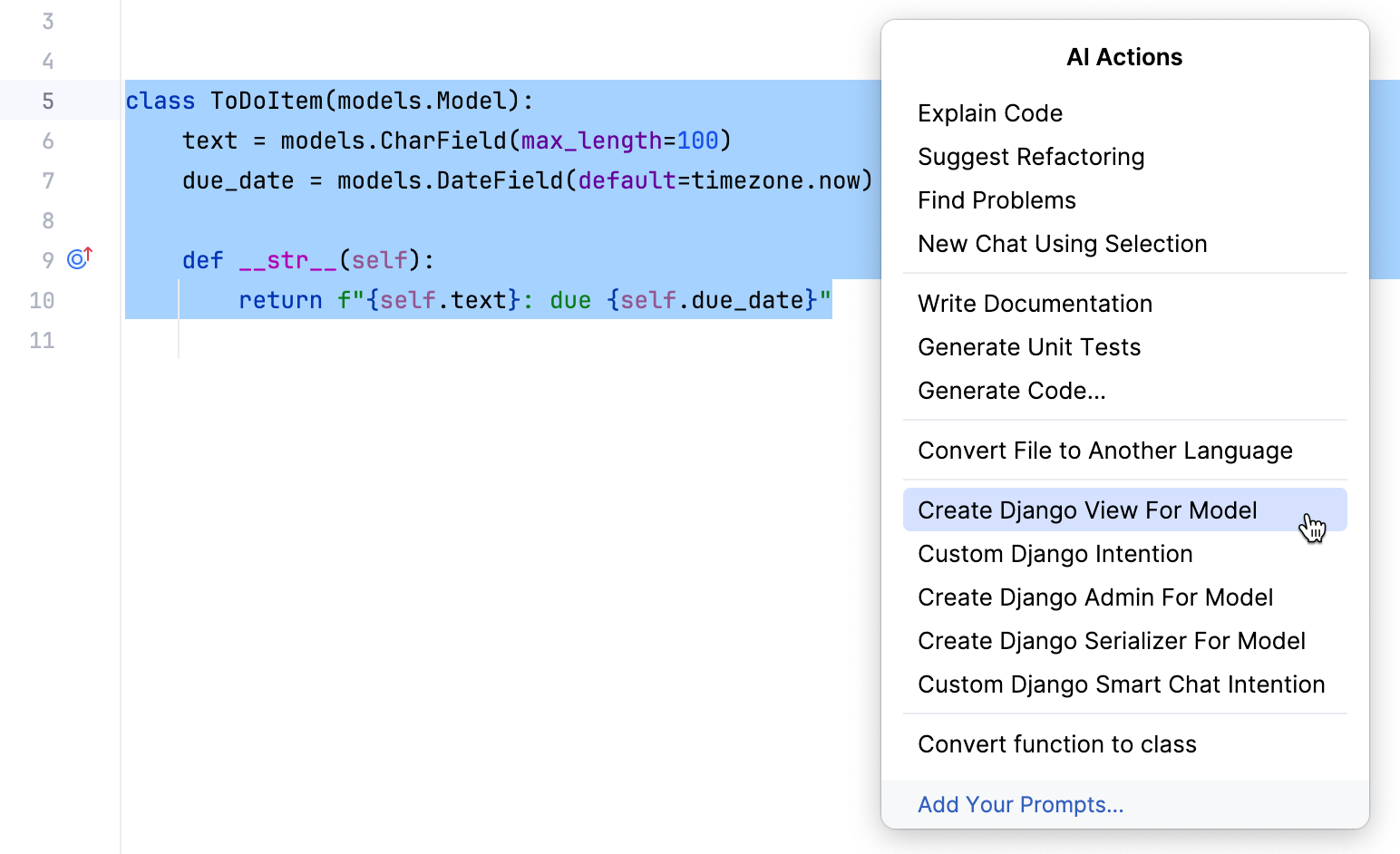
- Create Django View For Model
AI Assistant suggests the code of a class-based view for the selected model along with the steps required to implement it in your project.
This action is available only for Django models.
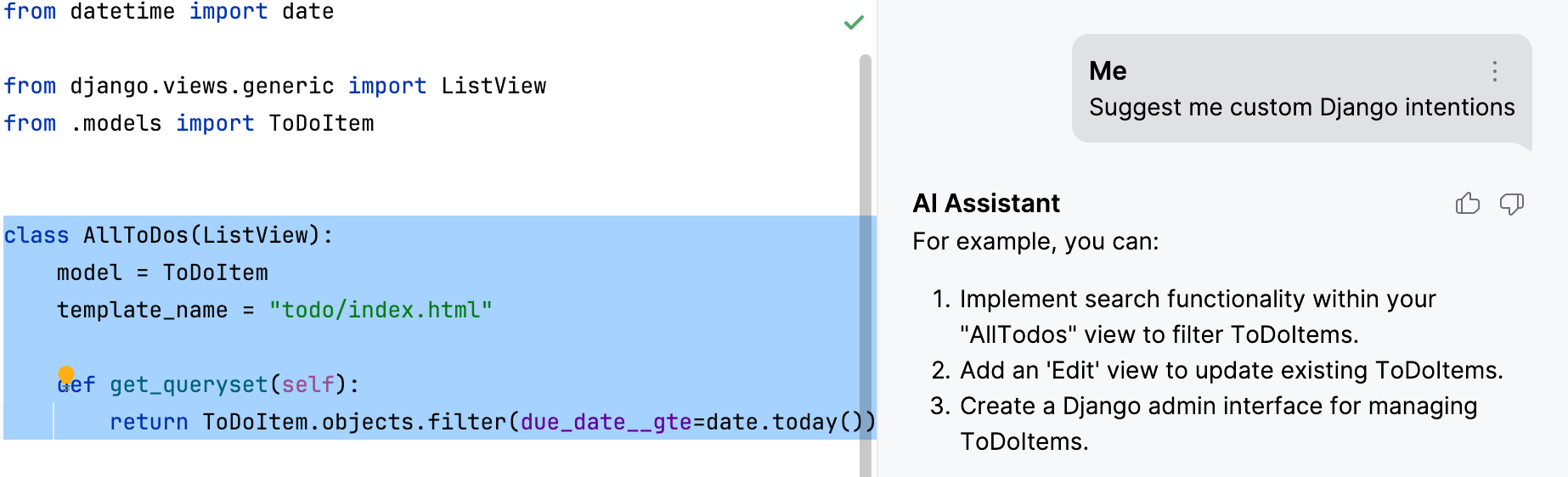
- Custom Django Intention
AI Assistant provides the possible actions for the selected entity.
- Create Django Admin For Model
AI Assistant suggests the code required to register the selected model in the Django admin interface along with other necessary steps.
- Create Django Serializer For Model
AI Assistant suggests the code of a
Serializerclass along with other necessary steps.- Custom Django Smart Chat Intention
AI Assistant provides the possible actions for the selected entity taking into account the context of your project provided as attached elements in the chat.
Add your own prompts to prompts library
You can add your own prompts to the prompts library and use them via the AI Actions menu.
Do one of the following:
Right-click anywhere in the editor to open the context menu, then go to .
Press Alt+Enter, select AI Actions, and click Add your prompts.
Press Ctrl+Alt+S to open settings and then select .
Click
to create a new prompt.
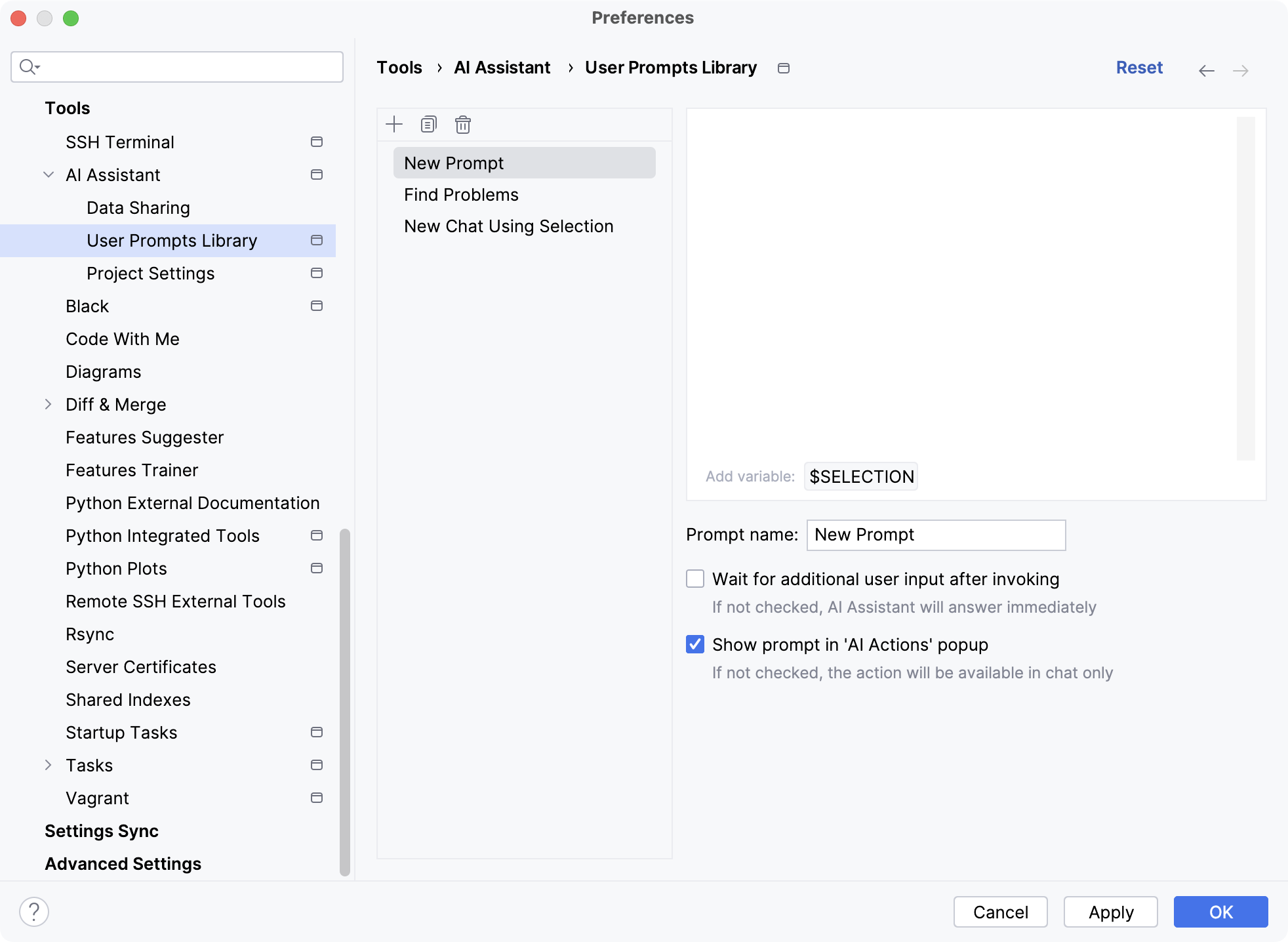
In the text field, write the prompt.
If needed, click the
$SELECTIONvariable to add a Markdown-formatted code block with current code selection and language name to the new prompt.Edit the new prompt name.
Select the first checkbox if you want AI Assistant to wait for you to make additional input in the chat after invoking the prompt.
Keep the second checkbox if you want your new prompt to be listed in the AI Actions menu.
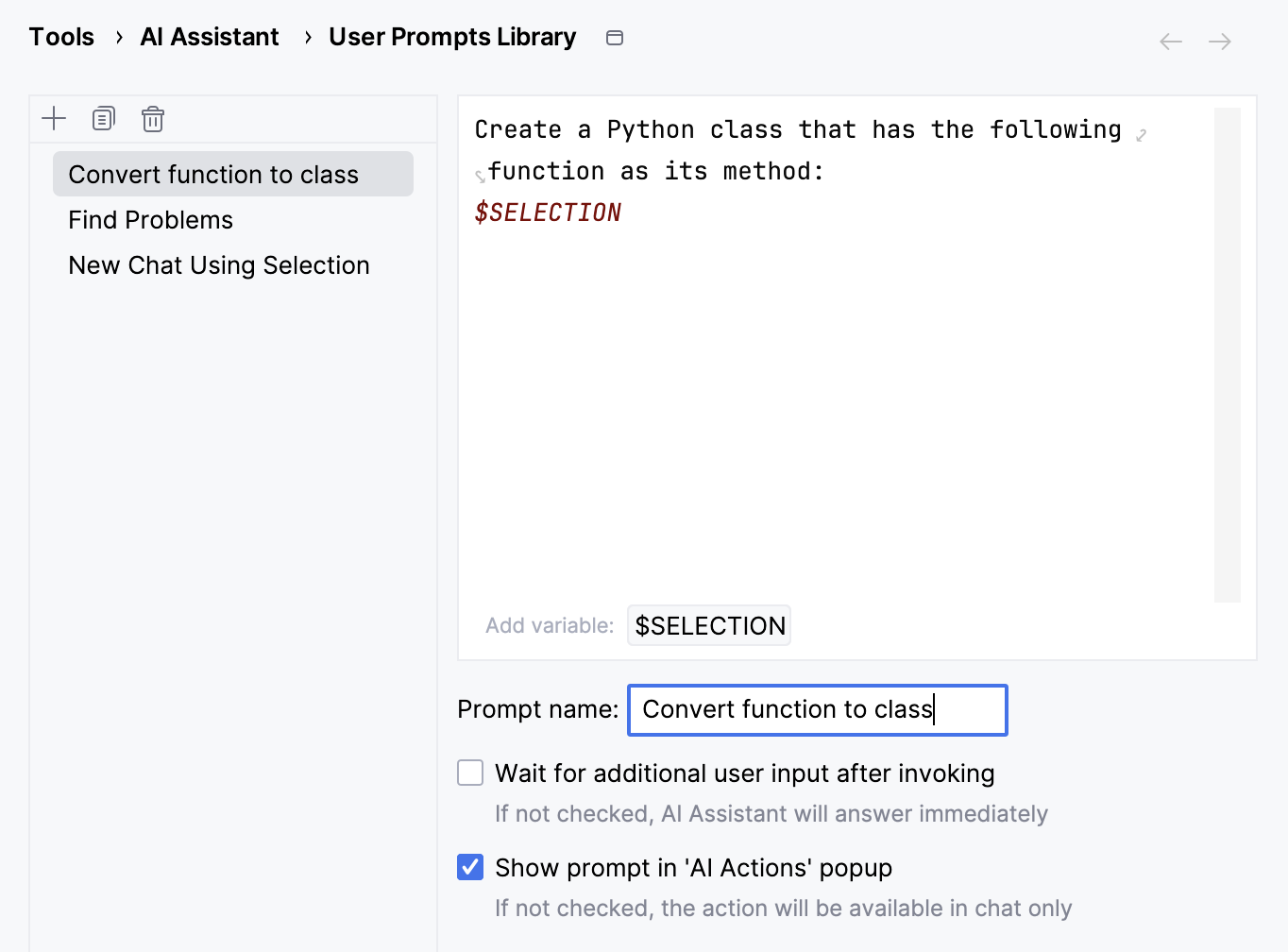
Click Apply.
Once you create a prompt, you can edit or delete it at any time.
You can also select a prompt from the list and move it up or down to change the order in which the prompts are displayed.