WSL2
Local client OS: Windows
Remote host OS: WSL Linux distributions
Sources location: local machine
Project model: CMake/Makefile/Compilation database
WSL (WSL 2) – Windows Subsystem for Linux – is a compatibility layer for running Linux binary executables natively on Windows 10 and later. Currently, it supports several Linux distributions, such as Ubuntu, OpenSUSE, and SLES.
With WSL toolchain set up for your project, you can build using a toolchain from Linux, and run/debug on WSL, without leaving CLion running on your Windows machine.
note
You don't need to install or run CLion inside WSL.
note
You can also try to use Remote Development to configure WSL.
Download and install a WSL distribution (for instance, Ubuntu) from Microsoft Store.
For this step, be sure to use at least Windows 10 or later with the latest “Fall Creators Update” (minimum version 1709, build 16299.15). See the official guide Install the Windows Subsystem for Linux for instructions.
To work with WSL 2, your Windows version should be 10 build 18917 or later. Follow these instructions to switch the distributive.
Note that CLion does not support legacy WSL, which you may have installed before upgrading your system to the build 16299.15 or later of Windows 10. In this case, you need to update your WSL distribution.
Run the Linux distribution.
Upon the first launch, the system may prompt you to enable the Windows optional feature. In this case, you need to do the following:
Open Windows PowerShell as Administrator and run
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-LinuxRestart your computer.
note
If you are using Linux distribution other than Ubuntu, ensure that the distribution has the iproute2 package installed or install it manually once the WSL instance is deployed.
Set up the Linux distribution environment:
Install cmake, gcc, or/and clang (and optionally build-essentials package), as follows:
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install cmake gcc clang gdb build-essential
In CLion, go to Settings | Build, Execution, Deployment | Toolchains.
Click
to create a new toolchain and select WSL.
In the Toolset field, select one of the available WSL distributions. The list includes the distributions detected by
wsl.exe --list, which includes the imported ones.note
If CLion cannot find your WSL executable, the reason might be the WSL issue fixed in Windows 10 version 1803. Try updating your system to version 1803 or later.
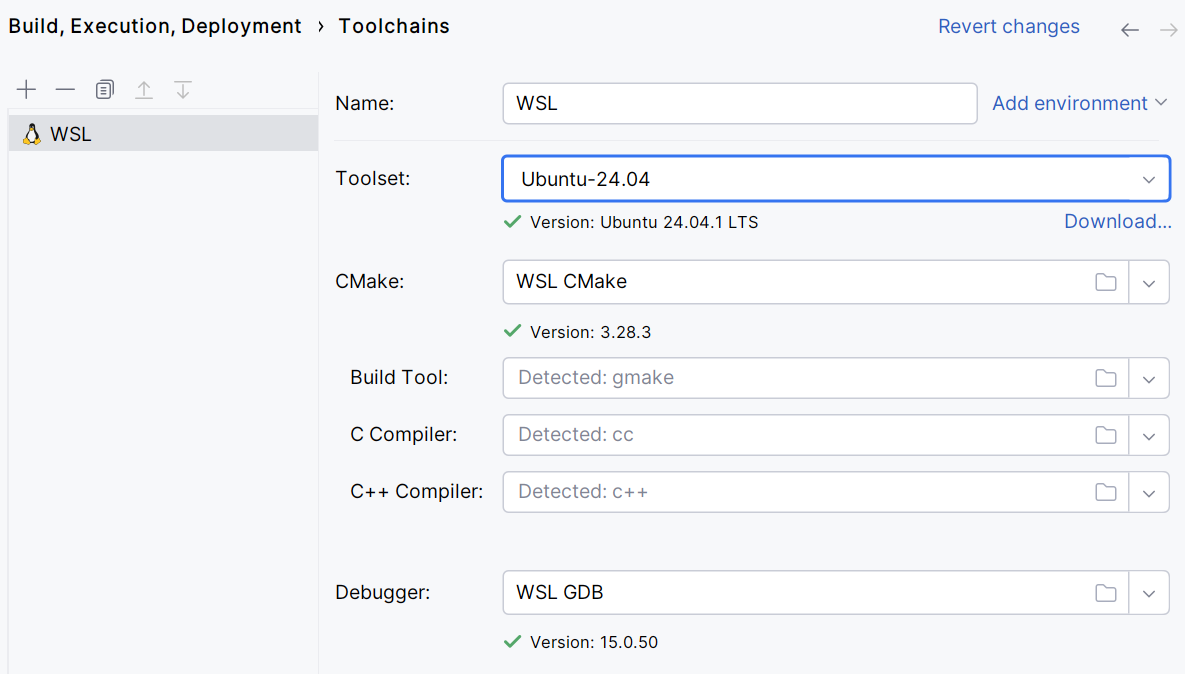
Wait for all the tools to be detected and save the settings.
tip
You can configure CLion to execute WSL commands in login (-l) shell. For more information, refer to this page.
Now to start using the toolchain, do the following:
CMakeMakefileSet the WSL toolchain as default (move it to the top of the list) or create an associated CMake profile.
tip
In order to run Valgrind on WSL, make sure to select the CMake profile associated with the WSL toolchain. For more information, refer to this instruction.
Switch to the WSL toolchain in Settings | Build, Execution, Deployment | Makefile.
Call Tools | Makefile | Clean and Reload Makefile Project.
In the Native Application configuration, point Executable to the binary using the
\mnt notation (for example,\.. \mnt ).\c \Users \jetbrains \CLionProjects \SimpleMakefile \runme
note
You need to perform the following steps to ensure that the building of a project works properly.
Run the Windows PowerShell as administrator.

Execute the following command to allow connections using WSL:
New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName "WSL" -Direction Inbound -InterfaceAlias "vEthernet (WSL)" -Action AllowThen execute the command to renew the firewall rules:
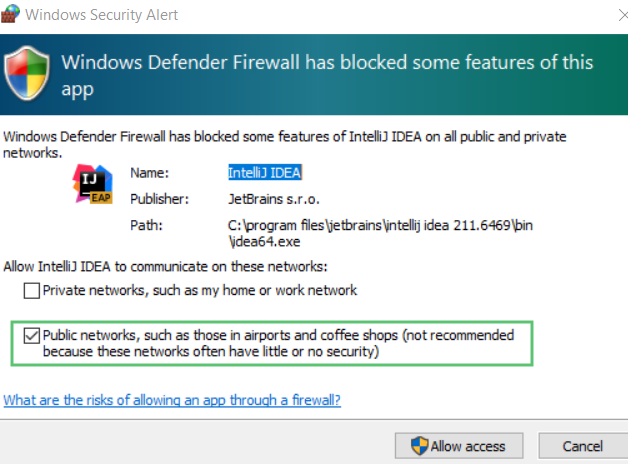
Get-NetFirewallProfile -Name Public | Get-NetFirewallRule | where DisplayName -ILike "IntelliJ IDEA*" | Disable-NetFirewallRulenote
If you are using another IDE, replace
IntelliJ IDEA*with its name.Now start the debugger session. When the Windows Firewall popup appears, select the Public networks checkbox.