Smart completion
This command filters the list of types, methods, and variables to match the expected type of expression. It works anywhere as long as ReSharper can determine the expected type of the expression, for example, right-hand sides of assignments, variable initializers, or return statements. If several return types are possible, ReSharper detects the most recently used symbol of an applicable type and automatically selects it in the lookup list. Type-Matching Completion can also suggest creating anonymous delegates, lambda expressions, and regular methods, as well as local variables for out parameters. In addition to that, in object initializers, Type-Matching Completion suggests fields/properties that were not yet assigned a value.
By default, smart completion items in C# and VB.NET are included in the suggestion lists of automatic and basic completion. If you want to change the default behavior, use the corresponding controls on the page of ReSharper options Alt+R, O.
Invoke smart completion
Place the caret at the position where you're going to type your code.
Press Control+Shift+Space.
Select a suggestion from the list and press Enter or start typing the initial letters of the identifier or its CamelHumps abbreviation to narrow down the list of suggestions.
When you use code completion over existing code items, you can either insert the selected completion suggestion before the existing item by pressing Enter or replace the existing identifier with the selected suggestion by pressing Tab. If necessary, you can change the default shortcuts on the page of ReSharper options Alt+R, O.
When you select items in completion lists using keyboard, the selection will jump to the first item after the last item and vice versa. You can disable this behavior by clearing Loop selection around ends of a list on the page of ReSharper options Alt+R, O.
Complete method calls
When choosing a method call from the completion list, by default ReSharper automatically inserts a pair of parentheses ( ) and sets the caret between them. You can change this behavior with the Automatically insert parenthesis after completion option on the page of ReSharper options Alt+R, O.
Note that you can type the opening parenthesis ( instead of Tab or Enter when a method is selected in the completion list. In this case the pair of parentheses will be inserted regardless of this option.
Exclude types and namespaces from completion suggestions
You may want some types or namespaces not to be suggested, for example, if you have something similar to a system type in your solution, say MyFramework.MyCollections.List, but you are not actually using it. To exclude such items from the suggestions, add them to the Exclude from import and completion list on the page of ReSharper options Alt+R, O.
The format of the entries is Fully.Qualified.Name, Fully.Qualified.Name.Prefix*, or *Fully.Qualified.Name.Suffix. Generic types are specified as List`1.
Examples of smart completion
You can use the following examples to get an idea of how smart type-matching completion works with various code items:
After a return statement
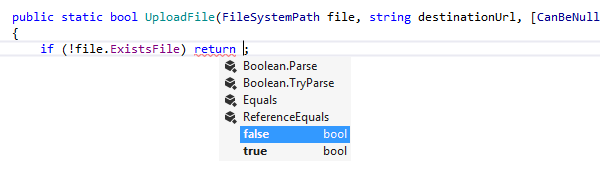
In the right-hand side of assignments
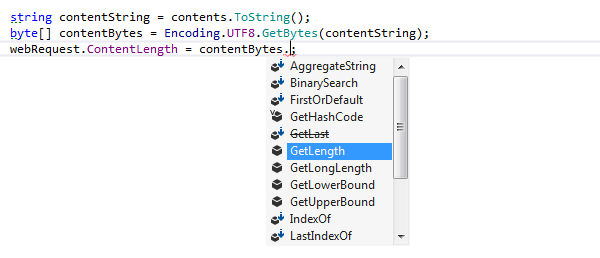
In cast expressions
Before:

After launching Type-Matching Completion (since there's a single option in this case, ReSharper inserts the expected type without displaying a list):

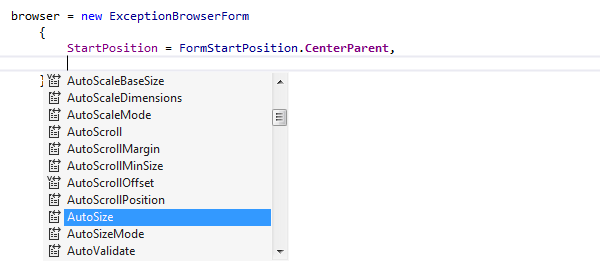
In object initializers
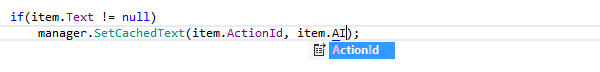
ReSharper provides Type-Matching Completion for setting properties in object initializers that were not previously set for a particular object:
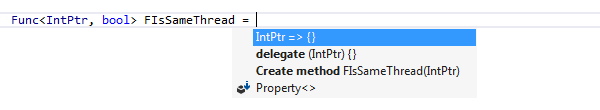
In lambda expressions
In addition to traditional anonymous and named methods, Type-Matching Completion readily generates lambda-expression syntax:
Creating a local variable in place of an out parameter

Using CamelHumps
This feature is supported in the following languages and technologies:
The instructions and examples given here address the use of the feature in C#. For more information about other languages, refer to corresponding topics in the Languages and frameworks section.