Create files and directories
RubyMine enables you to create arbitrary files or language-specific files. You can create Ruby files, classes or modules, tests, HTML files, stylesheets, JavaScript/TypeScript files, and so on. Such language-specific files can be created with initial content using templates. For example, the RSpec test created from a template contains a skeleton for an example group. If necessary, you can customize these templates or add new ones.
In this topic, we'll show you how to create files and directories, and how to use templates.
Create a Ruby file, class, or module
RubyMine enables you to create Ruby files or generate classes and modules. To create a new Ruby file, class, or module, do the following:
In the Project view Alt+1, select the directory where you want a class to be created, and press Alt+Insert.
From the popup menu, select Ruby File/Class.
In the New Ruby File/Class popup, do one of the following:
To create a new Ruby file, enter its name and make sure that File is selected.
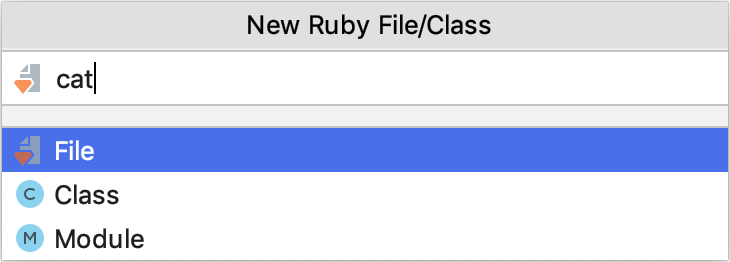
To create a Ruby class, switch to Class and specify the class name.
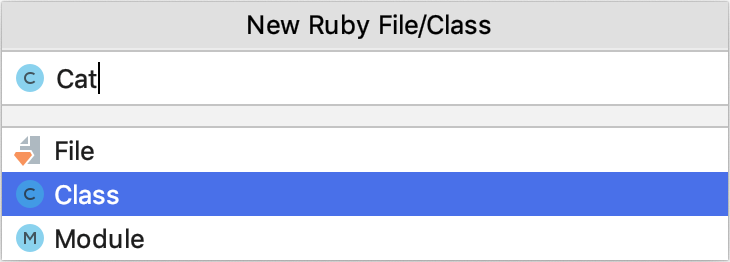
RubyMine allows you to create classes prepended by modules. If required, prepend the class name with the module name:
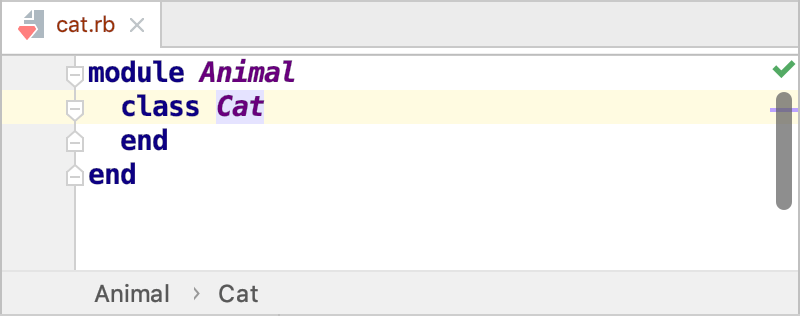
In this case, the created file will look as follows:
tip
Note that names of Ruby classes and modules should start with an uppercase letter.
To create a Ruby module, switch to Module and specify the module name.
Press Enter.
Create a directory
To create a directory:
In the Project view Alt+1, right-click the directory where you want to create a new one and select New | Directory from the context menu. Alternatively, click the parent directory, press Alt+Insert, and then select Directory from the list.
In the popup that opens, specify the directory name. To create several nested directories, use slashes as separators, for example, views/shared.
Create an empty file
To create an empty file with an arbitrary extension:
In the Project view Alt+1, select the directory where you want to create a file, press Alt+Insert, and then select File from the list.
In the New File dialog that opens, type the filename and extension. You can type the whole directory structure before the new filename. If the nested directories do not yet exist, they will be created.
If the specified extension is not associated with any file type recognized in RubyMine, the Register New File Type Association dialog opens where you can associate the extension with one of the recognized file types. See Set file type associations for details.
tip
If there are no appropriate file types for the new extension, most likely, you need to install the corresponding repository plugin as described in Manage plugins.
File templates
RubyMine allows you to create new files with initial content using templates. You can customize these templates or add new ones.
File template variables
A file template can contain variables, which are replaced by their values when the template is applied. A variable is a string that starts with a dollar sign $ followed by the variable name. The variable name may optionally be enclosed in curly braces. For example, $MyVariable and ${MyVariable} are different notations of the same variable.
Custom template variables
Besides predefined template variables, it is possible to specify custom variables. If necessary, you can define the values of custom variables right in the template using the #set directive.
For example, if you want to use your full name instead of your login name defined through the predefined variable ${USER}, use the following construct:
#set( $MyName = "John Smith" )If the value of a variable is not defined in the template, RubyMine will ask you to specify it when the template is applied.