Terminal
Open: View | Tool Windows | Terminal or AltF12
Configure: Settings CtrlAlt0S | Tools | Terminal
RubyMine includes an embedded terminal emulator for working with your command-line shell from inside the IDE. Use it to run Git commands, set file permissions, and perform other command-line tasks without switching to a dedicated terminal application.
This functionality relies on the Terminal plugin, which is bundled and enabled in RubyMine by default. If the relevant features aren't available, make sure that you didn't disable the plugin.
Press CtrlAlt0S to open the IDE settings and then select Plugins.
Open the Installed tab, find the Terminal plugin, and select the checkbox next to the plugin name.
Initially, the terminal emulator runs with your default system shell, but it supports many other shells, such as Windows PowerShell, Command Prompt cmd.exe, sh, bash, zsh, csh, and so on. For information about changing the shell, see Terminal settings.
From the main menu, select View | Tool Windows | Terminal or press AltF12.
By default, the terminal emulator runs with the current directory set to the root directory of the current project. For information about changing the default start directory, see Terminal settings.
Right-click any file (for example, in the Project tool window or any open editor tab) and select Open in Terminal to open the Terminal tool window with a new session in the directory of that file.
tip
You can open the terminal as an editor tab: right-click the Terminal tool window header and select Move to Editor.
To start a new session in a separate tab, click
on the toolbar or press CtrlShift0T.
To run multiple sessions inside a tab, right-click the tab and select Split Right or Split Down in the context menu.
The Terminal saves tabs and sessions when you close the project or RubyMine. It preserves tab names, the current working directory, and even the shell history.
To close a tab, click on the Terminal toolbar or press CtrlF4.
Press Alt0→ and Alt0← to switch between active tabs. Alternatively, you can press Alt0↓ to see the list of all terminal tabs.
tip
Configure shortcuts for the terminal actions in the IDE settings (CtrlAlt0S), under Keymap | Plugins | Terminal.
On the toolbar, click
.
Click New SSH Session, enter the address of a host to which you want to connect, and provide authentication data.
Or, if you have configured SSH configurations, you can select one of them from the list.
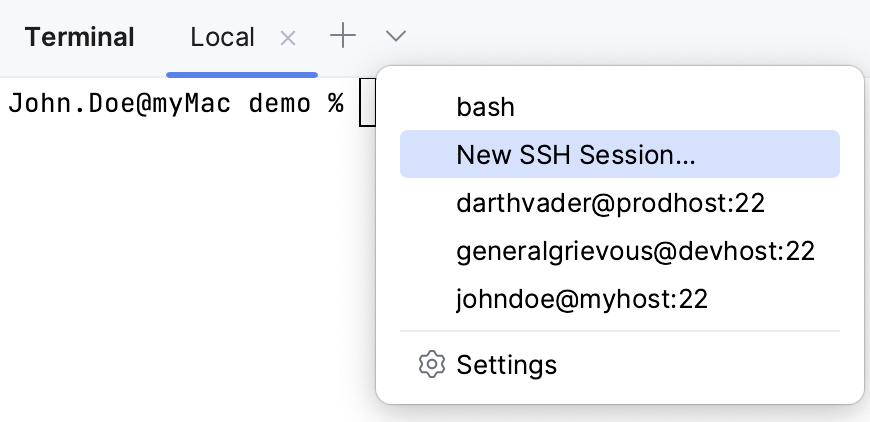
To terminate the connection, click in the terminal tab.
Right-click the tab and select Rename Session from the context menu.
tip
Just like with system terminal tabs, you can rename RubyMine Terminal tabs programmatically. For example, use
title MyTitleif your interpreter is Windows Command Prompt orecho -en "\033]0;MyTitle\a"for bash and zsh. This feature is available if the Show application title checkbox is selected in Advanced Settings.
To search for a certain string in a Terminal session, press Ctrl0F. This searches all text in the session: the prompt, commands, and output.
By default, the search is not case-sensitive. You can click Match case in the search box to make it case-sensitive.
Press CtrlAlt0S to open the IDE settings and then select Tools | Terminal. For more information, see Terminal settings.
tip
For advanced settings, select Advanced Settings and scroll down to the Terminal group. For more information, see Advanced Settings: Terminal.
Instead of running a specific command in the integrated terminal and reading console output, you can use the relevant IDE feature, like a tool window or a dialog that implements this functionality. For example, the diff viewer actually runs the diff command in the system shell to produce results. Another example is the Log tab in the Git tool window, which is based on the output of the git log command.
Type a supported command in the terminal and notice how it is highlighted.
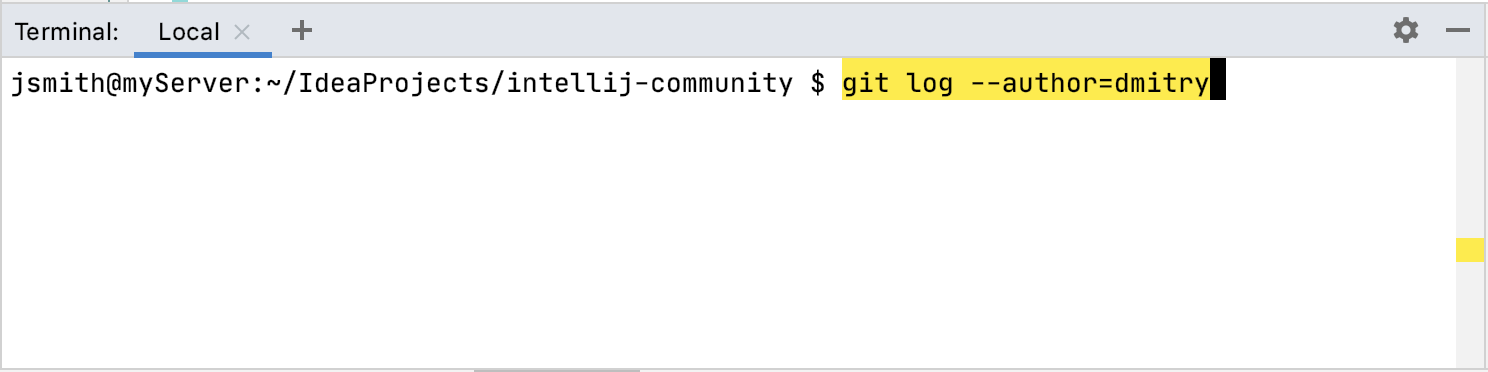
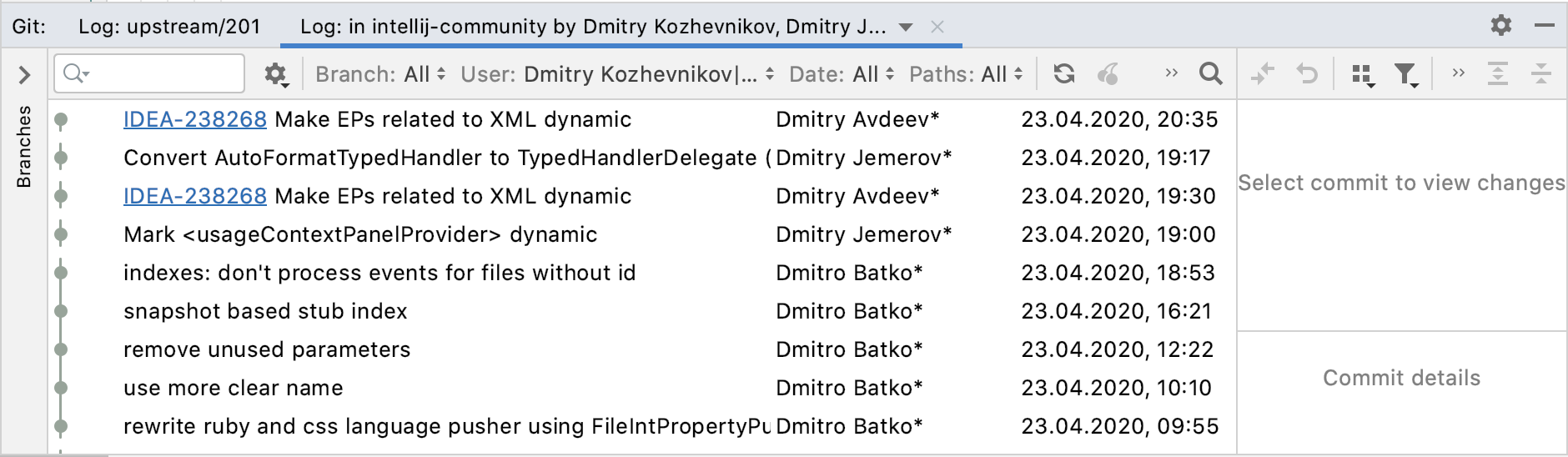
Instead of pressing Enter, which runs the command in the terminal, press CtrlEnter to open the corresponding GUI element. In this example, it will open the Log tab of the Git tool window and filter commits by authors with “dmitry” in their usernames.
This feature also works with most of the commands recognized by Run Anything (press Ctrl twice), depending on what plugins you have installed. To run a highlighted command in debug mode (use the Debug tool window instead of Run) press CtrlShiftEnter.
If you want to disable this feature, click on the title bar of the Terminal window and clear the Run Commands using IDE option.
Thanks for your feedback!