Pull Members Up refactoring
ReSharper | Refactor | Pull Members Up…
To assign a shortcut, go to Tools | Options | Environment | Keyboard and find the ReSharper_PullUp command.
This refactoring helps to move type members and implemented interfaces from a derived type up the inheritance hierarchy to a base type. For example, if you have MyDerivedClass : MyBaseClass, IMyInterface, this refactoring can help you move members of MyDerivedClass to MyBaseClass or IMyInterface or to any of their ancestors. The refactoring can also move the entire implementation of IMyInterface to MyBaseClass or any of its ancestors.
tip
The reverse functionality is available with the Push Members Down refactoring refactoring.
In the example below, we invoke the refactoring on MyDerivedClass to add void Foo() implemented there to IMyInterface:
Before refactoring
interface IMyInterface{} class MyDerivedClass : IMyInterface{ public void Foo() { Console.WriteLine("Hello"); }}After refactoring
interface IMyInterface{ void Foo();} class MyDerivedClass : IMyInterface{ public void Foo() { Console.WriteLine("Hello"); }}Select a type in one of the following ways:
In the editor, place the caret at the name of a type.
Select a type in the Solution Explorer.
Select a type in the File Structure window window.
Select a type in the Class View.
Select a type in the Object Browser.
Select a type in the type dependency diagram.
Or, alternatively, select a member in the editor or in a tool window.
Do one of the following:
Press CtrlShift0R and then choose Pull Members Up.
Right-click and choose Refactor | Pull Members Up from the context menu.
Choose ReSharper | Refactor | Pull Members Up… from the main menu.
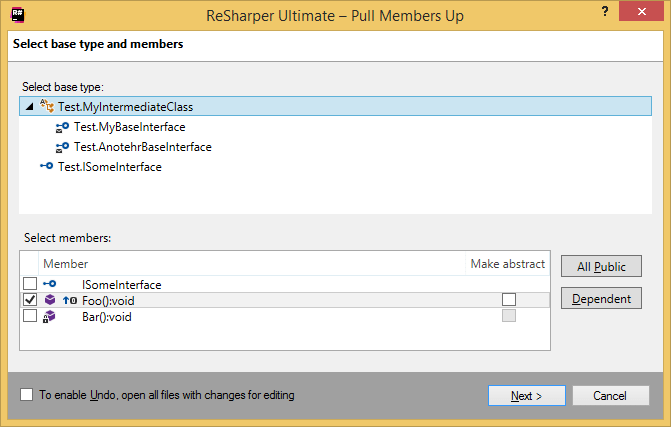
The Pull Members Up dialog will open.
Select a destination base type from the list of available types. Base types are displayed as a reversed hierarchy where types from the top of the hierarchy are displayed as most inner nodes.
Select members and/or interfaces that you want to move. You can also click All Public to quickly select all public members and/or Dependent to select members that are referenced by other selected members, implement the selected interfaces, or override members in base classes.
For any member, you can select Make abstract (if applicable) to create an abstract member in the target base class and leave its implementation in the current class.
To apply the refactoring, click Next.
If no conflicts are found, ReSharper performs the refactoring immediately. Otherwise, it prompts you to resolve conflicts.
This feature is supported in the following languages and technologies:
The instructions and examples given here address the use of the feature in C#. For more information about other languages, refer to corresponding topics in the Languages and frameworks section.