Regular expression syntax reference
This section is a brief summary of regexp syntax that can be used for creating search and replace as well as issue navigation patterns.
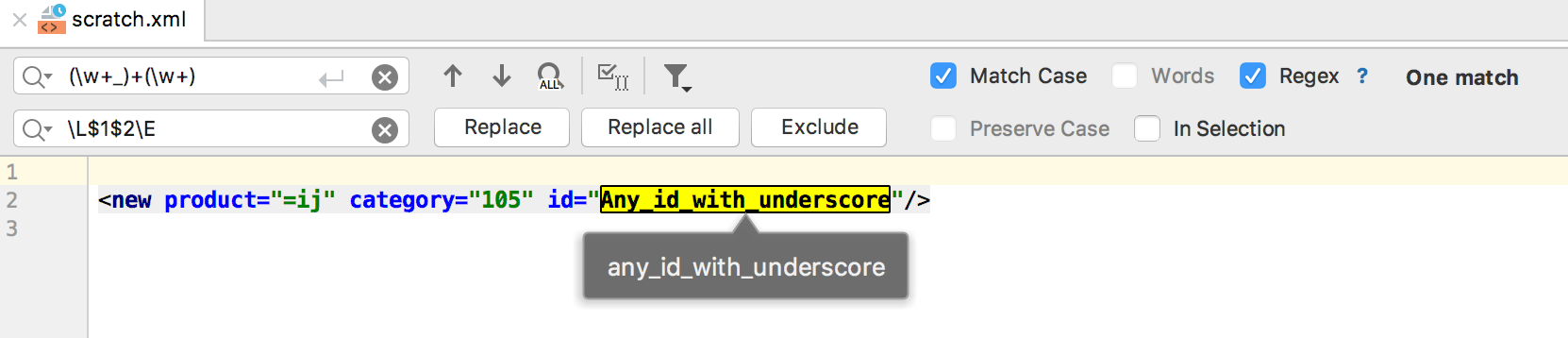
Note that JetBrains Rider has a wide range of features for regular expression assistance, such as syntax highlighting and IntelliSense, in your code.
RegEx syntax reference
Character | Description |
|---|---|
| Marks the next character as either a special character or a literal. For example:
|
| Matches the beginning of input. |
| Matches the end of input. |
| Matches the preceding character zero or more times. For example, "zo*" matches either z or zoo. |
| Matches the preceding character one or more times. For example, "zo+" matches zoo but not z. |
| Matches the preceding character zero or one time. For example, |
| Matches any single character except a newline character. |
| Matches subexpression and remembers the match. If a part of a regular expression is enclosed in parentheses, that part of the regular expression is grouped together. Thus a regex operator can be applied to the entire group.
|
x | Matches either x or y. For example, |
{ | n is a non negative integer. Matches exactly n times. For example, |
{ | n is a non negative integer. Matches at least n times. For example,
|
| m and n are nonnegative integers. Matches at least n and at most m times. For example, |
| A character set. Matches any one of the enclosed characters. For example, |
| A negative character set. Matches any character not enclosed. For example, |
| A range of characters. Matches any character in the specified range. For example, "[a-z]" matches any lowercase alphabetic character in the range a through z. |
| A negative range characters. Matches any character not in the specified range. For example, |
| Matches a word boundary, that is, the position between a word and a space. For example, |
| Matches a non-word boundary. |
| Matches a digit character. Equivalent to |
| Matches a non-digit character. Equivalent to |
| Matches a form-feed character. |
| Matches a newline character. |
| Matches a carriage return character. |
| Matches any white space including space, tab, form-feed, and so on. Equivalent to |
| Matches any nonwhite space character. Equivalent to |
| Matches a tab character. |
| Matches a vertical tab character. |
| Matches any word character including underscore. Equivalent to |
| Matches any non-word character. Equivalent to |
| Matches num, where num is a positive integer, denoting a reference back to remembered matches. For example, |
| Matches n, where n is an octal escape value. Octal escape values should be 1, 2, or 3 digits long. For example,
Octal escape values should not exceed 256. If they do, only the first two digits comprise the expression. Allows ASCII codes to be used in regular expressions. |
| Matches n, where n is a hexadecimal escape value. Hexadecimal escape values must be exactly two digits long. For example, Allows ASCII codes to be used in regular expressions. |
| Finds a |
| This regex entered in the search field, means that you are trying to find a |
| Changes the case of the next character to the lower case. Use this type of regex in the replace field. |
| Changes the case of the next character to the upper case. Use this type of regex in the replace field. |
| Changes the case of all the subsequent characters up to |
| Changes the case of all the subsequent characters up to |
| This is a pattern for "negative lookahead". For example, |
| This is a pattern for "positive lookahead". For example, |
| This is a pattern for "positive lookbehind". For example, |
| This is a pattern for "negative lookbehind". For example, |
Since JetBrains Rider supports all the standard regular expressions syntax, you can check https://www.regular-expressions.info for more information about the syntax.