Getting started with C++
This tutorial helps you get started with C++ development in JetBrains Fleet. It covers installation, project setup, and working with C++ code.
Prerequisites
Download and install JetBrains Toolbox
Download and install JetBrains Toolbox.
For macOS, you can also download the installer that matches your processor type: Apple Silicon or Intel. Ensure you select the correct option based on your system's processor.
Download and install JetBrains Fleet
In JetBrains Toolbox, click Install next to the JetBrains Fleet icon.
Set up a workspace
Prepare a compilation database for your project
JetBrains Fleet supports C++ projects with compilation databases.
A compilation database is a JSON file named compile_commands.json that contains structured data about every compilation unit in the project.
Follow this guide to generate a compilation database for your project.
Open a project
Press ⌘ O or select File | Open from the main menu.
Select your project root folder and click Open.
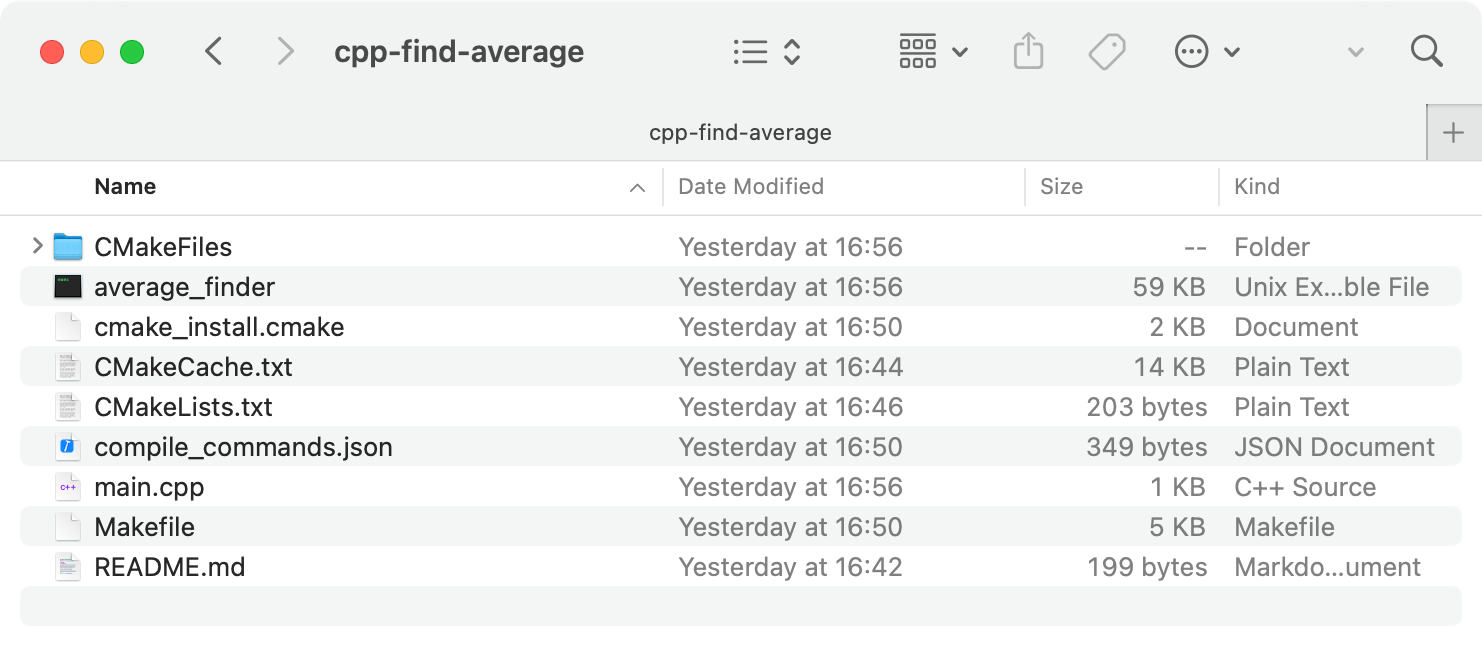
The opened directory becomes the root of your workspace:
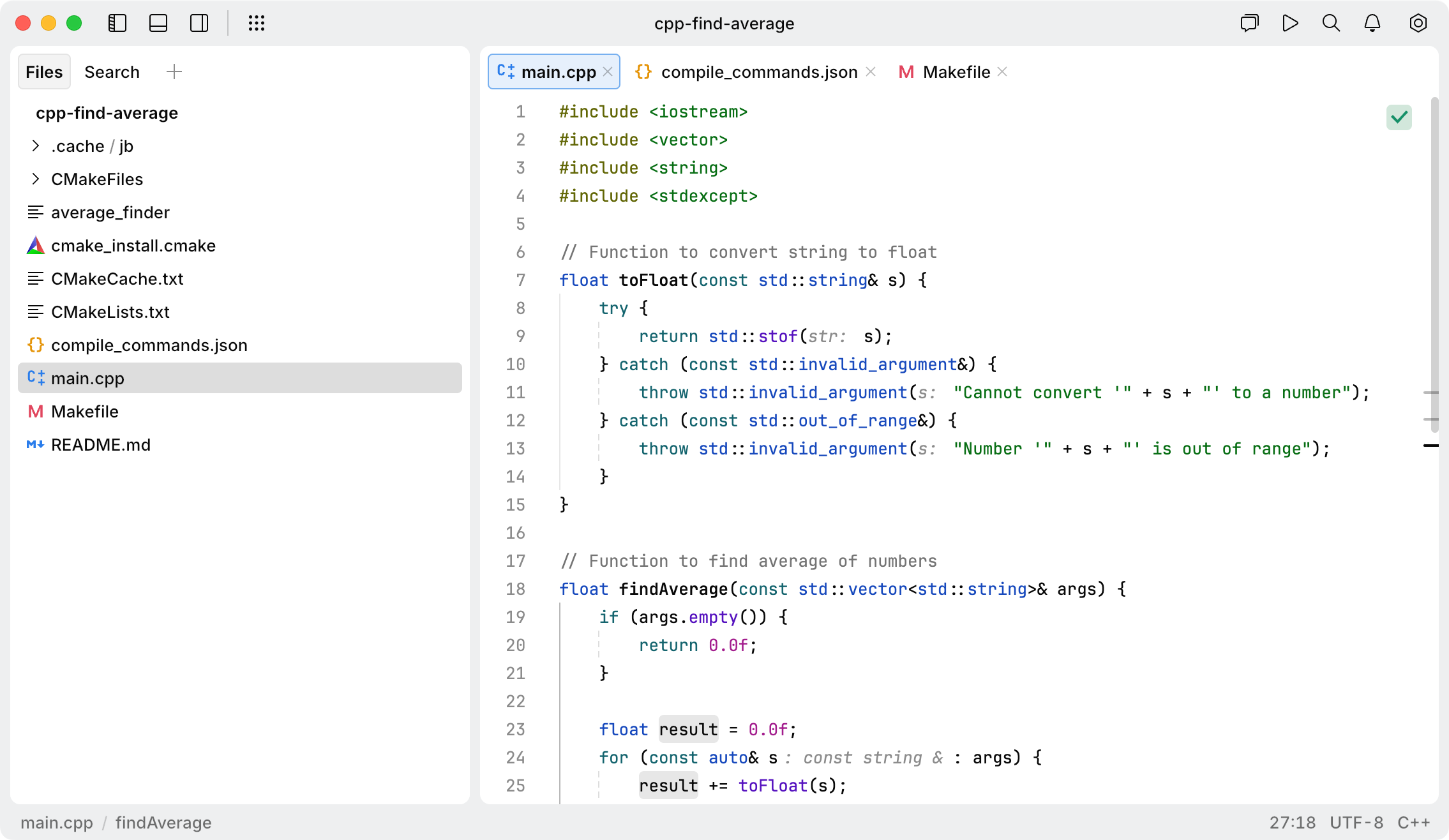
Coding assistance
JetBrains Fleet provides a variety of coding assistance features. Below are a few examples to help you get a sense of how they work in practice. This is not a complete list, but a good starting point for exploring what JetBrains Fleet can do.
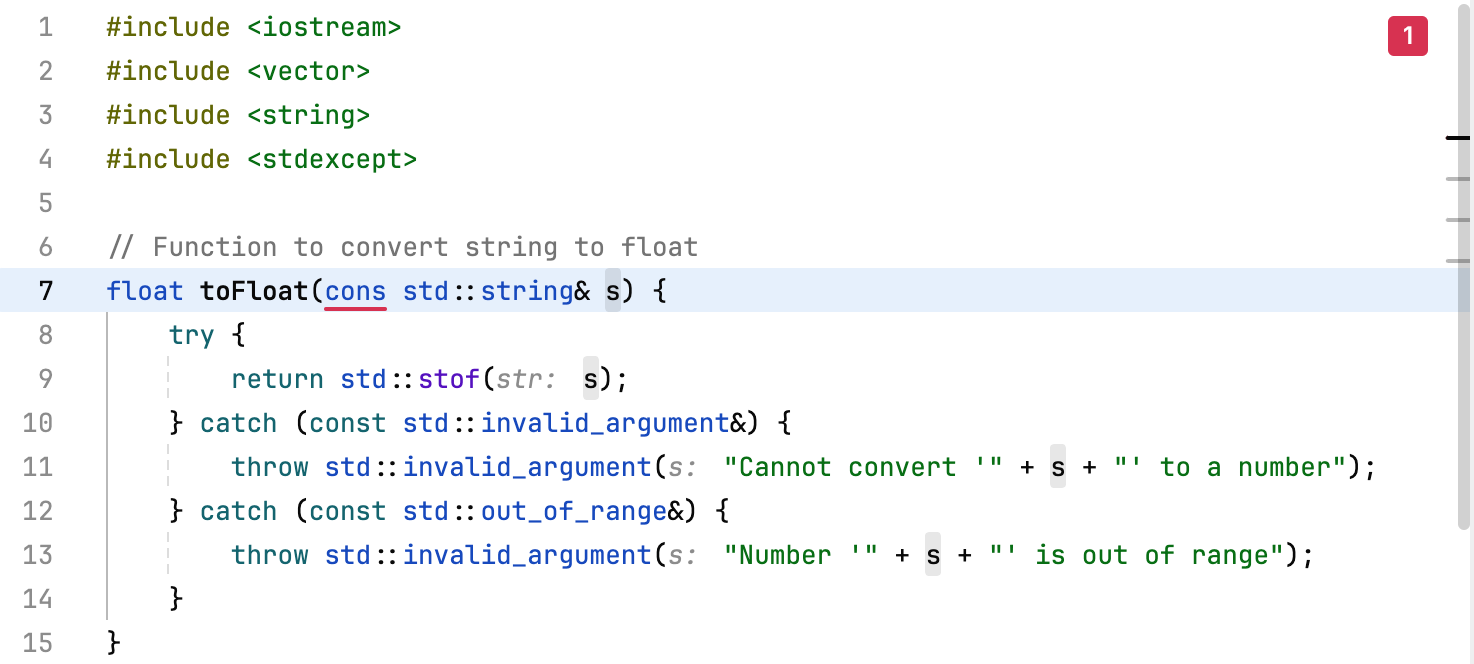
Spot syntax errors
Syntax errors in your code are highlighted in red:
Complete code automatically
Context-aware completion provides a list of suggestions for names, types, and keywords:
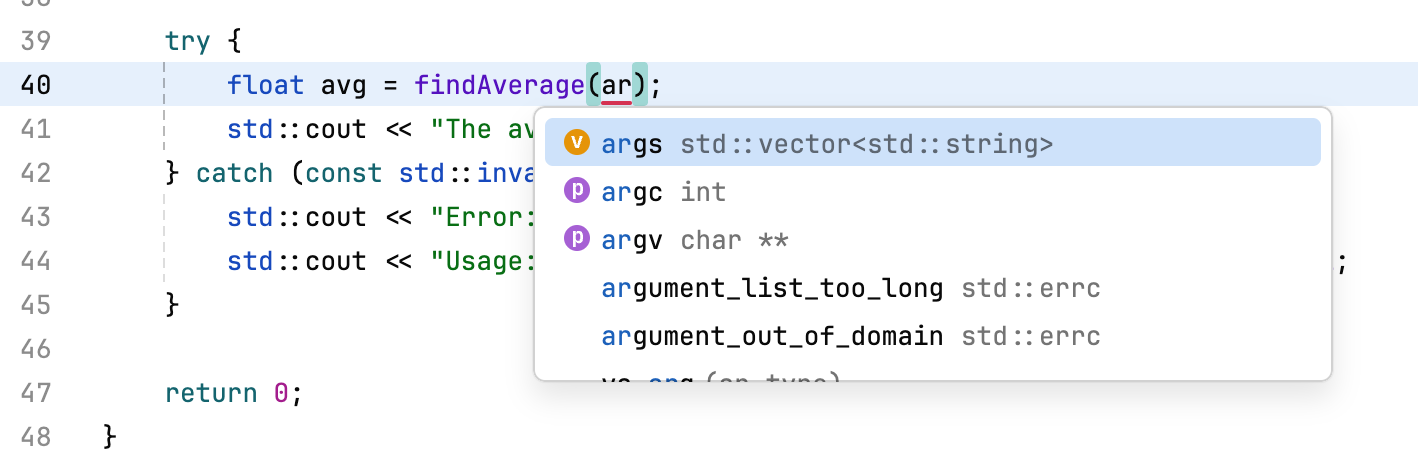
Some suggestions are templates for common code constructs. Select one from the list and press Tab to move the caret between editable fields:
Available code snippets include:
typedef [type] [name];
using [name] [type];
namespace [name] = [namespace];
using namespace [identifier];
using [qualifier]::[name];
using typename [qualifier]::[name];
template<class [name]>
template<typename [name]>
switch ([condition]) { [cases] }
case [expression]:
goto [label];
dynamic_cast<[type]>([expression])
static_cast<[type]>([expression])
reinterpret_cast<[type]>([expression])
const_cast<[type]>([expression])
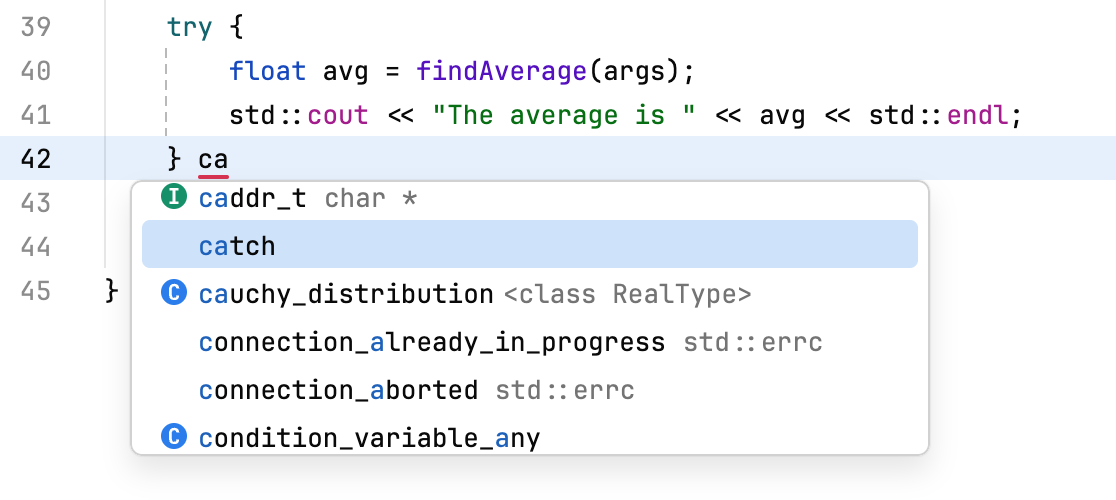
catch ([declaration]) { [statements] }
concept [name] = [constraint];
#define [macro]([args])
Reduce caret jumps
To transform an already typed expression without moving the caret, type a dot at the end. Postfix completion options will appear in the list of suggestions:
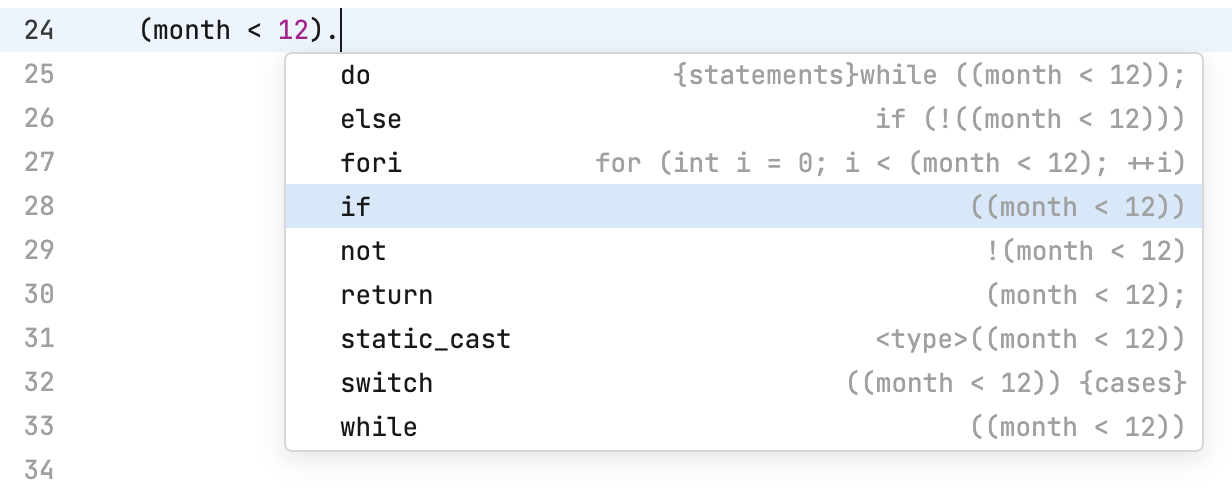
For example, if you select if, the initial expression will be wrapped in an
ifstatement:
View parameter information
Press ⌘ I to get the list of parameter names in a function call:
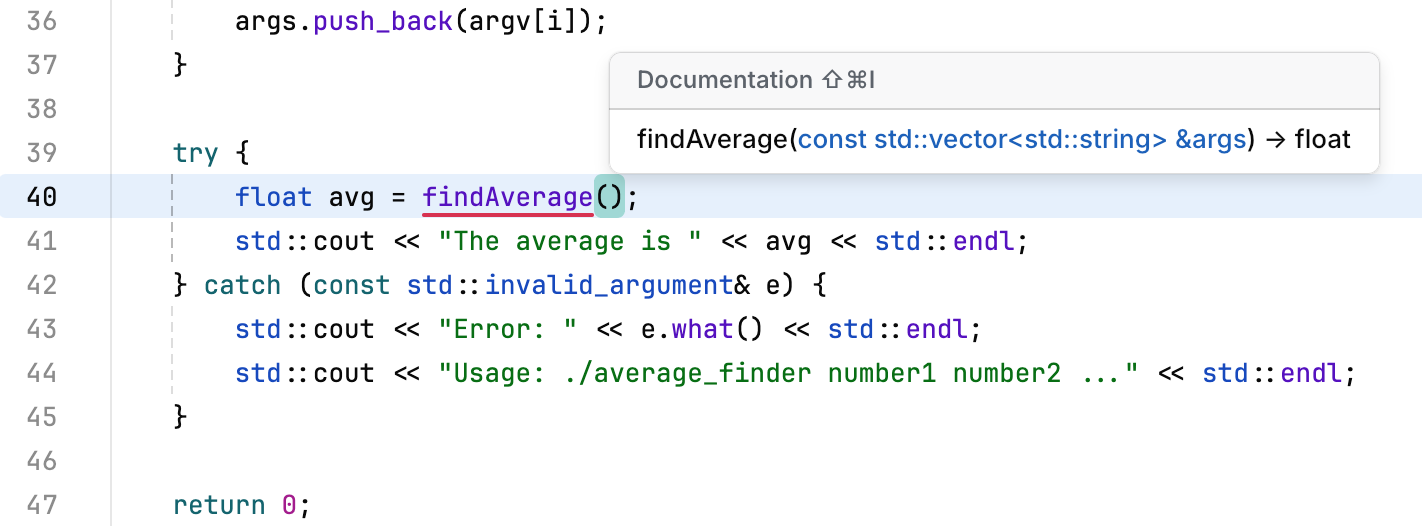
Click Show all to view all the usages.
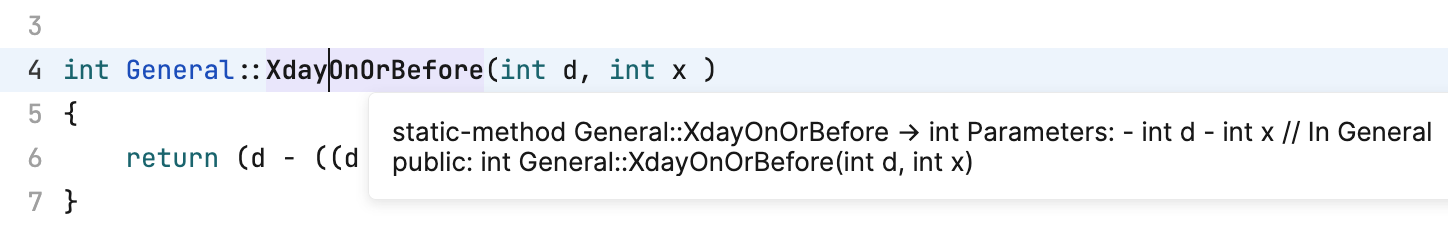
Check documentation in a popup
Hover over a class, function, field, or another element to see where and how it is defined:
Rename code items
Select the item you want to rename, press ⌃ R, and enter the new name:

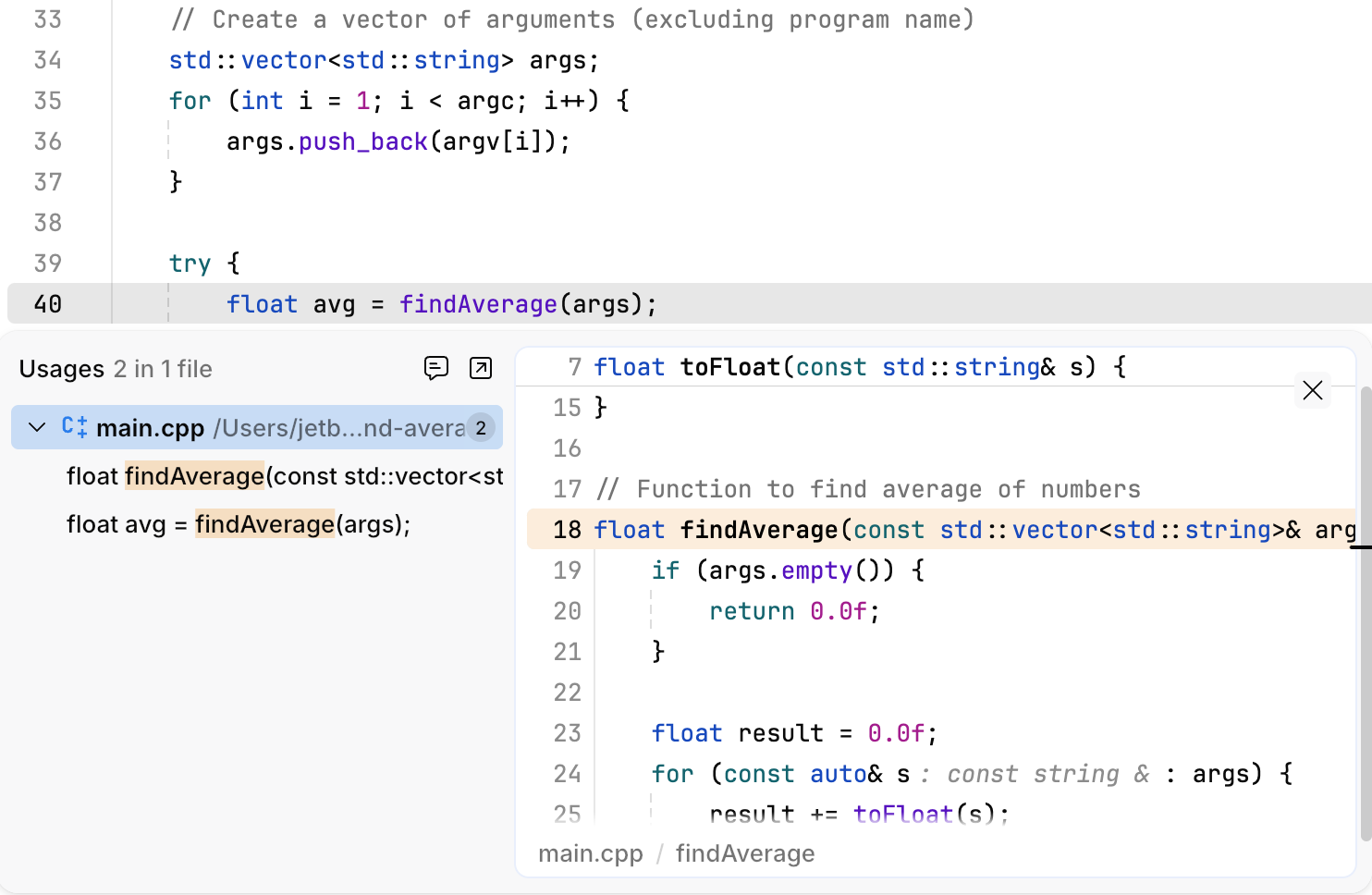
Navigate the codebase
Navigate to a symbol’s declaration by pressing ⌘ B.
Find usages of a symbol by pressing ⌘ U:
Navigate between errors using ⌘ E and ⌘ ⇧ E.
Build and run your program
JetBrains Fleet does not provide built-in automation for building and running C/C++ applications.
However, you can use language-agnostic run configurations to define custom build and run steps. Below is an example using CMake:
Troubleshooting
LSP can't start
The following message indicates that JetBrains Fleet might not have been able to download Clangd due to a firewall restriction.
Follow these steps to manually install Clangd as a workaround:
Download Clangd from the Maven repository.
Copy the downloaded files to the corresponding JetBrains Fleet directory:
For JetBrains Clangd:
/home/user/.cache/JetBrains/Fleet/language_server/jbclangd/*
For Upstream Clangd:
/home/user/.cache/JetBrains/Fleet/language_server/clangd/*
Restart JetBrains Fleet.