Generations
The Generations view shows how objects from the selected set are distributed among generations. Use this view to determine whether you have too many large objects (which are collected less efficiently, which leads to heap fragmentation) or objects that live too long (for example, potential memory leak).
The list of heaps consists of the following columns:
Name | Description |
|---|---|
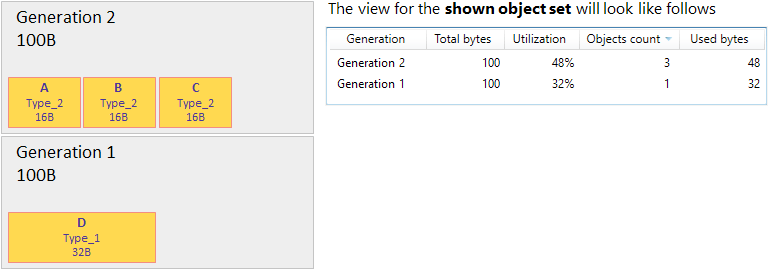
Generation | A certain heap where objects from the set can be allocated: Generation 0, 1, 2, Large object heap, or Frozen object heap. |
Total, bytes | The size of a certain heap defined by GC. |
Utilization | A ratio that shows what part of a heap is occupied by objects from the set. |
Object count | The number of objects from the set allocated in a certain heap. |
Used, bytes | Size of objects from the set allocated in a certain heap. |
Example
Select objects for further analysis
In the Generations view, you can select the following subjects for further analysis:
Objects of a particular generation.
Objects exclusively retained (dominated) by the whole object set.
To select objects of a particular generation
Do one of the following:
Double-click the corresponding generation.
Right-click the generation and choose Open this object set.
After this, the [Generation_name] subject will be added to the analysis path on the left and the list of desired objects will be displayed in the Group by Types view.
To select the objects that are exclusively retained by the analyzed objects set
Click the
 Open objects retained by this set button.
Open objects retained by this set button.After this, the Exclusively retained objects subject will be added to the analysis path on the left and the list of desired objects will be displayed in the Group by Types view.
The Group by Generations view for the 'All Objects' set
If you analyze the All objects object set, the Generations view provides additional information about the fragmentation of all heaps allocated for your app.
Use this view to determine whether you have too many large objects (which are collected less efficiently, which leads to heap fragmentation) or objects that live too long (for example, potential memory leak). The main point of your interest here should be Large Object Heap as the only part of the managed heap which is not compacted .
The list of heaps consists of the following columns:
Name | Description |
|---|---|
Map | A certain heap where objects from the set can be allocated: Generation 0, 1, 2, Large object heap, or Frozen object heap. |
Total, bytes | The size of a certain heap defined by GC. |
Utilization | A ratio that shows what part of a heap is occupied by objects from the set. |
Object count | The number of objects from the set allocated in a certain heap. |
Fragmentation | A level of fragmentation. The 0% fragmentation means that all free memory is located in a single block. Learn about how the fragmentation is calculated here. |