Connect and work with JetBrains Gateway
You can connect to a remote server using the SSH connection to develop, run and deploy your project.
Prerequisites for the remote host
You have installed a compatible SSH server on the Linux platform.
The Linux platform has any recent Linux AMD64 distribution such as Ubuntu 16.04+, RHEL/Centos 7+, and so on. There is no arm64 support yet. We recommend using machines with 2+ cores, 4GB+ of RAM, and 5GB+ of disk space.
You need to have the sftp subsystem enabled on the remote host.
JetBrains Gateway
JetBrains Gateway is a lightweight launcher that connects a remote server with your local machine, downloads necessary components on the backend, and opens your project in JetBrains Client.
Check out the quick video on how to start working with JetBrains Gateway.
You can use JetBrains Gateway as a standalone launcher or as an entry point from your IDE to connect to a remote server.
Launch JetBrains Gateway and connect to a remote server
Download and install the JetBrains Gateway app.
Alternatively, you can access JetBrains Gateway from the welcome screen of your IDE through the Remote Development option.
In the Remote Development wizard, click New Connection under the SSH Connection provider.
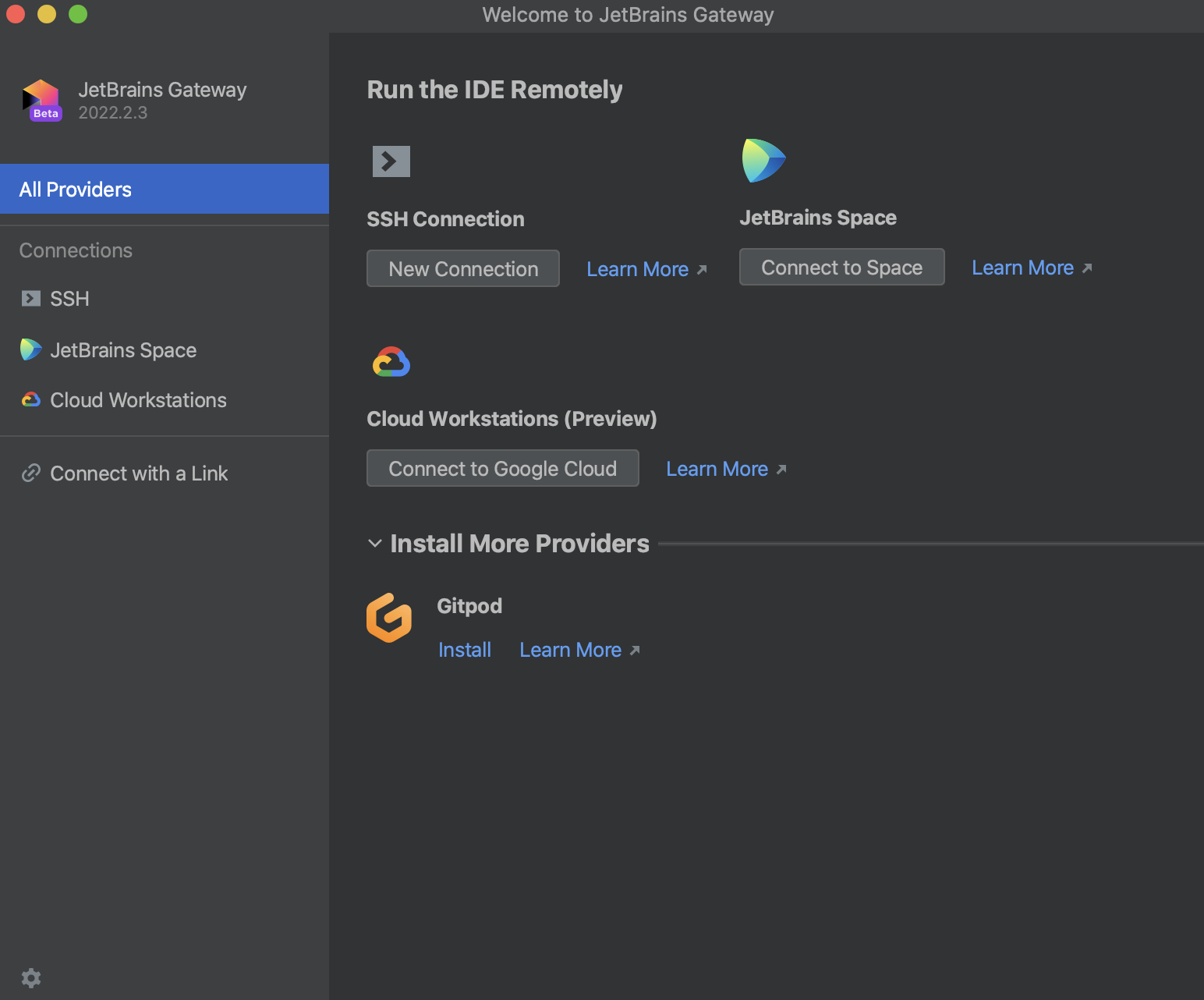
On the next page of the wizard, specify the SSH configuration through which you want to connect to a remote server.
Alternatively, click
to open the SSH Configurations dialog and configure the SSH settings.
In the SSH Configurations dialog, add the following information:
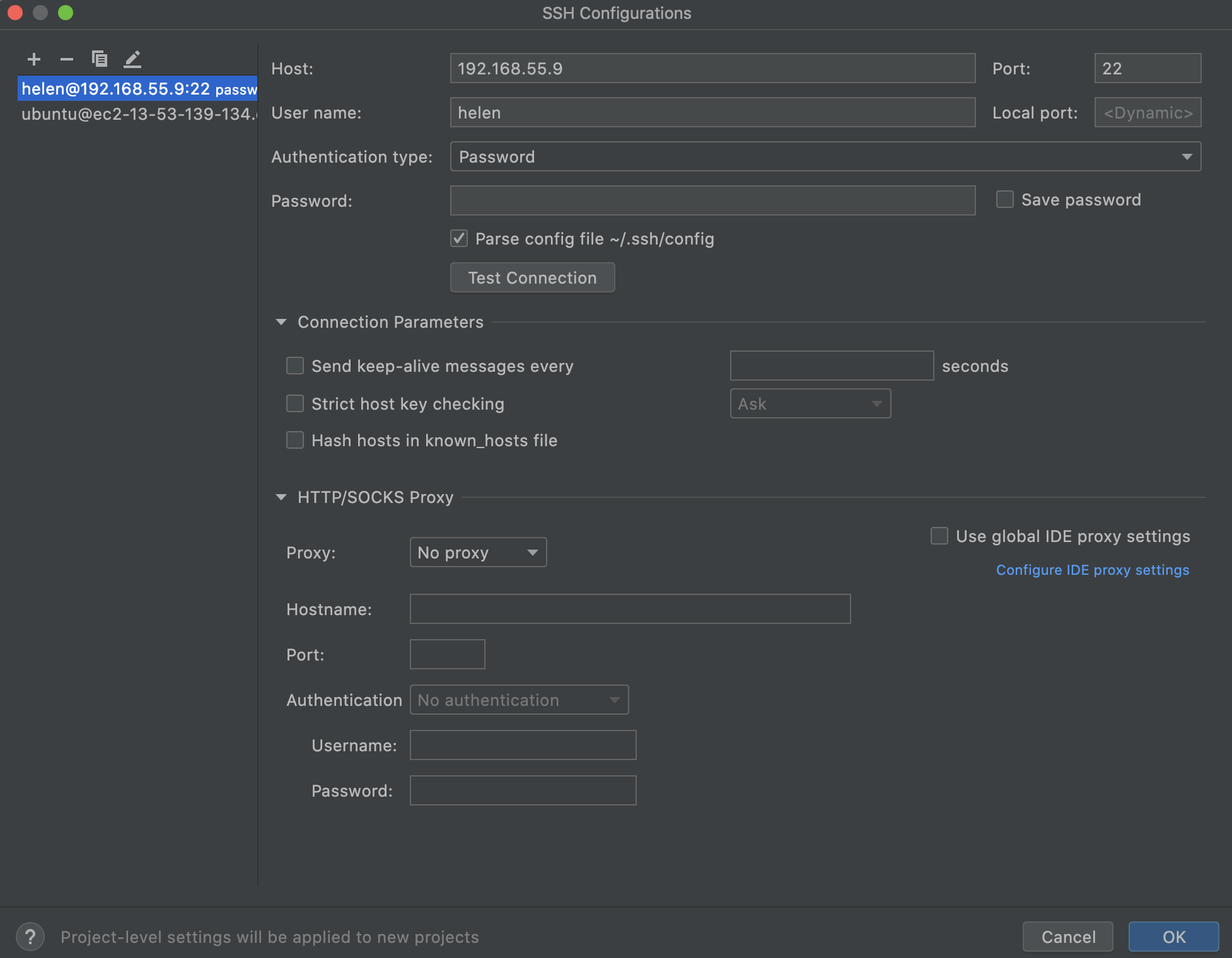
Host: specify the address of your remote server.
Port: specify the SSH port, which defaults to
22.Local port: specify the outgoing port.
For example,
TCP 10.101.0.1:50705->13.49.137.87:22 (ESTABLISHED).User name: specify the name of a user that will be used to connect to the remote server.
Authentication type: select one of the following authentication methods:
Password: to access the host with a password. To save the password in JetBrains Rider, select the Save password checkbox.
Key pair (OpenSSH or PuTTY): to use SSH authentication with a key pair. To apply this authentication method, you must have a private key on the client machine and a public key on the remote server. JetBrains Rider supports private keys that are generated with the OpenSSH utility.
Specify the path to the file where your private key is stored and type the passphrase (if any) in the corresponding fields. To have JetBrains Rider remember the passphrase, select the Save passphrase checkbox.
Parse config file ~/.ssh/config: select this option if you want JetBrains Gateway to use the
.ssh/configfile.
Test Connection: click this button to see whether the connection is established.
Connection Parameters: use this section to configure additional parameters for the connection.
HTTP/SOCKS Proxy: use this section to configure proxy settings. For more information, refer to Proxy settings.
Click OK to save the changes and return to the Welcome to JetBrains Gateway dialog.
Click Check Connection and Continue to check whether the connection is established.
On the next page, specify the JetBrains Rider version to download to the remote server. JetBrains Gateway displays a list of the IDEs versions that are available for downloading and the already installed ones.
You can also use "Other options" for setting the alternative sources of IDE installers.
The version of JetBrains Client downloaded to your local machine always matches the remote IDE version.
By default, the downloaded JetBrains Rider is located in the following folder on the remote server: ~/.cache/JetBrains/RemoteDev/dist. However, you can change it and install JetBrains Rider into a custom location with the following steps:
Click Other options and select the Customize install path option.
In the Install path field add the needed location for the installation.
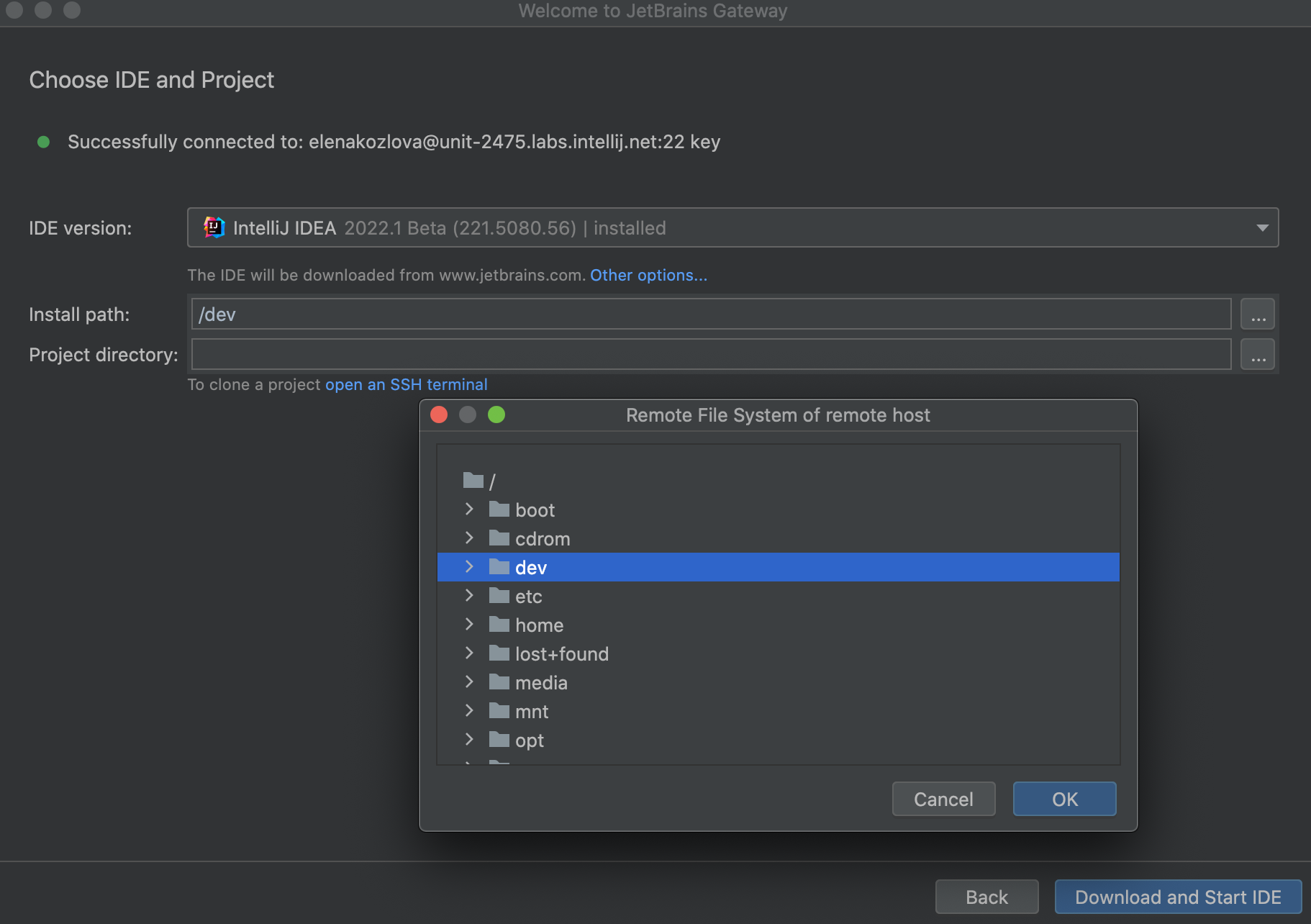
Add the path to your project on the remote host.
Click Upload IDE and Connect.
JetBrains Gateway downloads the IDE, and opens your remote project in JetBrains Client. The connection is shown in the JetBrains Gateway window, from which you can connect to other IDEs or disable the connection. This window is hidden to tray by default.
Open recent projects
In the JetBrains Gateway wizard, select SSH from the options on the left.
In the search field enter the name of your project to quickly navigate to it.
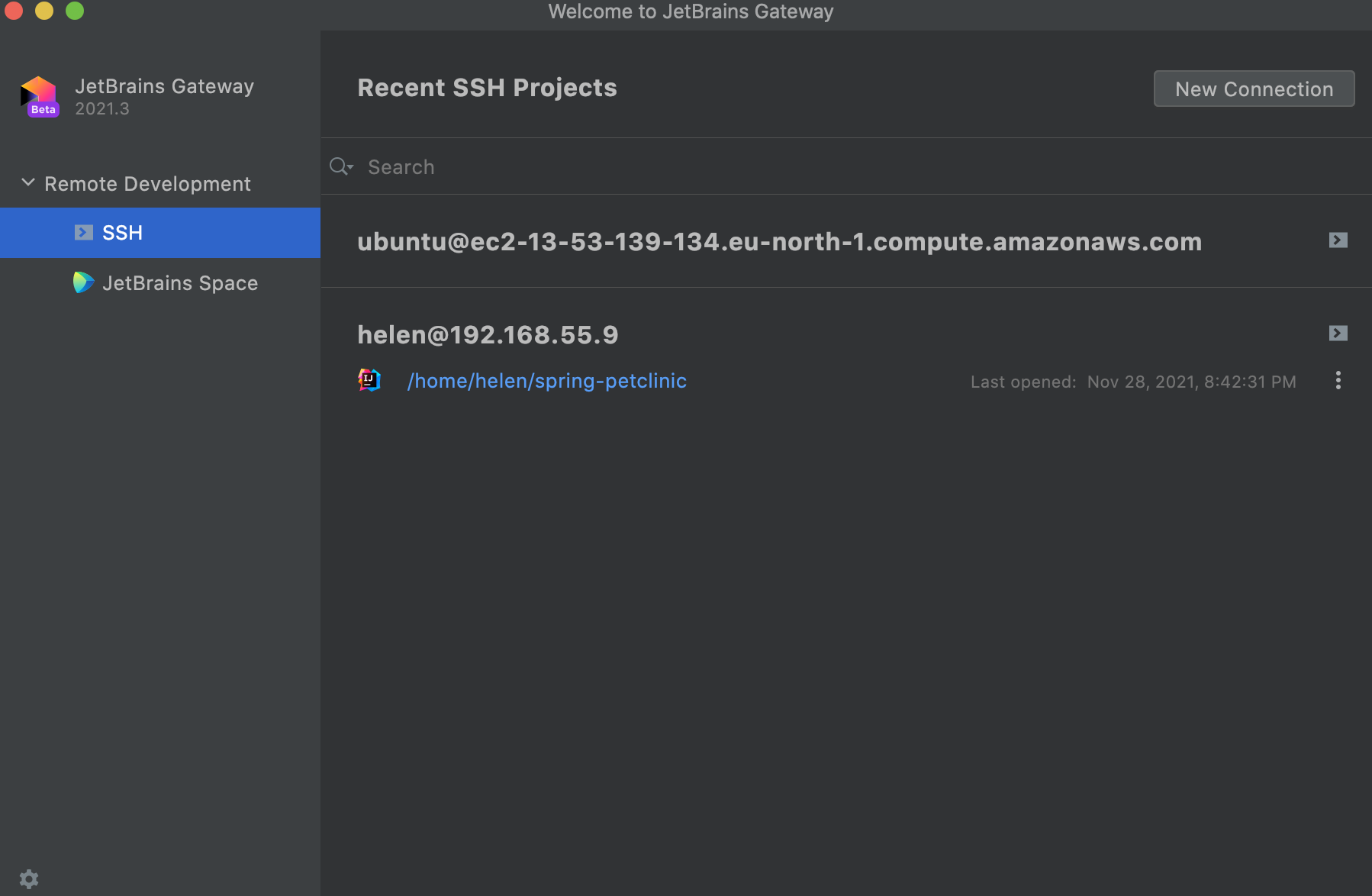
If you need to quickly access the terminal, click
.
Stop the running instance
In the JetBrains Gateway wizard, select SSH from the options on the left.
When your remote session is active, the Running indicator is displayed next to the project.
Click
next to the project and select Stop Instance to stop the remote session for that project.
You can also select Remove from Recent Projects to remove the project listed on the page altogether.
Uninstall the backend IDE version
In the JetBrains Gateway wizard, click
against the name of the remote server to open the list of installed IDE versions.
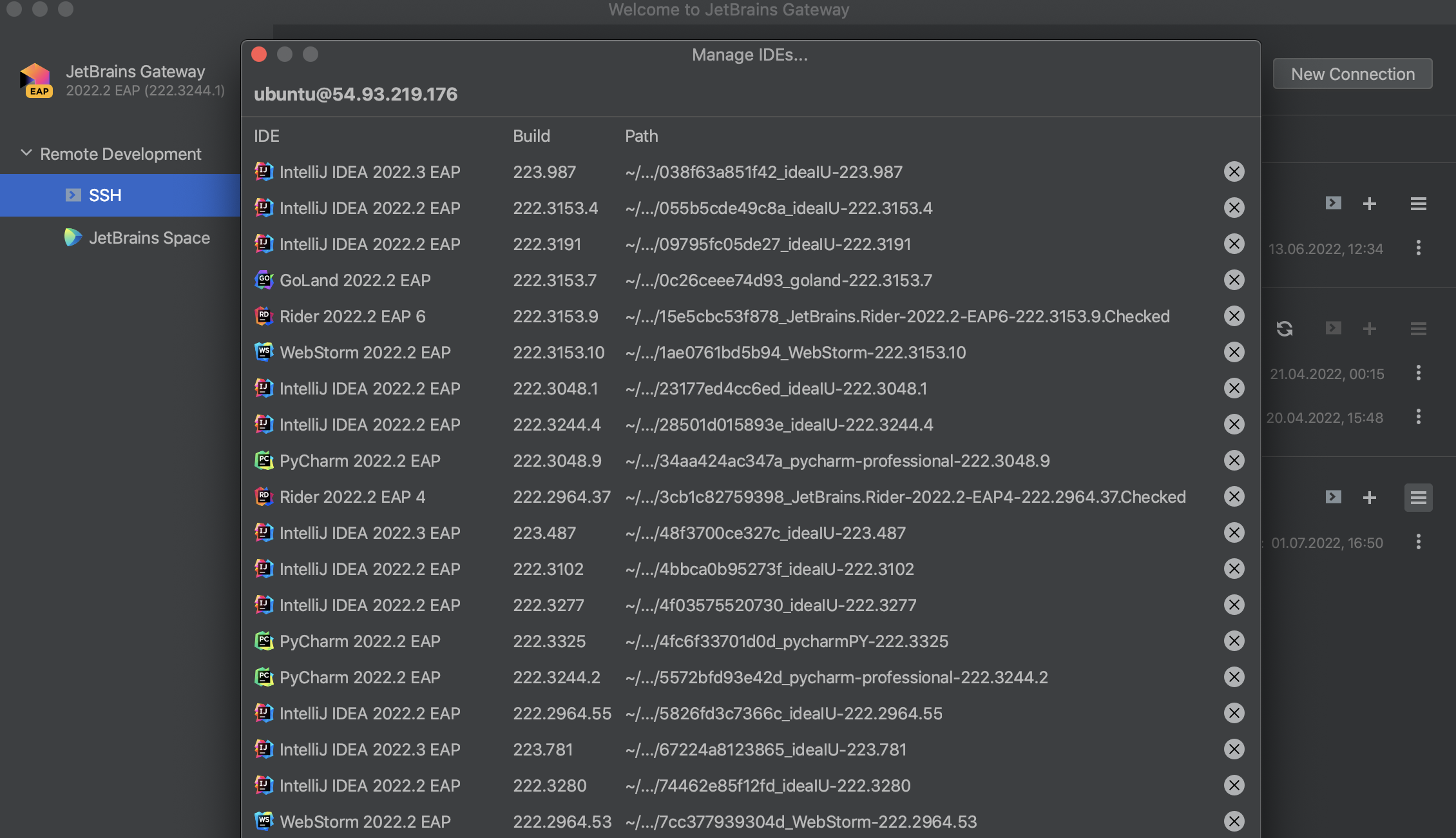
In the window that opens, click
against the backend IDE version you need to uninstall and click Yes to confirm the action.
Connect to a remote project at manually launched remote IDE (Server-to-client flow)
If you already have JetBrains Rider installed on your remote server, you can launch it manually and connect to the remote project started in that IDE. It works the same way as from JetBrains Gateway.
Use this approach if your company has a custom orchestration or in case your remote IDE starts automatically on its side.
The process can be described as follows:
Start a backend project in the remote IDE.
Select one of the connection links generated by the backend.
Open the link on your local machine.
The main script to run a remote IDE is remote-dev-server.sh, located in the bin subdirectory of your unpacked IDE.
Connect to remote IDE
Ensure you have or an IDE with this bundled plugin on your local machine.
Ensure you have an SSH connection to the remote machine and the JetBrains Rider IDE on it.
In the remote server's terminal, run the following command:
remote-dev-server.sh run /path_to_project/ --ssh-link-host host_server_address --ssh-link-user remote_side_user --ssh-link-port ssh_connection_portSee example:
~/ideaIU-213.3469/bin/remote-dev-server.sh run ~/spring-boot-example/ --ssh-link-host ec2-11-50-136-85.eu-north-1.compute.amazonaws.com --ssh-link-user ubuntuIf you don't pass the parameters, the script will use the default ones: 22 for port, system user's username, and host from the
hostnamecommand.If the project starts successfully, as an output, you should receive the following 3 links inside terminal:
Join link: tcp://127.0.0.1:5990...[ ]: contains the local address and port where the remote IDE is listening now.
To use it, ensure the remote machine should be accessible by this local address. For example, for inside-Docker IDE with forwarded/open ports.
Http link: https://code-with-me.jetbrains.com/remoteDev...[ ]: contains information about your host-port-user, the IDE and its version.
When opening in your local browser, it displays a welcome page and tries to call the local Gateway application with pre-filled connection settings values.
If no JetBrains Gateway application is found on the local machine, you'll be able to download it from the welcome page.
Gateway link: jetbrains-gateway://connect#idePath... [ ]: also contains information about your host-port-user, IDE and its version.
When opening in your local browser, it launches the local JetBrains Gateway application directly without a welcome page.
Copy the generated link and paste it into your local browser and allow it to launch Open JetBrains Gateway.
All these links can be also opened in the already launched JetBrains Gateway.
For this, on the JetBrains Gateway welcome screen, paste a link in the Connect to a Running IDE field, click Connect.
JetBrains Rider downloads the required version of JetBrains Client and opens the remote project inside it.
Registering previously installed remote IDE
Since version 221.5481, you can manually register an existing backend IDE on the remote server and make it visible for the Gateway.
To register the installed IDE and make it appear in the list of available builds follow these steps:
Enter remote server by SSH
Locate the folder with unpacked IDE, enter
binfolderIn the command line, execute the following command:
remote-dev-server.sh registerBackendLocationForGatewayFor example,
sh WebStorm-221.5591.52/bin/remote-dev-server.sh registerBackendLocationForGateway
Connect to Gitpod
JetBrains Gateway supports integration with Gitpod, an open-source orchestration and provisioning platform for automated developer environments.
Gitpod is available in JetBrains Gateway as a plugin that you can use to connect to the existing Gitpod workspaces or create a new one and work with it in JetBrains Rider.
Connect to your workspace on Gitpod
Launch JetBrains Gateway.
Select Remote Development from the options on the left.
In the Install More Providers section, locate Gitpod and click Install Plugin.
The installed plugin is added and you can locate it under the Remote Development node as well as in the Install More Providers section.
After the plugin installation, from the options on the right, locate Gitpod and click Connect to Gitpod. .
In the window that opens, select the IDE with which you want to work.
Click New Workspace.
JetBrains Gateway connects you to your Gitpod workspace in browser. Gitpod prepares the workspace and displays a notification about opening the workspace inside JetBrains Client.
Click Allow and then Yes in the authentication dialog.
The connection is established and the workspace with the project is opened in JetBrains Client where you can work further inside the IDE.
The created workspace is added to the Recent workspaces section. If you have existing workspaces they are added to the list of recent workspaces and you can connect to them at any time by clicking Connect against the needed workspace.
If you want to connect to JetBrains Gateway directly from the Gitpod, follow the Gitpod documentation.
Connect to Google Cloud
You can connect to a Cloud workstation with JetBrains Gateway to work on your remote project.
Before trying to connect to the Cloud workstation, make sure you have the following:
You have a Google Cloud cluster and configuration file properly set up
You have a Cloud workstation created
You have an access to a Cloud workstation
A Cloud workstation is available in JetBrains Gateway as a plugin that you can use to connect to the existing workstation or create a new one and work with it in JetBrains Rider.
Connect to your workstation in Google Cloud
Launch JetBrains Gateway.
Select Remote Development from the options on the left.
In the Install More Providers section, locate Cloud Workstations and click Install Plugin.
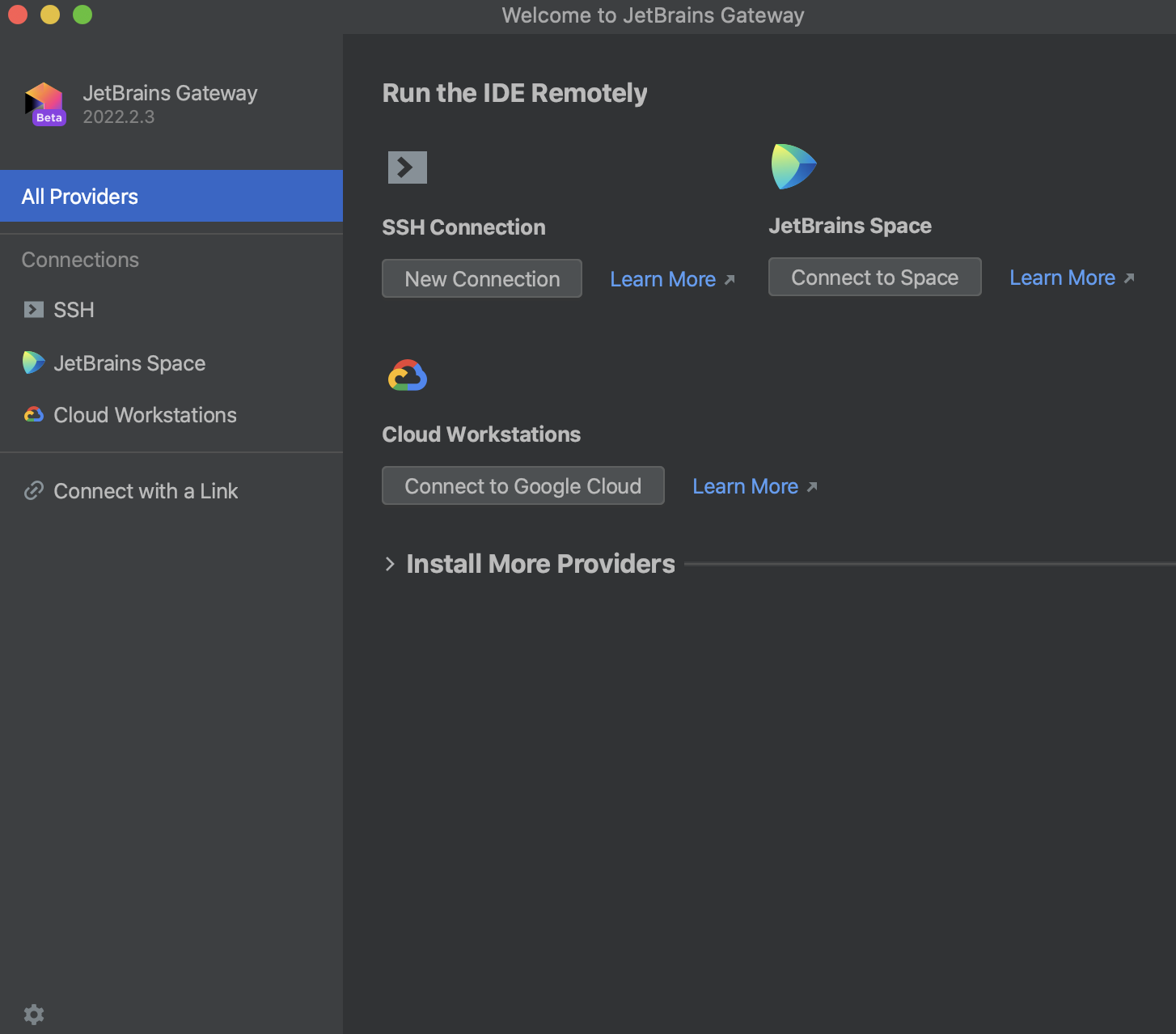
The installed plugin is added and you can locate it under the Remote Development node as well as in the Install More Providers section.
After the plugin installation, from the options on the right, locate Cloud Workstation and click Connect to Google Cloud.
In the window that opens, select a workstation with which you want to work and click Next.
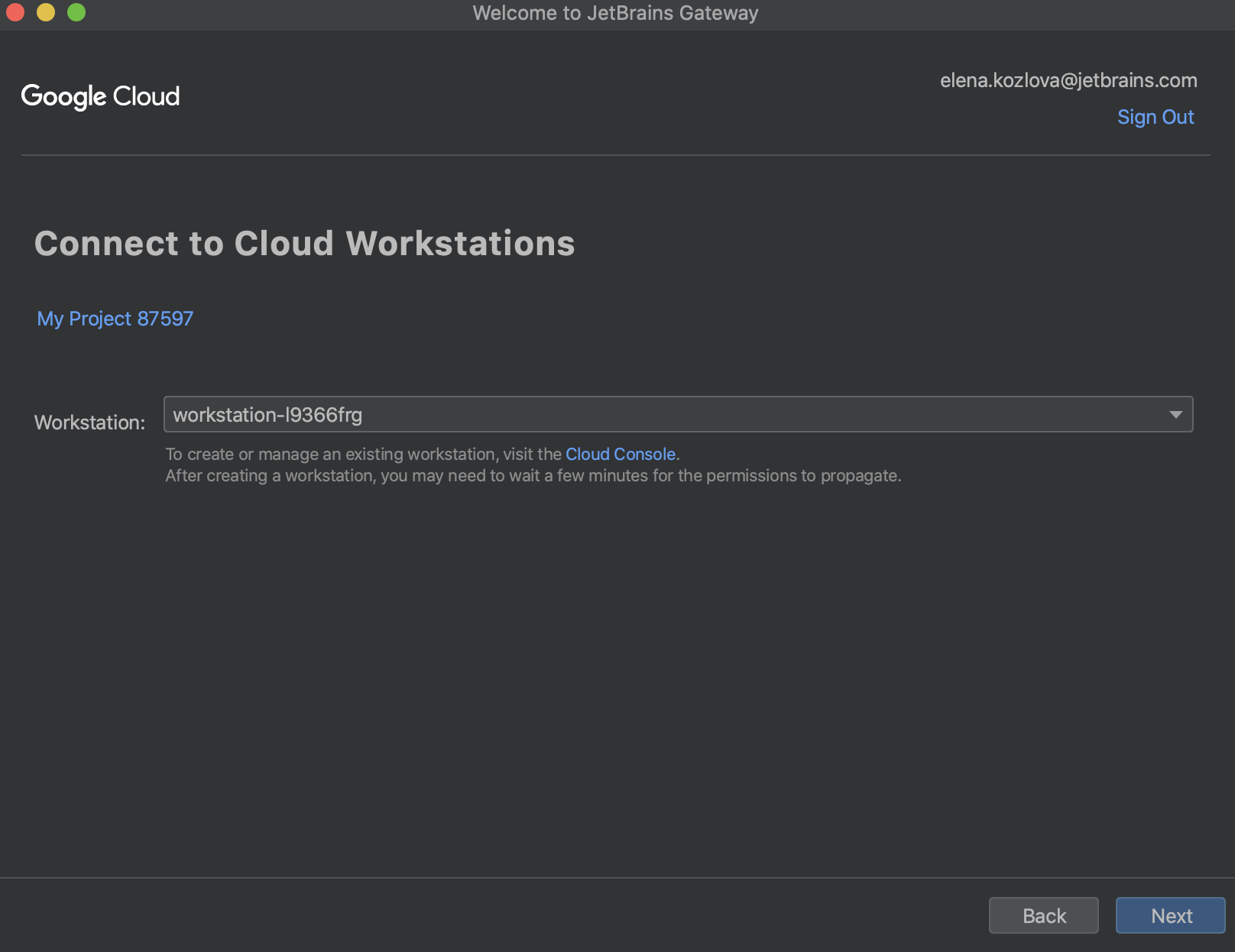
On the next page, select the IDE version that you have chosen as your code provider in your configuration file and a project with which you want to work.
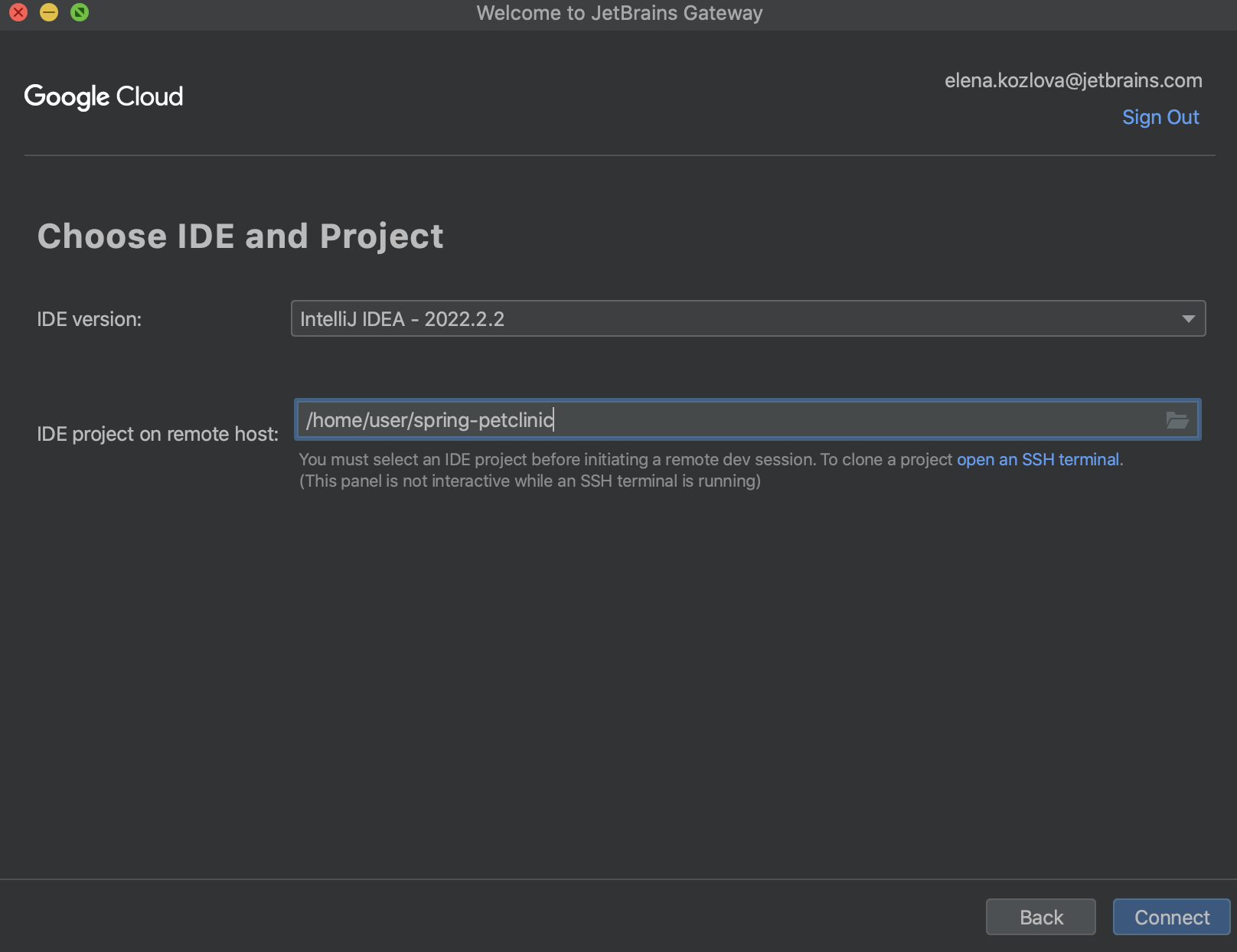
The connection is established and the workstation with the project is opened in JetBrains Client where you can work further inside the IDE.
Install plugins
You can install plugins that you need on the remote server. Note that plugins are installed per project. Each time you create a remote connection for a new project, you need to install the desired plugin.
Based on the scenario that you use for downloading JetBrains Rider on the remote server, you either install the plugin via the command line or use the UI of a remote project for your installation.
Install a plugin via the command line
If you manually configure JetBrains Rider on the remote server, use the following steps to add plugins:
From the JetBrains Marketplace page, find a page of the required plugin, select the Versions tab, and click any version to copy
pluginId(short name such asorg.rust.lang) of the plugin you want to install.Open the remote server, go to the JetBrains Rider instance where your project resides, and for which you want to download and install a third-party plugin.
By default, the downloaded JetBrains Rider instances are located in the following directory:
~/.cache/JetBrains/RemoteDev/distAdd the following command:
bin/remote-dev-server.sh installPlugins PROJECT_PATH pluginId(where
PROJECT_PATHis a path to your remote project andpluginIdis an ID you got from the JetBrains Marketplace page.)After the installation, unpack the downloaded plugin's archive.
By default, the installed plugin is placed into the following folder on the backend:
~/.cache/JetBrains/RemoteDev-IU/PROJECT_PATH/plugins/Continue with launching JetBrains Gateway and opening the remote project with the remotely installed plugin.
Install a plugin via UI
If you use JetBrains Gateway to download JetBrains Rider to a remote server, use the following steps to install plugins.
Open a remote project in JetBrains Client.
Press Ctrl+Alt+S to open the IDE settings and select .
Download the needed plugin the same way as you would in a regular JetBrains Rider project.
For more information on regular plugin installation, refer to Install plugins.
After you download and enable the plugin, click OK to save the changes.
The plugin is installed remotely. However, keep in mind that the plugin is installed per project.