Extract constant
Refactor | Extract/Introduce | Constant
CtrlAlt0C
The Extract Constant refactoring makes your source code easier to read and maintain. It also helps you avoid usage of hardcoded constants without any explanation about their values or purpose.
In the editor, select an expression or declaration of a variable you want to replace with a constant.
Press CtrlAlt0C to introduce a constant or select Refactor | Extract/Introduce | Constant in the main menu.
Alternatively, on the toolbar that appears, click Extract and select Constant.
note
By default, this extract refactoring will be applied in the editor via in-line controls. To change your settings to apply the refactoring via a modal, open the Settings dialog (CtrlAlt0S) , go to Editor | Code Editing, and in the Refactorings area select In modal dialogs.
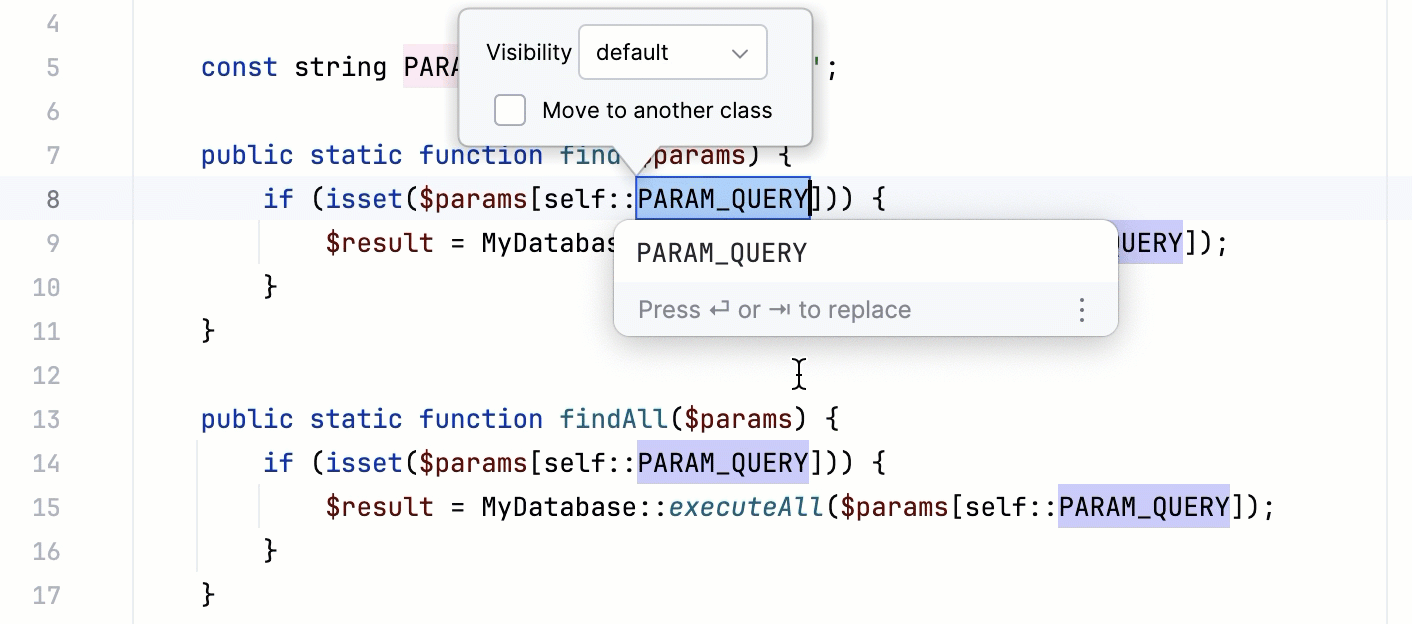
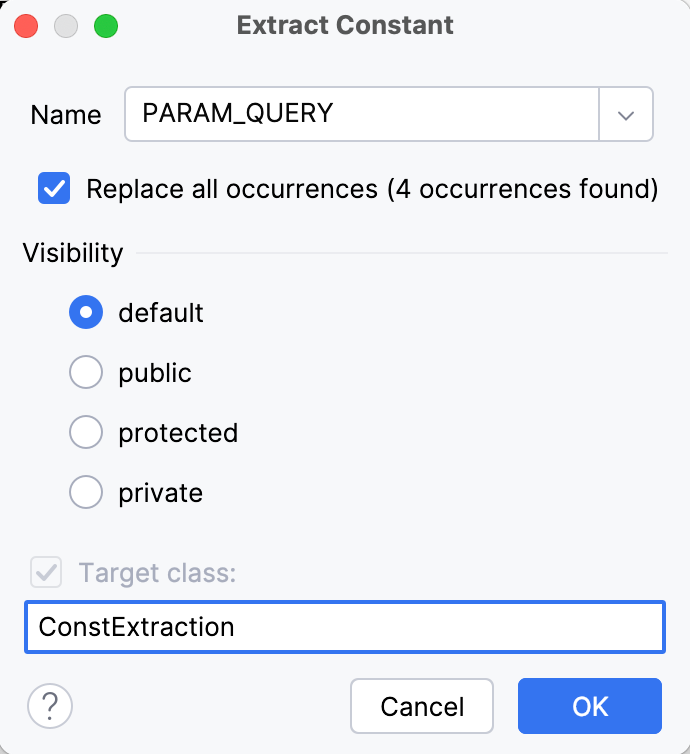
If more than one occurrence of the expression is found, specify whether you wish to replace only the selected occurrence, or all the found occurrences with the new constant.
Accept the proposed constant name or type your own name.
If required, select the Move to another class checkbox or choose the visibility scope (access level modifier) of the extracted constant. If you leave the default value selected, the constant will be implicitly defined as
publicwithout any modifier applied to it. Otherwise, you can choose the appropriate option to explicitly mark the constant aspublic,private, orprotected.Press Tab or Enter to complete the refactoring.
 Gif
GifIf you've selected the Move to another class checkbox, an Extract Constant dialog will be displayed to prompt you specify the target class.
When a constant is extracted within a class definition, the new constant is defined through the const keyword and referenced through the self keyword.
In PHP language version 7.1 and later, you can additionally mark the extracted constant as public, private, or protected.
Before | After |
|---|---|
| |
When a constant is extracted outside a class definition, you can choose whether it will be defined through the const keyword or through the define() function.
Before | After |
|---|---|
|
|
Before | After |
|---|---|
| |
Thanks for your feedback!