Python
All Qodana linters are based on IDEs designed for particular programming languages and frameworks. To analyze Python projects, you can use the following linters:
Qodana for Python is based on PyCharm Professional and licensed under the Ultimate and Ultimate Plus licenses,
Qodana Community for Python is based on PyCharm Community and licensed under the Community license.
To see the list of supported features, you can navigate to the Supported technologies and features section.
Before your start
If your project has external pip dependencies, set them up using the bootstrap key in the qodana.yaml file. For example, if your project dependencies are specified by the requirements.txt file in your project root, in the configuration file add the following line:
Run Qodana
JetBrains IDEs
You can run Qodana in PyCharm and send inspection reports to Qodana Cloud for storage and analysis purposes.
In PyCharm, navigate to .
On the dialog, you can configure Qodana.

This dialog contains the following components:
Name
Description
The
qodana.yamlfileIn the text field, you can set up code analysis used by Qodana in this file. You can learn more about available configuration options
The option
If you want to send reports to Qodana Cloud, you can check this option and paste the project token generated in Qodana Cloud
The option
By checking this option, you can save the Qodana configuration made on this dialog to the
qodana.yamlfile in the project root of your projectThe option
Using the baseline feature, you can skip analysis for specific problems
Click for analyzing your code.
On the tab of the tool window, see the inspection results.
CI/CD
Before running Qodana, create a Qodana Cloud account. In Qodana Cloud, generate a project token that will be used by Qodana for identifying and verifying a license. In Qodana Cloud, you can review inspection reports.
You can run Qodana using the Qodana Scan GitHub action as shown below.
On the tab of the GitHub UI, create the
QODANA_TOKENencrypted secret and save the project token as its value.On the tab of the GitHub UI, set up a new workflow and create the
.github/workflows/code_quality.ymlfile.To inspect the
mainandmasterbranches, as well as release branches and the pull requests coming to your repository, save this workflow configuration to the.github/workflows/code_quality.ymlfile:name: Qodana on: workflow_dispatch: pull_request: push: branches: # Specify your branches here - main # The 'main' branch - master # The 'master' branch - 'releases/*' # The release branches jobs: qodana: runs-on: ubuntu-latest permissions: contents: write pull-requests: write checks: write steps: - uses: actions/checkout@v3 with: ref: ${{ github.event.pull_request.head.sha }} # to check out the actual pull request commit, not the merge commit fetch-depth: 0 # a full history is required for pull request analysis - name: 'Qodana Scan' uses: JetBrains/qodana-action@v2024.1 env: QODANA_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.QODANA_TOKEN }}
More configuration examples are available in the GitHub Actions section.
Make sure that these plugins are installed on your Jenkins instance:
Docker and Docker Pipeline are required for running Docker images,
git is required for git operations in Jenkins projects.
Make sure that Docker is installed and accessible by Jenkins.
If applicable, make sure that Docker is accessible by the jenkins user as described in the Manage Docker as a non-root user section of the Docker documentation.
Create a Multibranch Pipeline project as described on the Jenkins documentation portal.
In the root directory of your project repository, create the Jenkinsfile.
Save this snippet to the Jenkinsfile:
Make sure that your project repository is accessible by GitLab CI/CD.
In the root directory of your project, create the .gitlab-ci.yml file and save this configuration in it:
In this snippet:
The
cachekeyword configures GitLab CI/CD caches to store the Qodana cache, so subsequent runs will be faster,The
scriptkeyword runs theqodanacommand and enumerates the Qodana configuration options described in the Shell commands section,The
variableskeyword defines theQODANA_TOKENvariable referring to the project token.
Assuming that you have already created your project and build configuration, follow the steps below.
In the TeamCity UI, navigate to the configuration page of a build where you would like to run Qodana.
On the page, click the button.
On the page that opens, select the runner.
On the page, click and configure the runner:
uniquely identifies this step among other build steps.
uniquely identifies this step among other build steps.
configures the build condition that will trigger this build step.
sets the directory for the build process, see the TeamCity documentation for details. You can leave this field empty if the
Checkout directoryparameter is specified on the tab.uniquely identifies the report to let you distinguish between multiple reports when several inspection steps are configured within a single build.
The checkbox configures Qodana report availability in the Test tab of the TeamCity UI. Using this option, you can view codebase problems along with other problems detected.
configures the Qodana linter.
is by default set to
Latest.defines an inspection profile:
Recommended (default)is one of the default profiles.Embedded profilelets you select a default profile, see the Existing Qodana profiles section for details.Path to the IntelliJ profilelets you specify the path to your custom profile. To use this option, make sure that you also configure the custom profile in theqodana.yamlfile.
configures a project token generated in Qodana Cloud.
configures the arguments accepted by a Docker image, see the Shell commands section for details.
lets you extend the default Qodana functionality, see the Options section for details.

Click the button.
Command line
You have two options to run Qodana locally: you can either run Qodana CLI or directly use the Docker image of Qodana. As Qodana linters are distributed in Docker containers, Docker needs to be installed on your local machine.
If you are using Linux, you should be able to run Docker under your current non-root user, check the installation page for details.
Here are the examples of how you can run Qodana locally.
Here, the QODANA_TOKEN variable refers to the project token.
If you omit the -l option, the Qodana for Python linter will run by default.
To start, pull the image from Docker Hub (only necessary to get the latest version):
Start local analysis with source-directory pointing to the root of your project and QODANA_TOKEN referring to the project token:
In your browser, open Qodana Cloud to examine analysis results and reconfigure the analysis, see the Inspection report section for details.
Explore analysis results
JetBrains IDEs
You can load the latest Qodana report from Qodana Cloud to your IDE as explained below.
In your IDE, navigate to .
In the dialog, click .

This will redirect you to the authentication page.
Select the Qodana Cloud project to link your local project with.

If you check the option, you will be able to receive the most actual and relevant reports from Qodana Cloud.

In this case, the IDE will search and fetch from Qodana Cloud the report that has the revision ID corresponding to the current revision ID (HEAD). If this report was not found, the IDE will select the previous report with the revision closest to the current revision ID (HEAD). Otherwise, the IDE retrieves the latest available report from Qodana Cloud.
On the tab of the tool window, view analysis results.
Qodana Cloud
Once Qodana analyzed your project and uploaded the analysis results to Qodana Cloud, in Qodana Cloud navigate to your project and review the analysis results report.
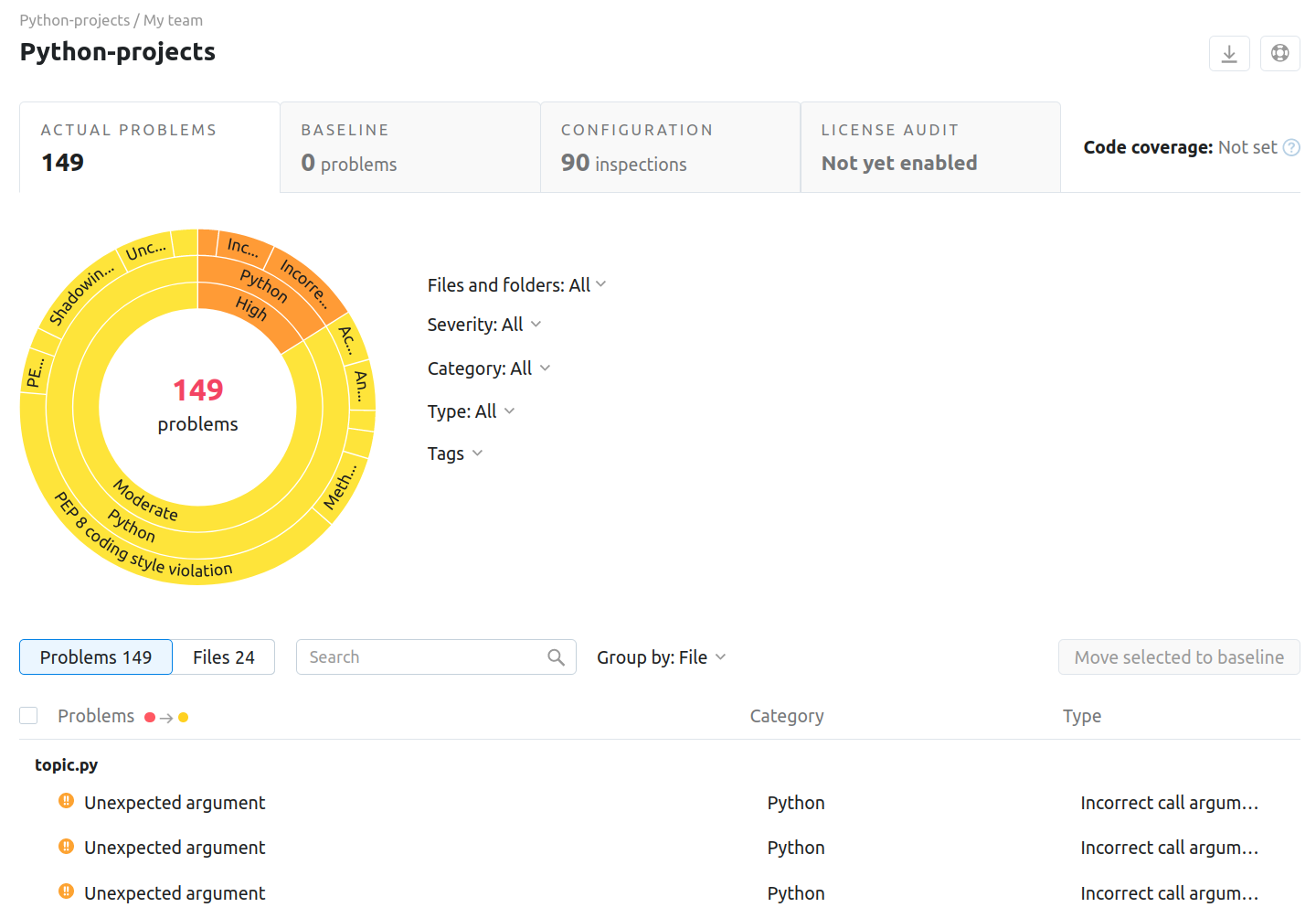
To learn more about Qodana report UI, see the Inspection report section.
Extend Qodana configuration
Adjusting the scope of analysis
Out of the box, Qodana provides two predefined profiles hosted on GitHub:
qodana.starteris the default profile and a subset of the more comprehensiveqodana.recommendedprofile,qodana.recommendedis suitable for running in CI/CD pipelines and mostly implements the default PyCharm profile, see the PyCharm documentation for details.
You can customize Qodana profiles using configurations in YAML and XML formats. To learn more about configuration basics, visit the Configure Qodana your way section.
Enabling the baseline
You can skip analysis for specific problems using the baseline feature. Information about a baseline is contained in a SARIF-formatted file.
JetBrains IDEs
In your IDE, navigate to the tool window.
In the tool window, click the tab.
On the tab, click the button.
On the dialog that opens, expand the section and specify the path to the baseline file, and then click .
CI/CD
This snippet contains the args: --baseline,qodana.sarif.json line that specifies the path to the SARIF-formatted baseline file:
The stages block contains the --baseline <path/to/qodana.sarif.json> line that specifies the path to the SARIF-formatted baseline file:
You can use the --baseline <path/to/qodana.sarif.json> line in the script block to invoke the baseline feature.
Command line
In these snippets, the --baseline option configures the path to the SARIF-formatted file containin a baseline:
Enabling the quality gate
You can configure quality gates for the total number of project problems and specific problem severities in both linters, and code coverage thresholds available only in the Qodana for Python linter, by saving this snippet to the qodana.yaml file:
Analyzing pull requests
CI/CD
On the tab of the GitHub UI, create the
QODANA_TOKENencrypted secret and save the project token as its value.On the tab of the GitHub UI, set up a new workflow and create the
.github/workflows/code_quality.ymlfile.Add this snippet to the
.github/workflows/code_quality.ymlfile:name: Qodana on: workflow_dispatch: pull_request: push: branches: # Specify your branches here - main # The 'main' branch - 'releases/*' # The release branches jobs: qodana: runs-on: ubuntu-latest permissions: contents: write pull-requests: write checks: write steps: - uses: actions/checkout@v3 with: ref: ${{ github.event.pull_request.head.sha }} # to check out the actual pull request commit, not the merge commit fetch-depth: 0 # a full history is required for pull request analysis - name: 'Qodana Scan' uses: JetBrains/qodana-action@v2024.1 env: QODANA_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.QODANA_TOKEN }}
In the root directory of your project, save the .gitlab-ci.yml file containing the following snippet:
Here, the --diff-start option specifies a hash of the commit that will act as a base for comparison.
Information about configuring TeamCity for analyzing pull and merge requests is available on the TeamCity documentation portal.
Command line
To analyze changes in your code, employ the --diff-start option and specify a hash of the commit that will act as a base for comparison:
Supported technologies and features
This table contains the list of technologies supported by both linters.
Programming languages | Python |
Frameworks and libraries | Django Google App Engine Jupyter Pyramid |
Databases and ORM | MongoDB MySQL Oracle PostgreSQL SQL SQL Server |
Markup languages | CSS HTML JSON and JSON5 RELAX NG XML YAML |
Scripting languages | Shell script |
Here is the list of Qodana features supported per each linter.
Feature | Qodana Community for Python | Qodana for Python |
|---|---|---|
✔ | ✔ | |
✔ | ✔ | |
✔ | ||
✔ | ||
✔ | ||
✔ |