RubyMine Quick Start
RubyMine is an integrated development environment (IDE) that helps you be more productive in every aspect of Ruby/Rails projects development – from writing and debugging code to testing and deploying a completed application. RubyMine is available for different platforms including macOS, Windows, and Linux.
In this tutorial, we’ll show you the main RubyMine capabilities using a fork of a sample application created for the Ruby on Rails Tutorial. Before starting this tutorial, do the following:
Install Git.
Install the Ruby distribution for your platform.
Install and set up RubyMine.
We'll perform all steps using RubyMine installed on macOS.
First of all, we need to clone the repository containing the sample application:
Run RubyMine and click Clone Repository on the Welcome Screen.

In the Clone Repository dialog, do the following:
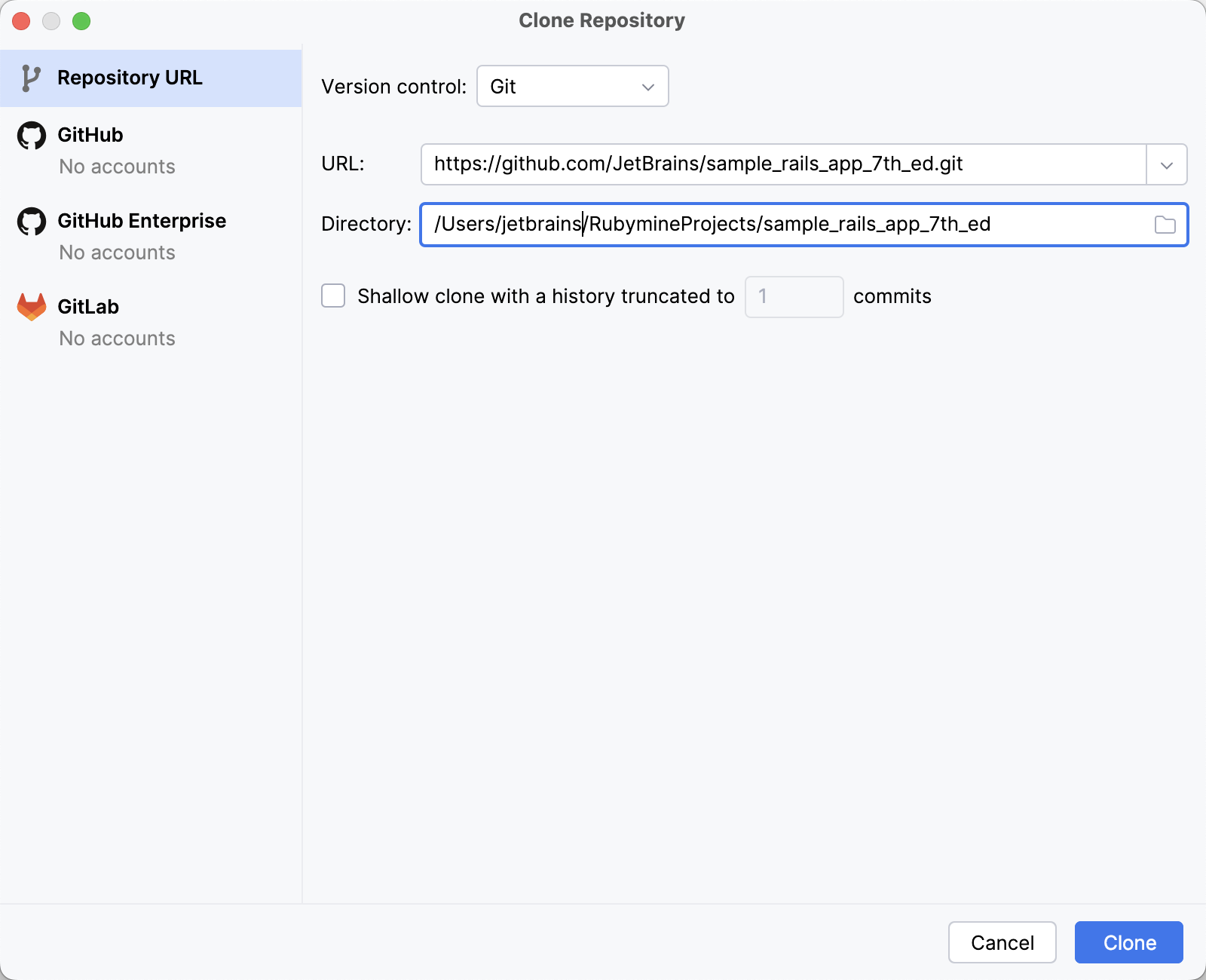
Make sure that Git is selected in the Version control field.
Insert the following address in the URL field:
https://github.com
/JetBrains /sample_rails_app_7th_ed.git
Click the Clone button. RubyMine will show a progress bar indicating a cloning process.
After cloning the repository, RubyMine opens the project and starts the indexing process. You can see the progress in the Status Bar.
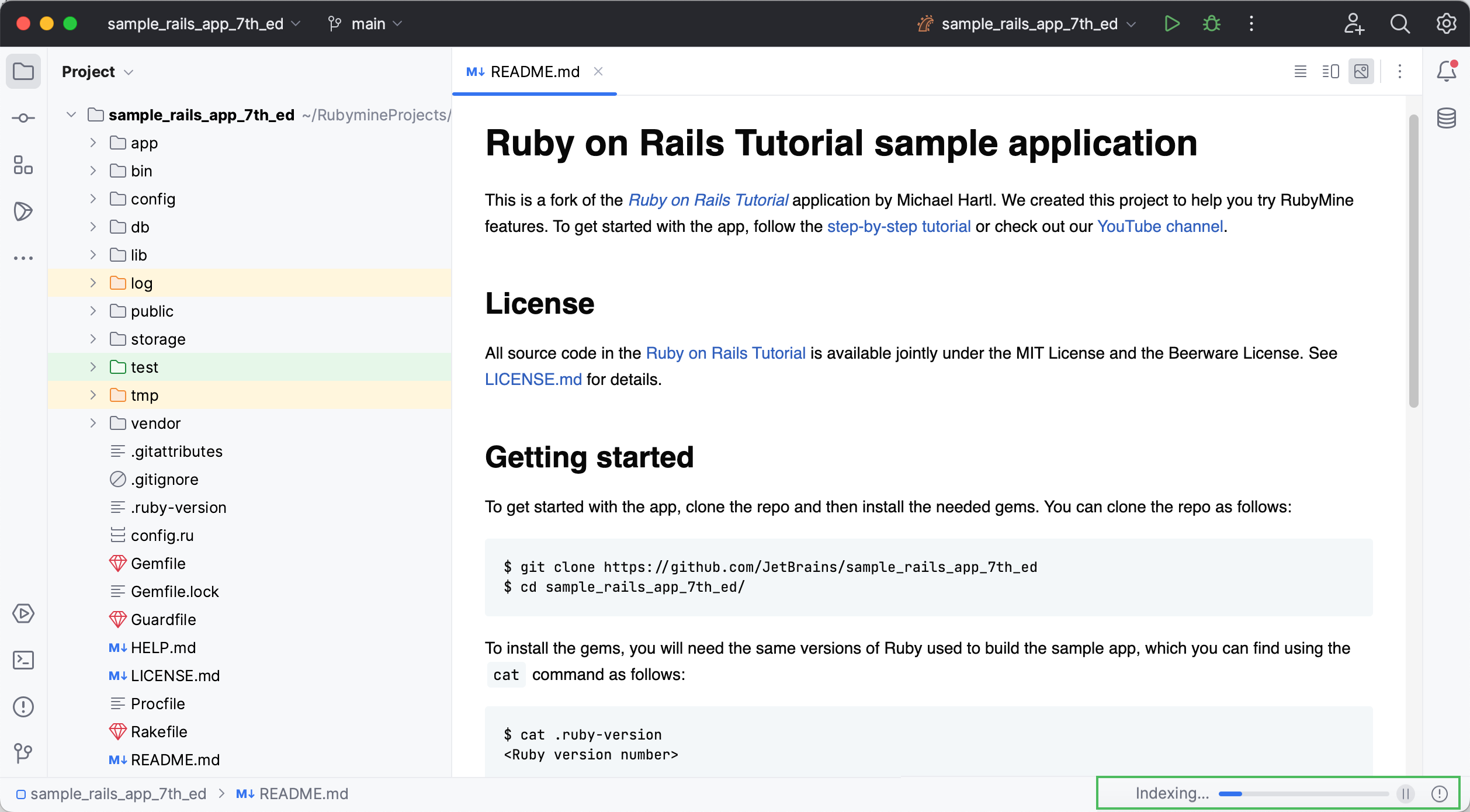
RubyMine indexes your project to analyze its sources and collects the information on available files, class and method definitions, and so on. This is required for code insight features such as code completion and navigation.
tip
Indexing occurs when you open a project for the first time, install dependencies, add new files to a project, get updates from a version control system, or switch branches.
After you’ve opened the project, it is necessary to select the required Ruby interpreter and install the dependencies specified in the project's Gemfile:
Press CtrlAlt0S to open the Preferences dialog.
Go to the Languages & Frameworks | Ruby SDK and Gems page and choose the required interpreter.

note
In this tutorial, we use RVM to manage Ruby interpreters. You can also use interpreters managed by other version managers or installed using the package management system of your operating system.
Click OK.
Now, let’s install the gems specified in the Gemfile. RubyMine allows you to use Bundler to manage gems. Press Ctrl twice and start typing bundle install. Then, select the
bundle installcommand from the list and press Enter.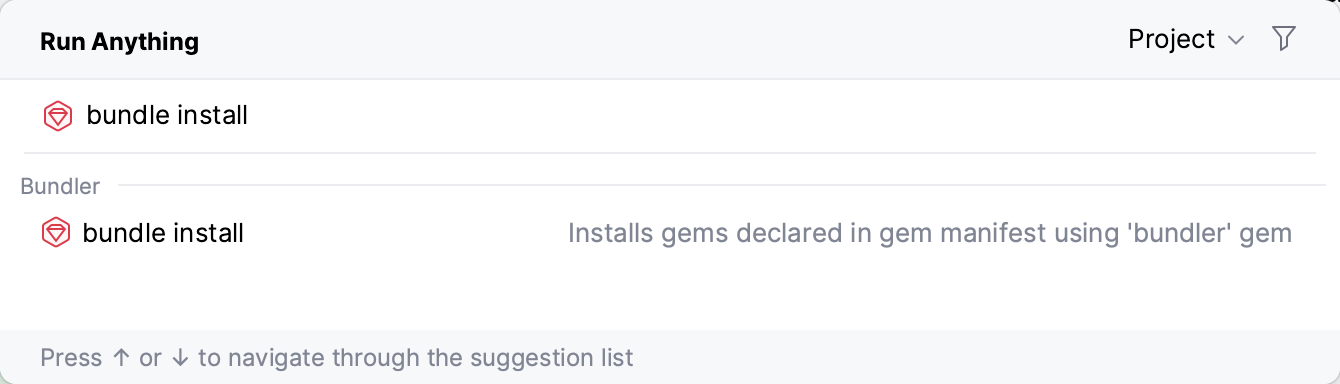
(Optional) If the current project interpreter does not have the required Bundler version specified in Gemfile.lock, RubyMine suggests installing it.
In the Bundle Install dialog, add the following argument:
--without productionThen, click Run.

Wait until RubyMine installs all gems.
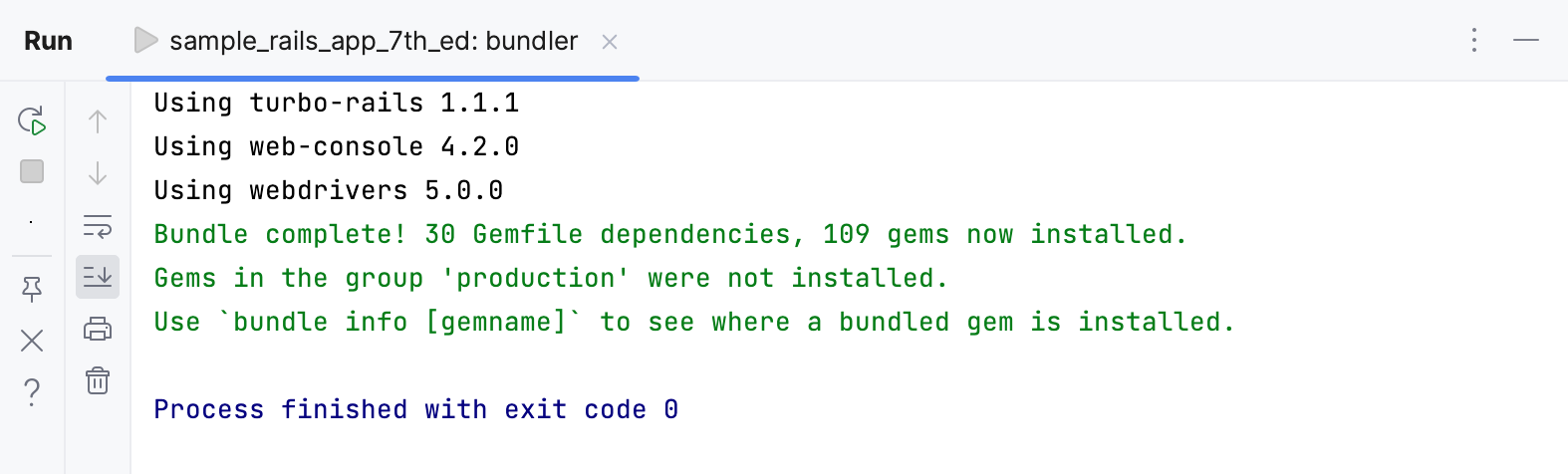
Before running our Rails application, we need to migrate the database.
Press Ctrl twice and type
db:migrate. Select rake db:migrate in the dropdown and press Enter.
Leave the default settings in the invoked Execute ‘db:migrate’ dialog and click OK.

This creates the development.sqlite3 database in the db folder.
Run
rake db:migrateone more time as described in the first step. This time, set the Environment option to test in the Execute ‘db:migrate’ dialog and click OK. The created test.sqlite3 database will be used to run tests.
RubyMine provides rich navigation capabilities to explore projects of any sizes. You can navigate between files, go to declarations, search entities of any types, and so on.
The Project view (Alt01) on the left side of the IDE displays the project structure. You can use it to open any file in your project, create new files, and so on.
Go to declaration allows you to navigate to the declaration of a symbol from any symbol usage. To see this capability in action, press CtrlShift0N, start typing users_controller, select the users_controller.rb file and press Enter.

In the opened users_controller.rb file, place the caret next to the User class and press Ctrl0B.
You'll jump to the class declaration in the user.rb file.
Note that you can jump not only to project entities but to definitions within external libraries (which are gems in our case). For instance, keeping Ctrl pressed, hover over the has_many method. When the method turns into a hyperlink, click it without releasing the key.
RubyMine will open the method definition within the ActiveRecord Rails module.
Let’s try ou the Find usages action. In the users_controller.rb file, scroll down to the edit method, place the caret next to it and press AltF7. In the Find window, you can explore the places where this action is used.
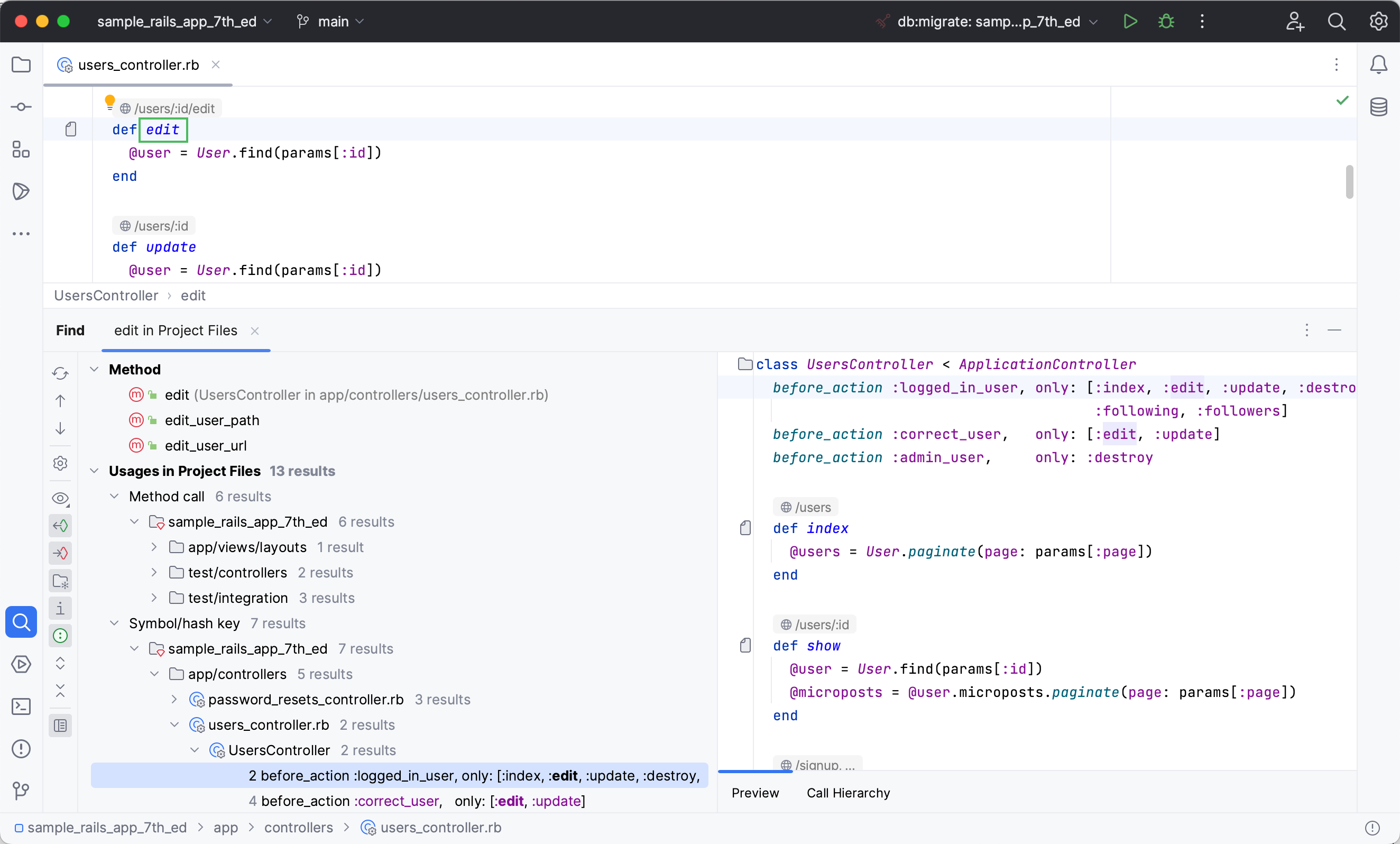
When working on a specific Rails entity, like a controller, you can navigate to the related view, model, test, or helper. Place the caret next to the edit method, press CtrlAltHome, select View and press Enter. RubyMine will open the edit.html.erb file containing the corresponding view.
You can use the same shortcut within a view or use the icon in the editor gutter to quickly go to the corresponding action.
The next RubyMine feature allows you to search for files, classes, symbols, or options and jump to the entity you need.
Let’s try to find the destroy action within UsersController. Press Shift twice and start typing destroy. RubyMine lists all the found results where your query is found. Select the destroy action from UsersController and press Enter.
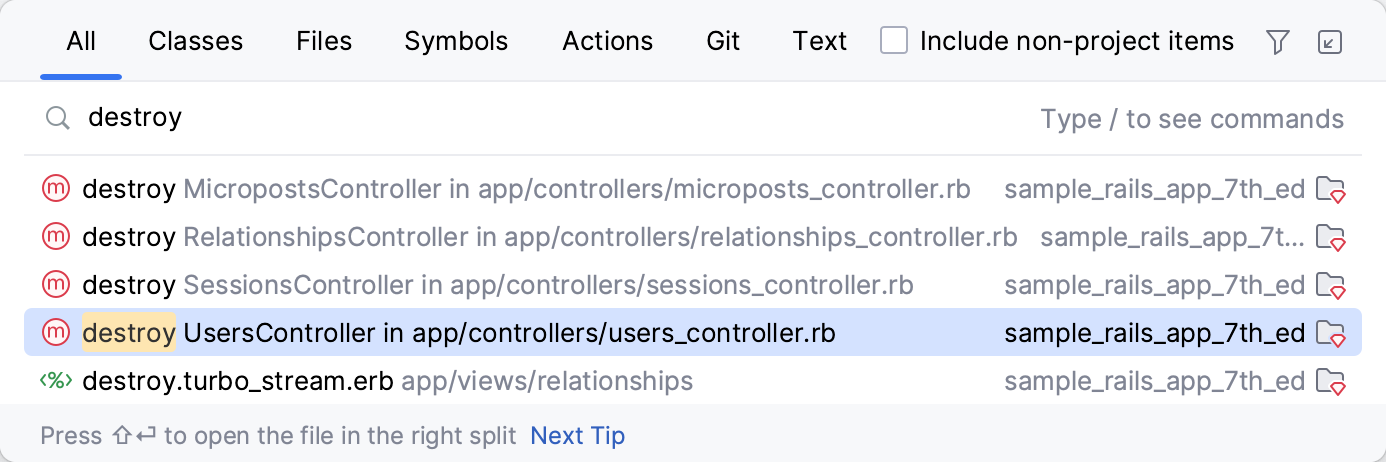
The users_controller.rb file will be opened and the caret will be placed on the definition of the destroy action.
RubyMine provides multiple code editing features available in the editor that allow you to speed up the development process. These include code completion, refactorings, code inspections, and so on.
RubyMine can help you complete the names of classes, methods, keywords, and so on. When you invoke code completion, RubyMine analyzes the context and suggests the choices applicable to the current caret position.
For instance, open the users_controller.rb file and go to the index method declared in the UsersController class. Type the following code inside the method and then type dot.
@user = UserBecause the User class is inherited from the ApplicationRecord module, the editor will display all inherited members.
After that, start typing first to filter the list and find the corresponding member from the Querying module, and press Enter.
note
You can also invoke code completion manually by pressing CtrlSpace.
Intentions help you apply various code changes quickly: convert statements for better code style, add strings to locale dictionaries, use language injections, and so on.
To see intentions in action, open the user.rb file and scroll down to the User.digest method, which uses a multiline ternary operator ?:. According to the Ruby Style Guide, it is preferable to replace such an operator with the if/then/else/end block. To do this, place the caret at this ternary expression (for instance, next to ActiveModel) and press AltEnter. Press Enter to convert a ternary operator to the if/then/else/end block.
tip
You can check your code and detect possible issues using inspections.
Refactoring is the process of modifying source code in order to make it easier to maintain and extend, but without changing its behavior. Let’s look at some refactoring features available in RubyMine.
Rename refactorings allow you to rename classes, methods, files, variables, and parameters with all the references to them in the code corrected accordingly. Open the user.rb file and scroll down to the downcase_email method raised in the before_save callback. Place the caret next to this method and press CtrlShift0I to see its definition.
Press Esc, then press CtrlAltShift0T. Select Rename in the Refactor This popup, which suggests various refactorings.
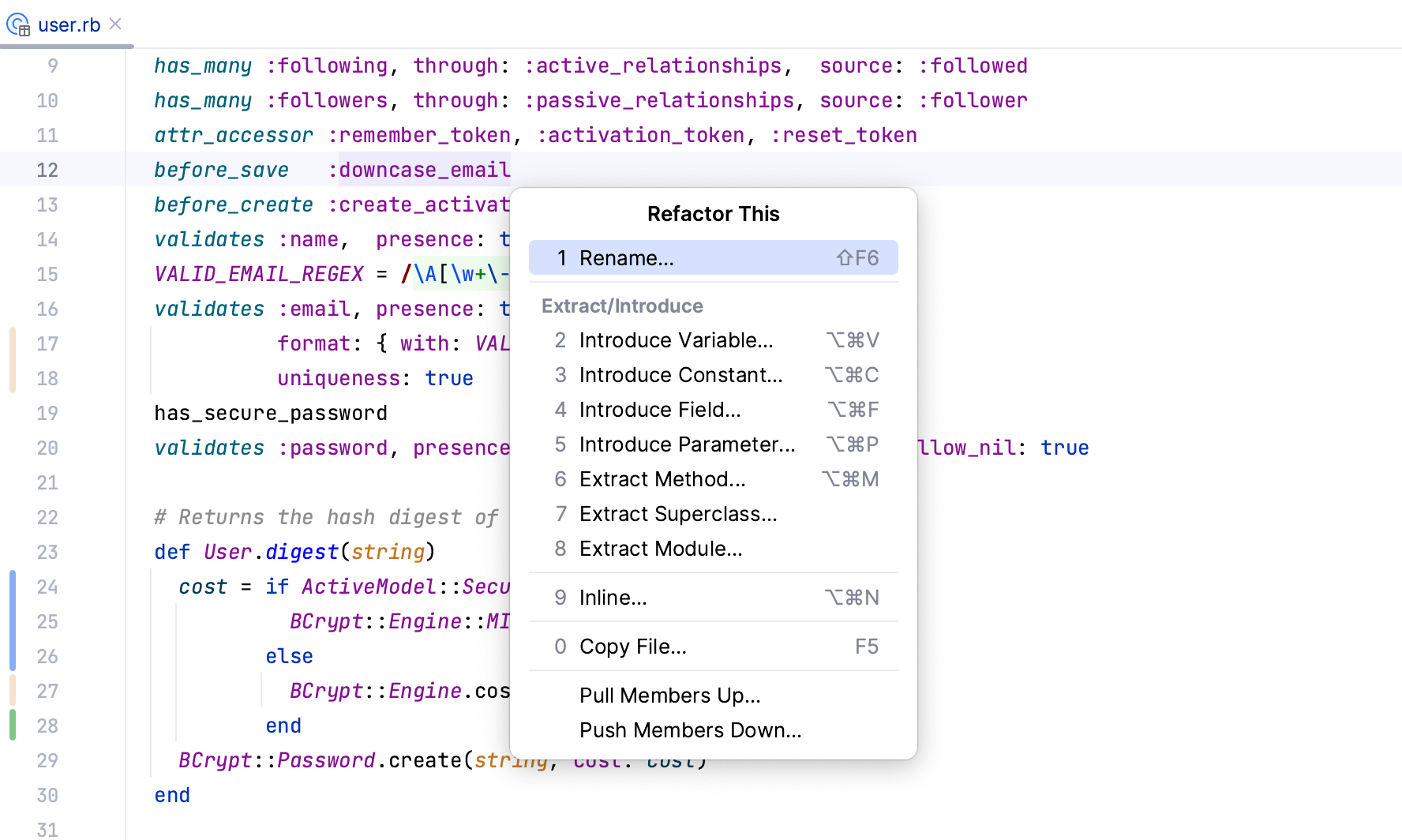
In the Rename dialog, specify a new method name (lowercase_email in our case) and click Refactor
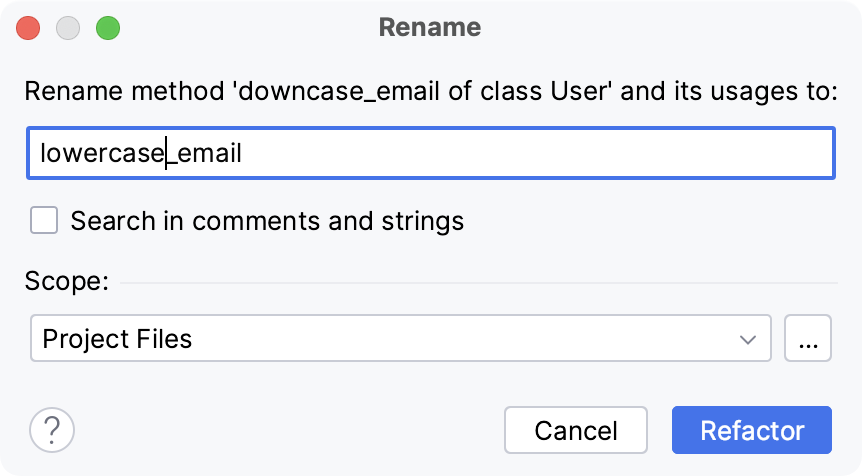
The Refactoring Preview window will display all references to the renamed method.
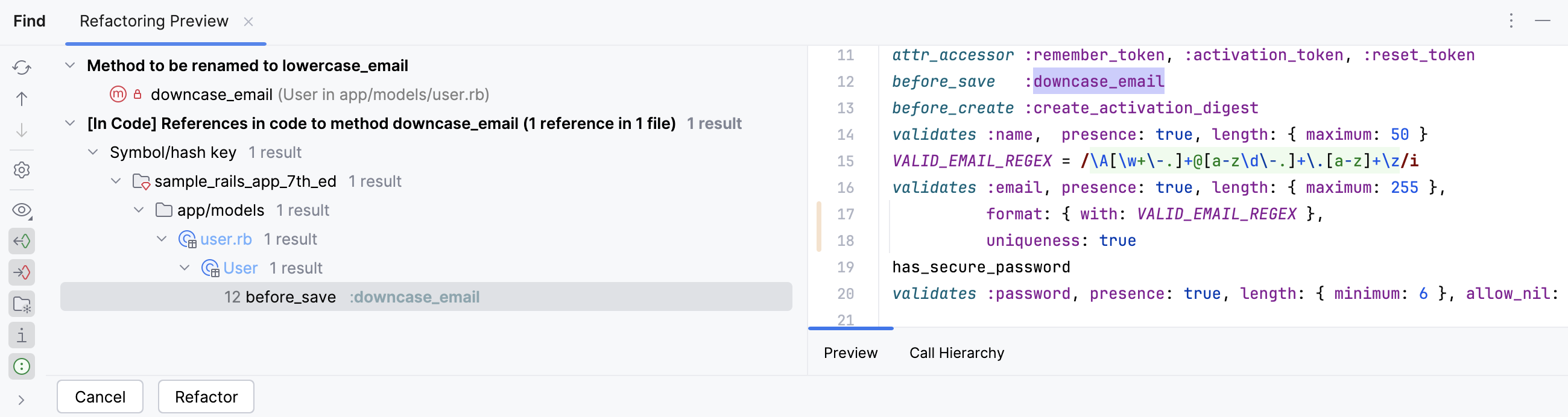
Click Refactor to rename the method in all places.
RubyMine allows you to reformat source code to meet the requirements of your code style.
Let's reformat the code of the user.rb file. Open this file and press CtrlAlt0L.
RubyMine will reformat the entire file and display a number of changed lines.
In this part, we’ll perform static code analysis and detect problems.
RubyMine supports multiple inspection types and, moreover, allows displaying RuboCop offenses inside the IDE. The RuboCop inspection is enabled in RubyMine by default and requires the RuboCop gem to be added to the project interpreter. If this gem is not installed, RubyMine will suggest doing this.

Let’s open the Gemfile containing a list of gems used by the application. Hover over the warning displayed for the active_storage_validations gem.
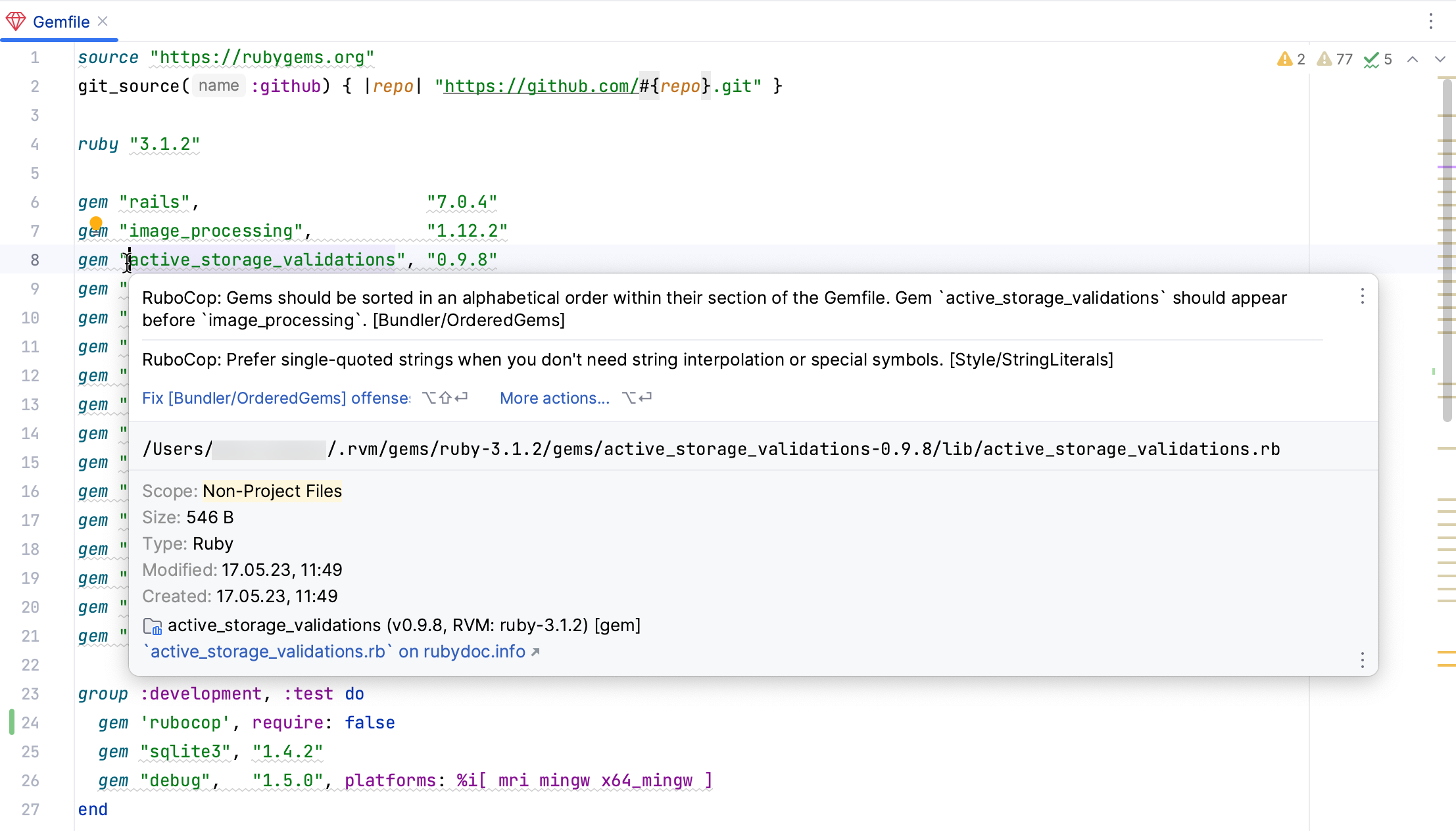
RubyMine will display a Rubocop message that notifies you about the necessity to order gems in the alphabetical order (refer to OrderedGems).
Place the caret next to the active_storage_validations gem and press AltEnter. The editor will suggest fixing all issues related to incorrect gems ordering. Press Enter to do this.
You can also check the entire project and display all warnings in a single report. To do this, select Code | Inspect Code in the main menu. In the invoked dialog, you can specify the required inspection scope.
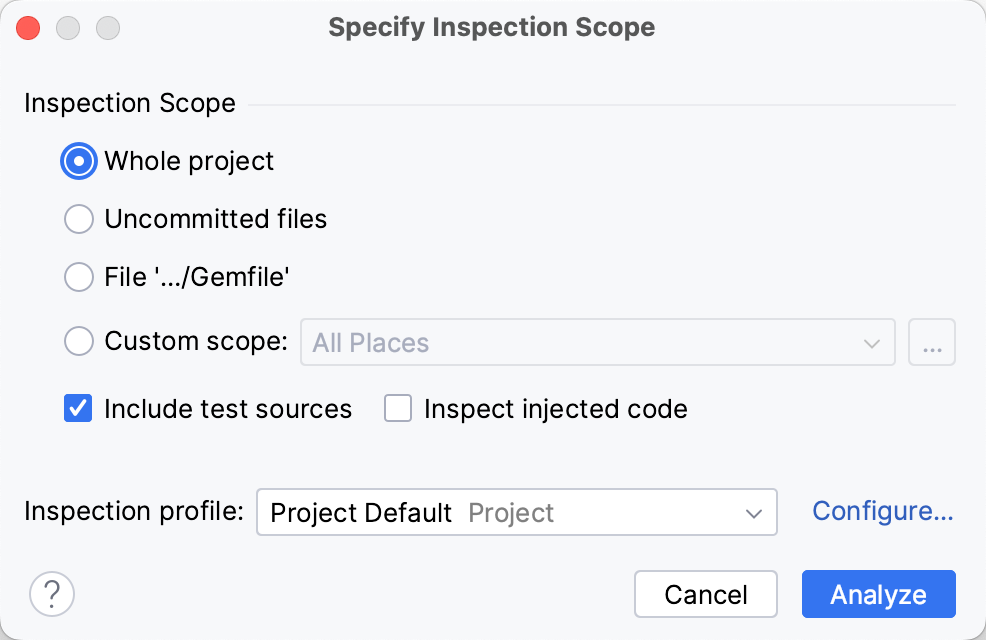
Leave the Whole project option and click Analyze. The inspection results window will show warnings for a whole project.
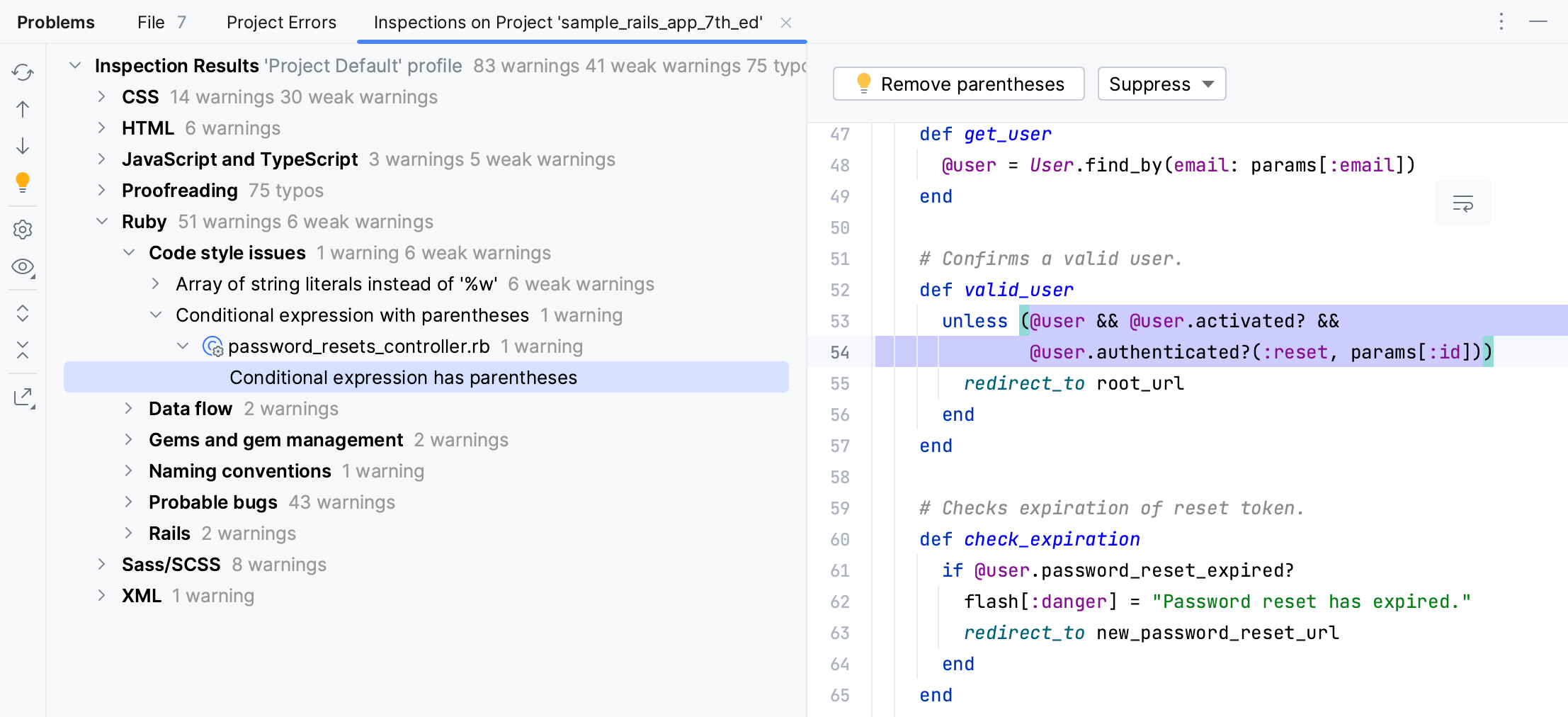
You can navigate through this report and fix or suppress specific warnings.
RubyMine enables you to use different testing frameworks such as Minitest, RSpec or Cucumber.
Our project contains Minitest tests in the test folder. To run all tests, open the Project view by pressing Alt01. Then, right-click the test folder and select Run 'All tests in test' from the context menu.
RubyMine will run and display test results in the Run tool window.
Now let’s see how to run a specific test. Open the users_controller_test.rb file, scroll down to the should redirect index when not logged in test, and click the Run button on the left gutter next to this test.
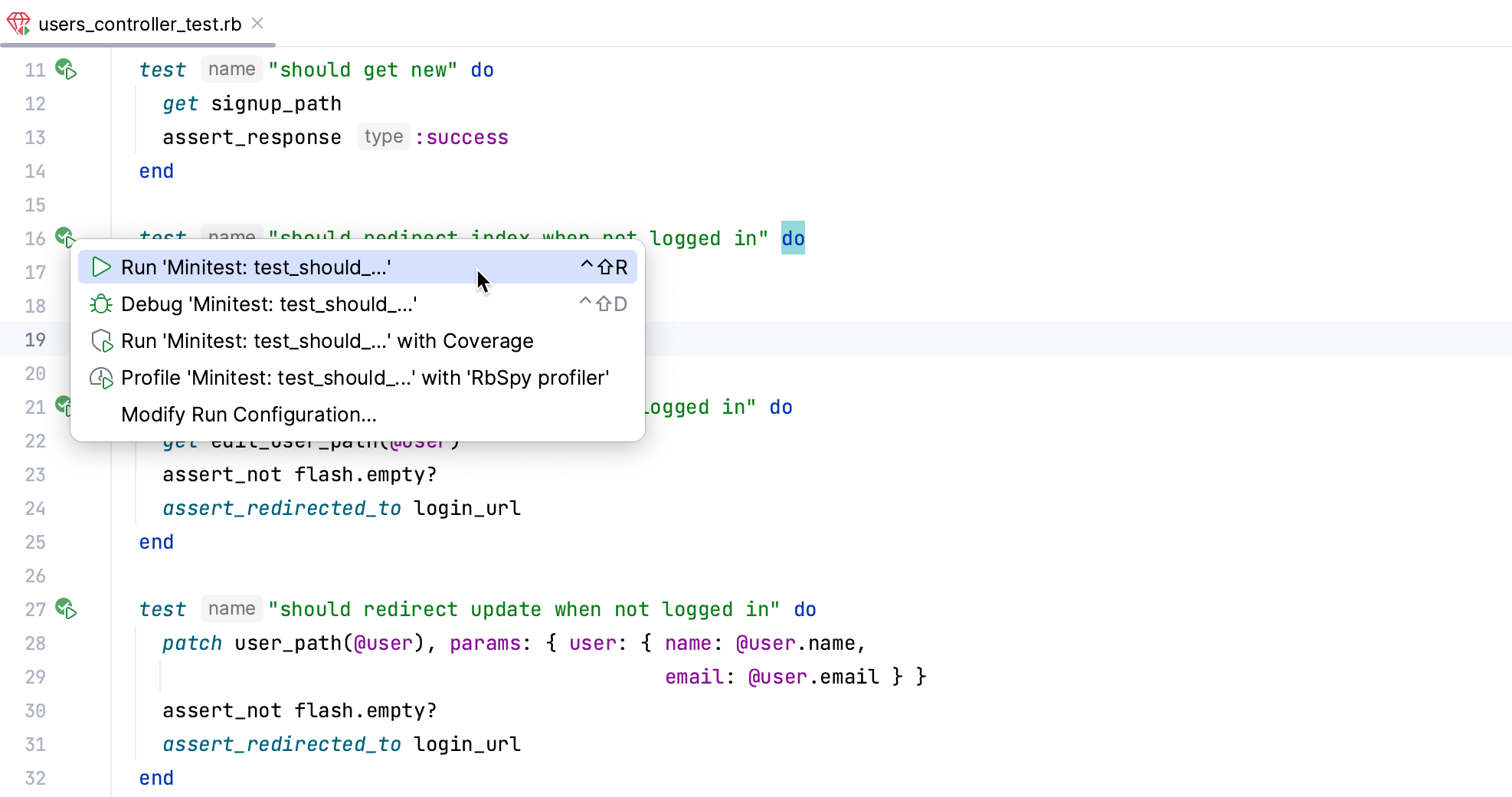
In the invoked menu, select Run ‘Minitest: test_should_...’. RubyMine will display the result for this test.
Now let’s go back to users_controller_test.rb and break two tests. For the should get new and should redirect index when not logged in tests, comment out the get signup_path and get users_path lines. To do this, select these lines and use the Ctrl0/ shortcut.
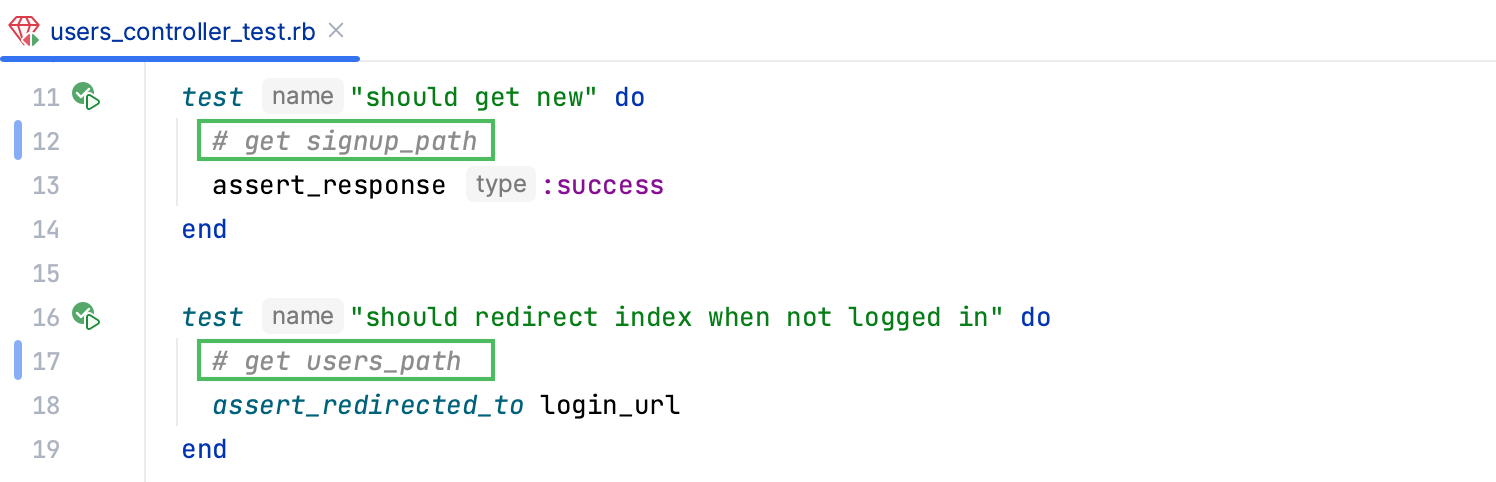
Run all tests again as described in Run all tests. You can see now that these tests failed.
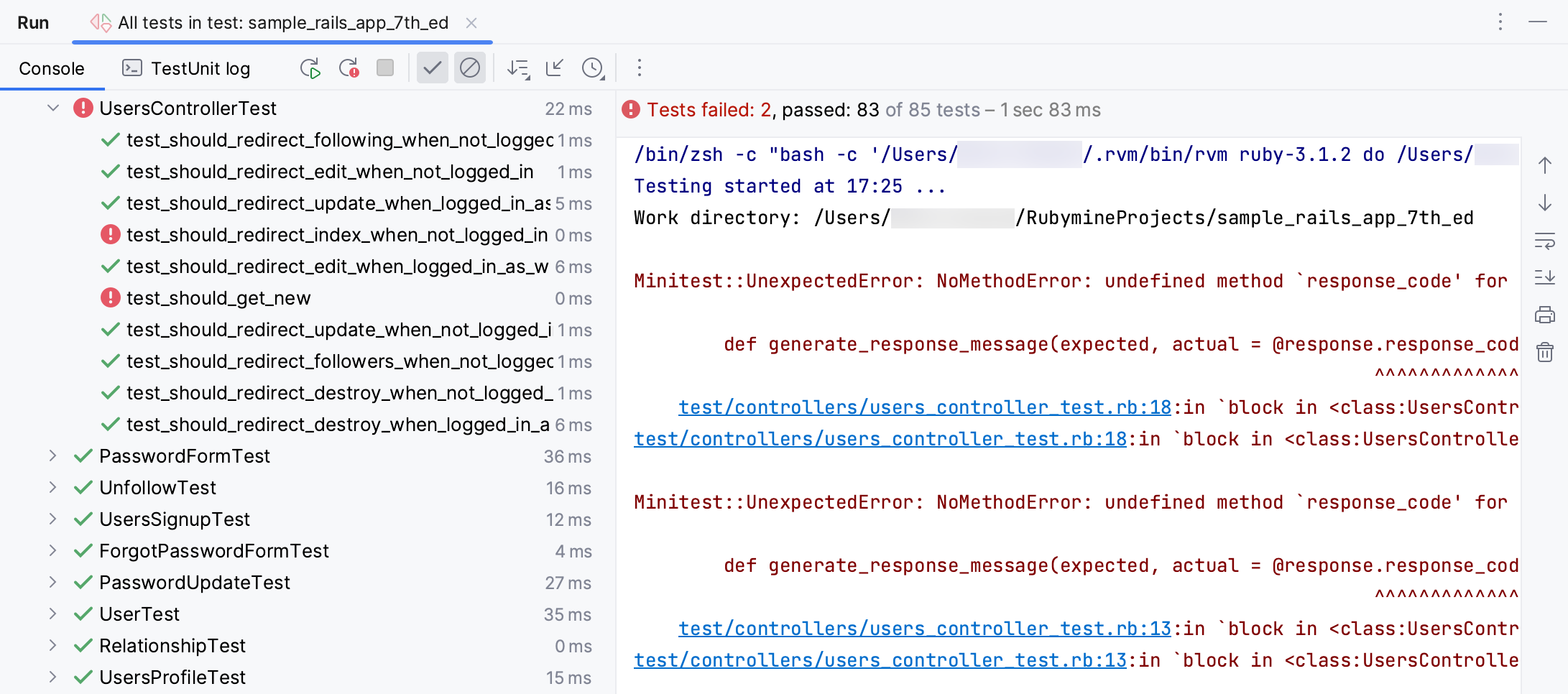
Let’s fix these tests in the currently opened users_controller_test.rb file by uncommenting the same lines: get signup_path and get users_path. Use the same Ctrl0/ shortcut. We can now rerun only these failed tests using the button.
Now we are ready to run our application.
To run our Rails application, press Ctrl twice and start typing sample_rails_app. Select the sample_rails_app_7th_ed configuration from the list and press Enter.
RubyMine will show the process of preparing the application to run.
Go to the 0.0.0.0:3000 address used by a web server to see our working application.
One of the key features of RubyMine is debugging support. The debugger provides various ways to examine the state of a running application. You can step through your code and check variable values, set watches on variables to see when values change, and so on.
tip
Our sample application uses the puma web server, which default worker timeout equals 60 seconds. For debugging purposes, it can be useful to set this timeout to a larger value. To do this, open the config/puma.rb file and specify the worker_timeout option.
First, open the users_controller.rb file. Set a breakpoint within the create method next to the line where a new user is created.
To start debugging, press Ctrl twice and start typing sample_rails_app. Select the sample_rails_app_7th_ed configuration from the list, hold down the Shift key (the dialog title will change to Debug), and press Enter.
If the debase and ruby-debug-ide gems required for debugging have not been installed yet, RubyMine suggests installing them.

After installing the gems, the Debug tool window will show the application output.
Open a browser on the local machine and specify the application address 0.0.0.0:3000.

Click the Sign up now! button. On the Sign up page, enter your credentials and click Create my account.
The program will stop when it reaches the breakpoint.
You can now examine the application state and the values of variables.
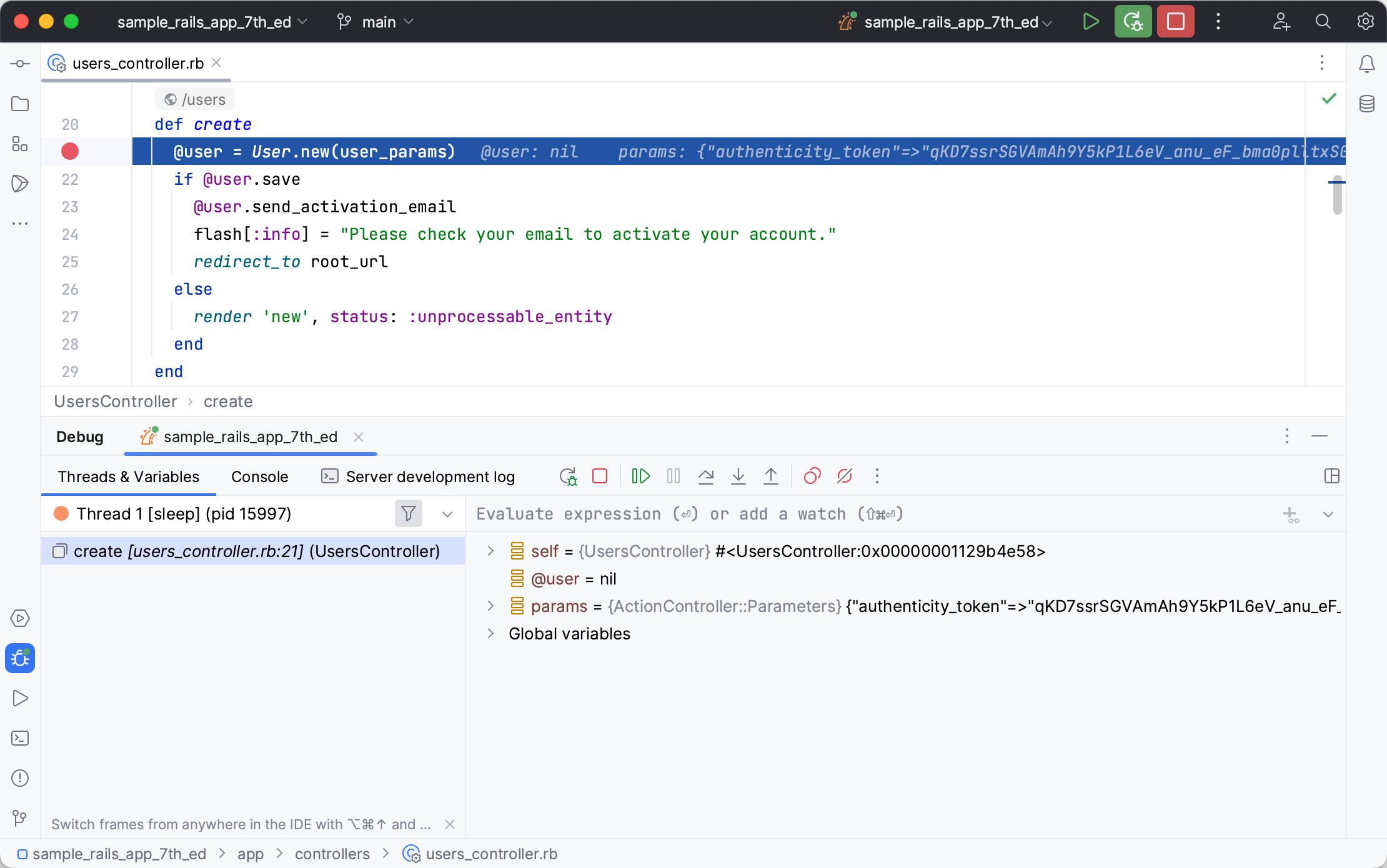
The Threads & Variables pane displays the application threads and the corresponding call stacks. In our case, the create method is called in Thread 1. In the right part of the pane, you can examine variables available in the current context.
tip
Use the
button to show or hide calls of methods from external libraries.
Let’s add the user_params variable to the list. On the right side of the pane, type user_params in the search field and click .
Then, click the icon next to this variable and then expand the @parameters variables in the same way. You will see the user credentials specified in the Sign up form.
Once the breakpoint is hit, we can step through the code.
Step over proceeds to the next line in the current scope (for example, goes to the next line), without descending into any method calls on the way.
The User object is not created yet and the @user variable not initialized (equals nil).
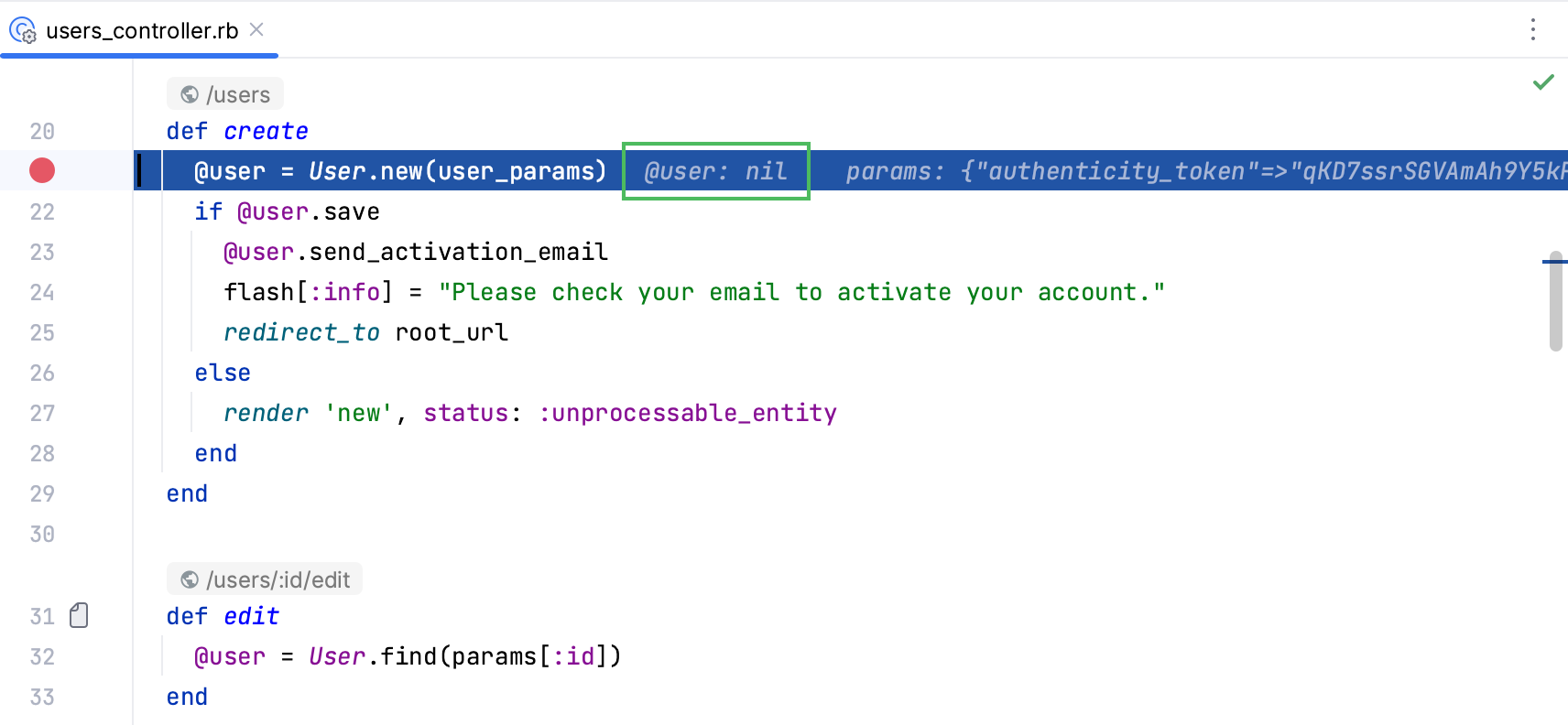
Press F8 or click in the Debug tool window toolbar. The debugger will go to the next line - the
if statement, and the @user variable will be initialized.
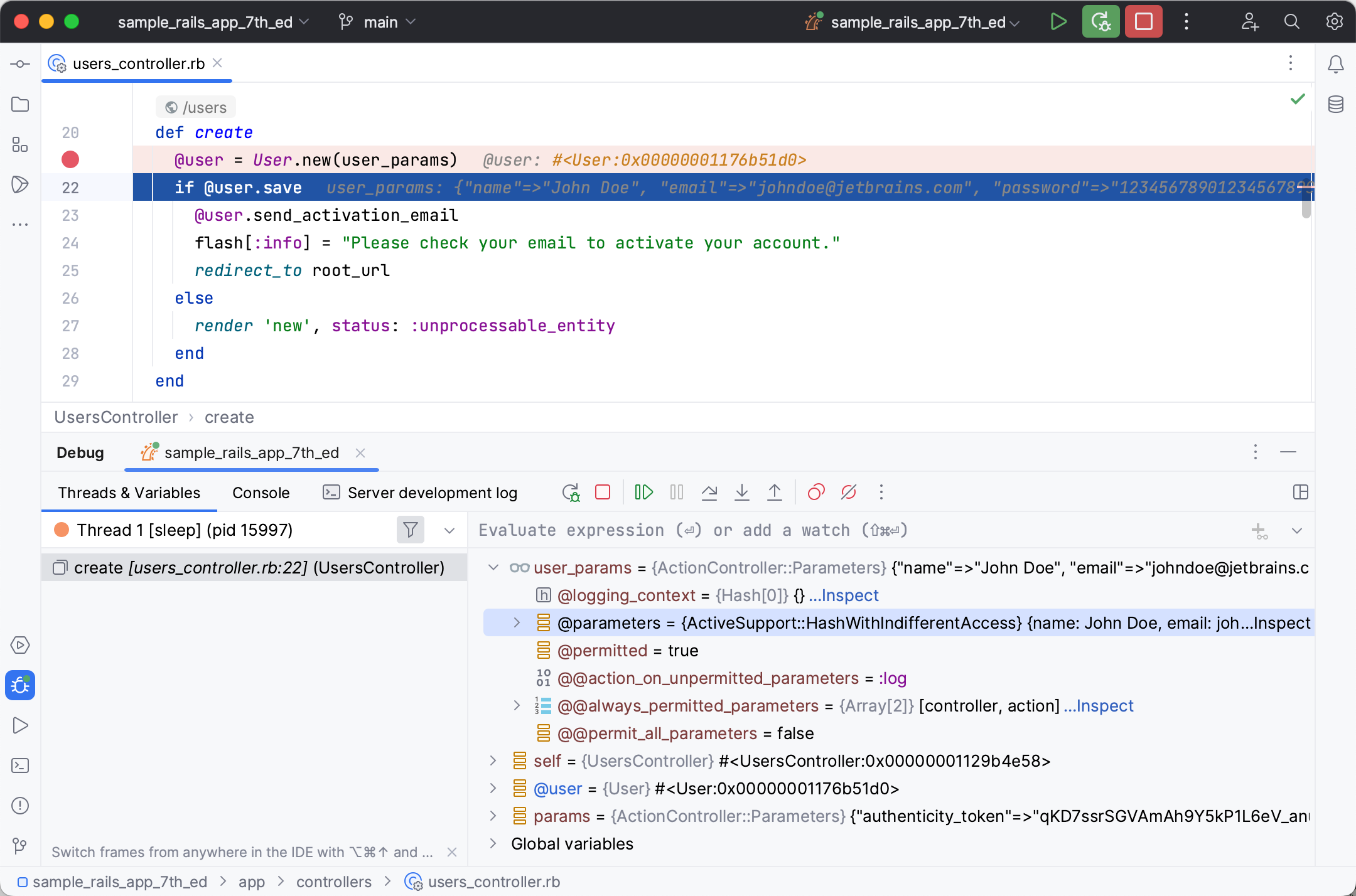
Use the icon to expand and examine @user properties.
Step into will cause the debugger to descend into the method calls or blocks on the current line and follow them through. If there are multiple method calls or blocks, you can choose the required target.
Click to resume program execution. Go to the browser again and create another user in the Sign up form. The script will stop when it reaches the line where a user is created.
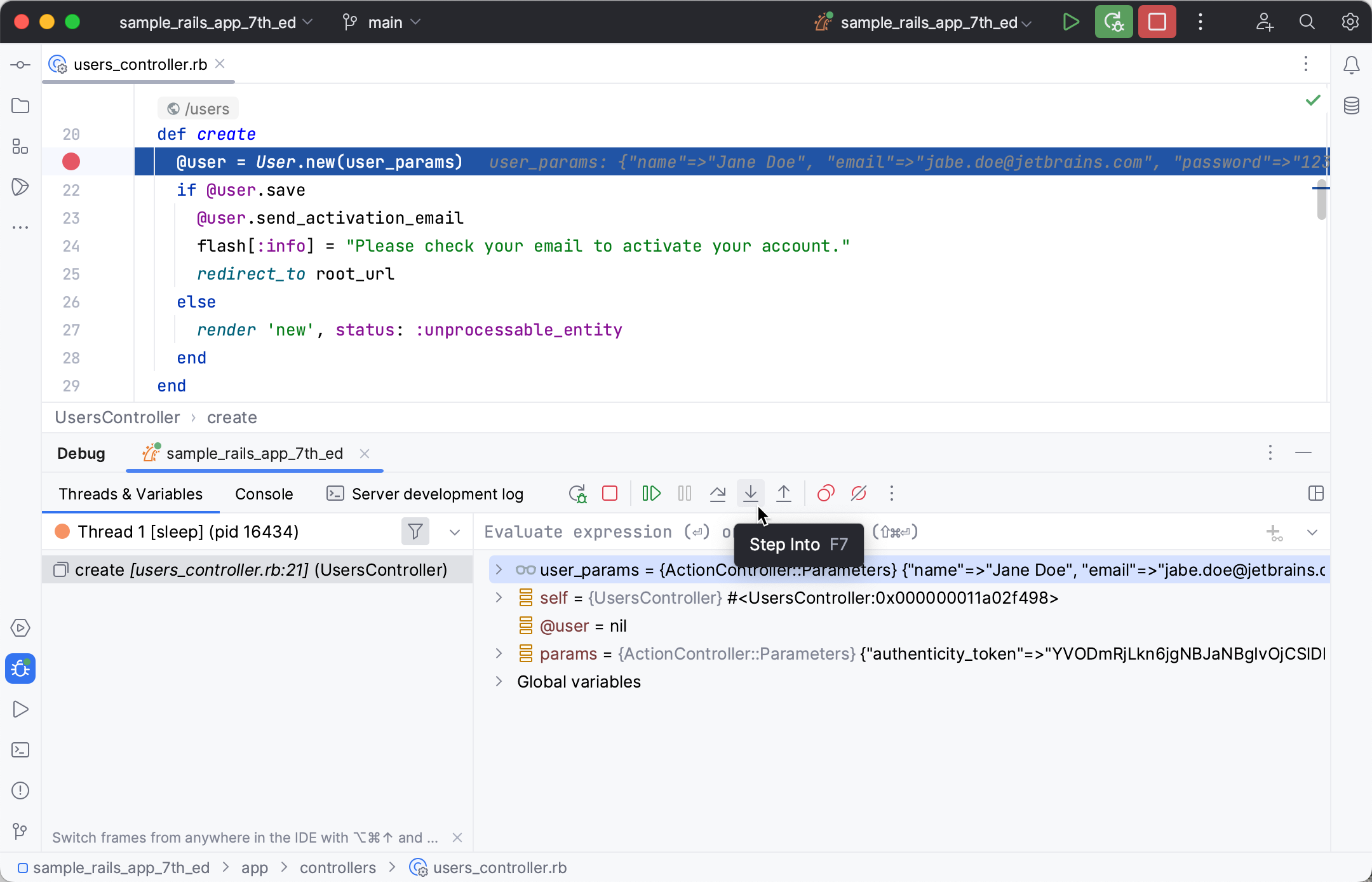
Press F7 or click the button. The editor will set a focus on the
user_params method. You can use arrow keys or Tab to choose the required method to step into (new or user_params in our example). Select user_params and press Enter. The program execution will jump to the user_params method definition.
If you press F7 another time, the debugger will suggest selecting between the params and require methods from the StrongParameters module.
The debugger has the Console tab that enables you to interact with a debugged application with an IRB-like console.
Start typing user_params in the console, select the corresponding variable, and press Enter.
The Console window will display the values of variables.
Thanks for your feedback!