Columns
A column is a piece of data that is stored by a table. This data belongs to a particular type. A column may include text, numbers, or pointers to files in the operating system. Some relational database systems allow columns to include more complex data types like whole documents, images, or video clips.
Columns ( ) can be found in the Database tool window.
For the reference on other node and object icons, refer to the Data sources and their elements chapter of Database tool window topic.
For the table column icons, refer to the Possible icon combinations for columns chapter.
Hide, sort, filter, and group tree objects using the tree objects view options in the View Options menu.
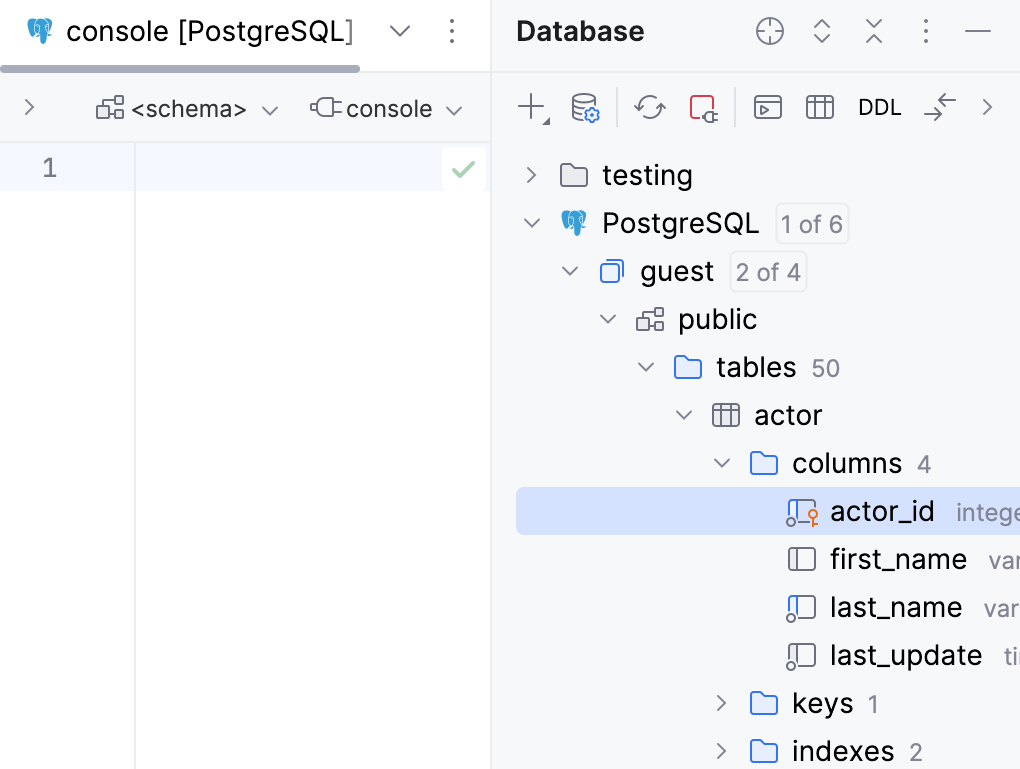
Add a column
In the Database tool window, expand the data source tree until the nodes of tables.
Right-click the table node and select .
In the Modify dialog that opens, enter the name of your column in the Name field.
In the Preview pane, you can view and change the generated SQL code.
Click OK to add your column.
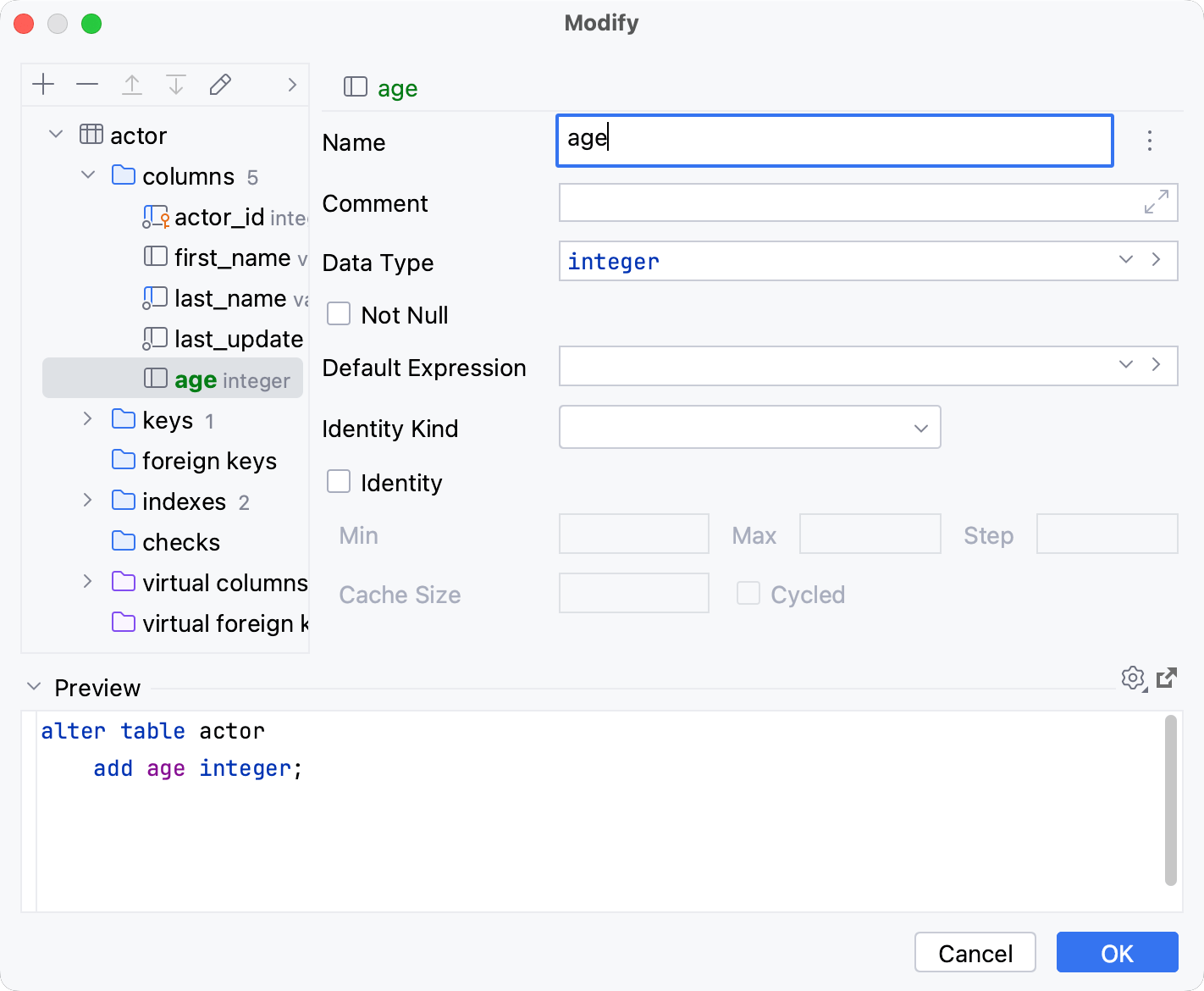
Delete a column
Right-click a column and select . Alternatively, press Delete.
Click OK to save your changes and close the dialog.
For more information about the dialog options, refer to Confirm Drop Dialog.
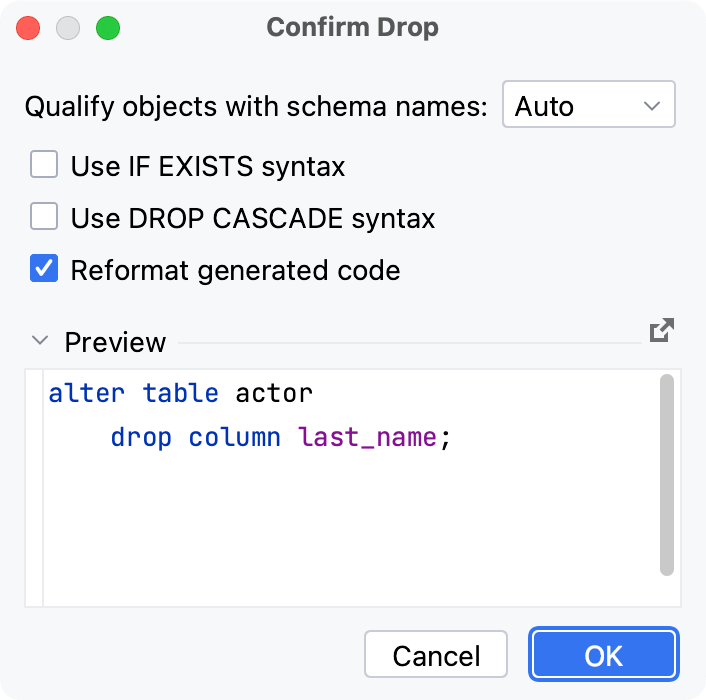
Modify a column
Starting with PyCharm 2022.1, you can change database-specific parameters of a column. The IDE generates fields for the Modify dialog automatically according to the properties received during the introspection. For example, by using this dialog in PostgreSQL, you can add and edit column check constraints.
In the Database tool window, right-click a column and select Modify Column.
In the Modify dialog, specify object settings that you need.
Click OK to save your changes.
Reorder columns
To reorder columns, drag the corresponding cells in the header row.
Hide columns
To hide a column, right-click the corresponding header cell and select Hide column.
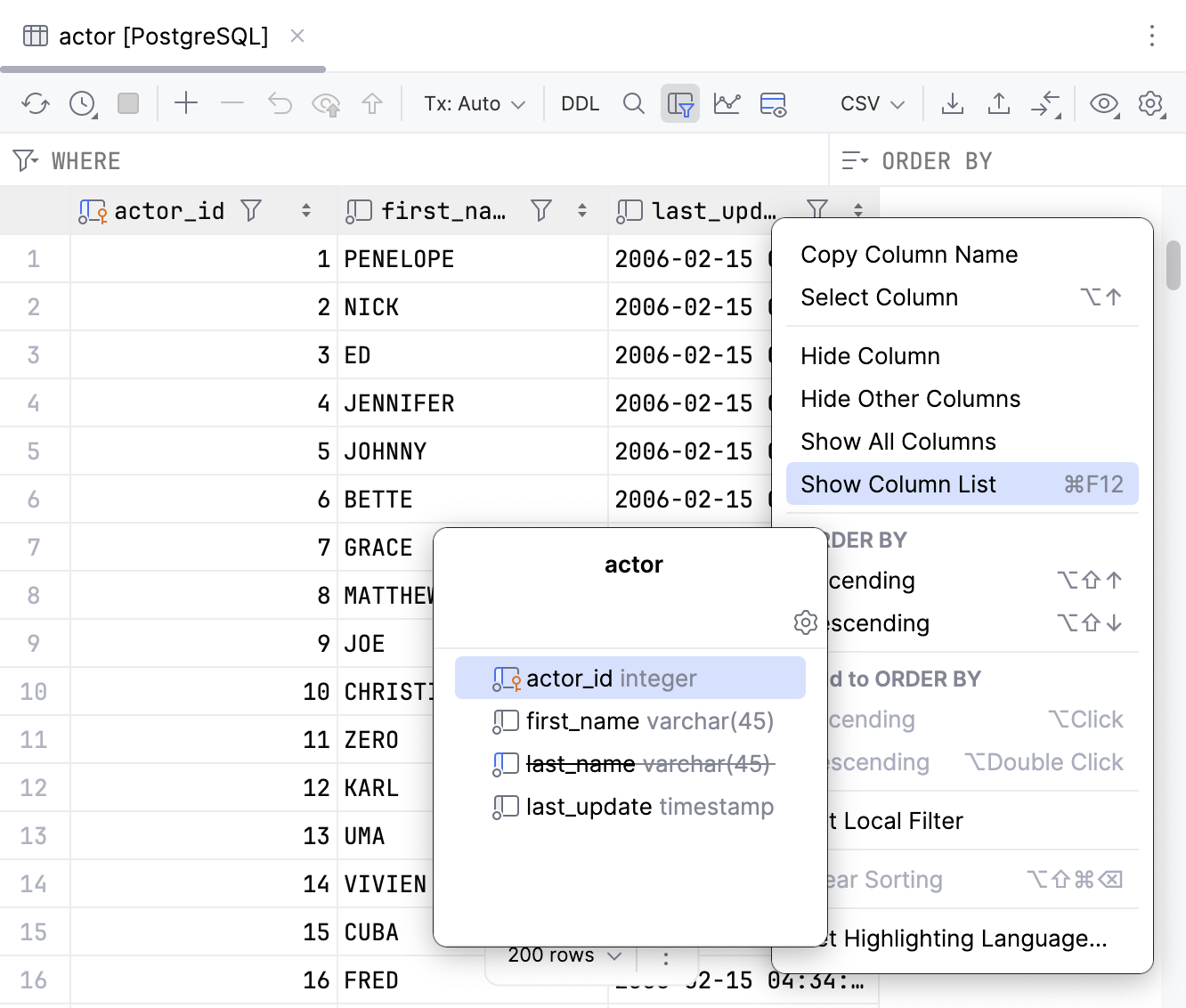
Alternatively, you can right-click any of the cells in the header row and select Show Column List Ctrl+F12. In the column list popup window, select a column name and press Space. You can hide all columns. To search through the column list, start typing a column name in the Show Column List window.
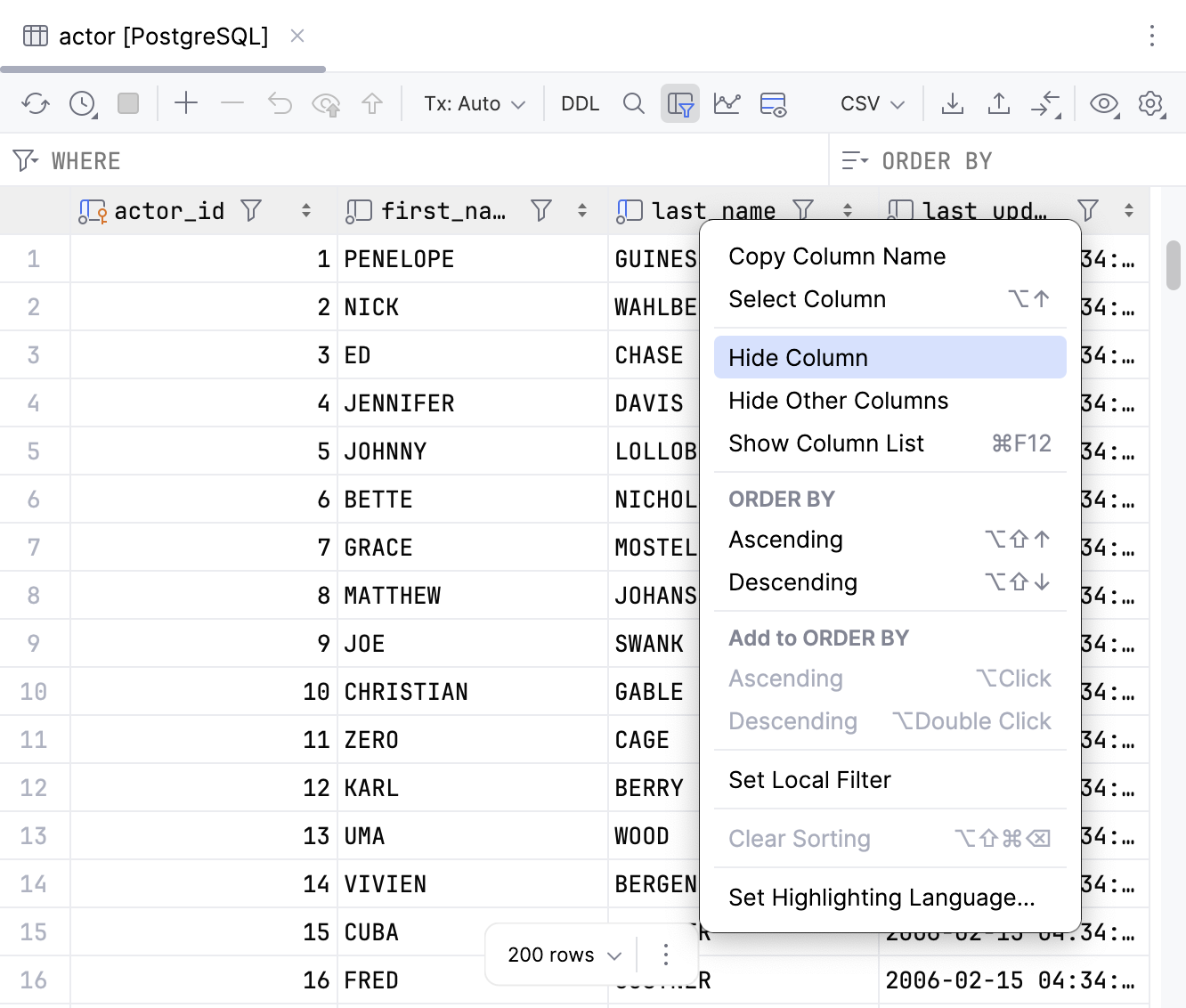
Show columns
Select the hidden column (a strikethrough column name) and press Space.
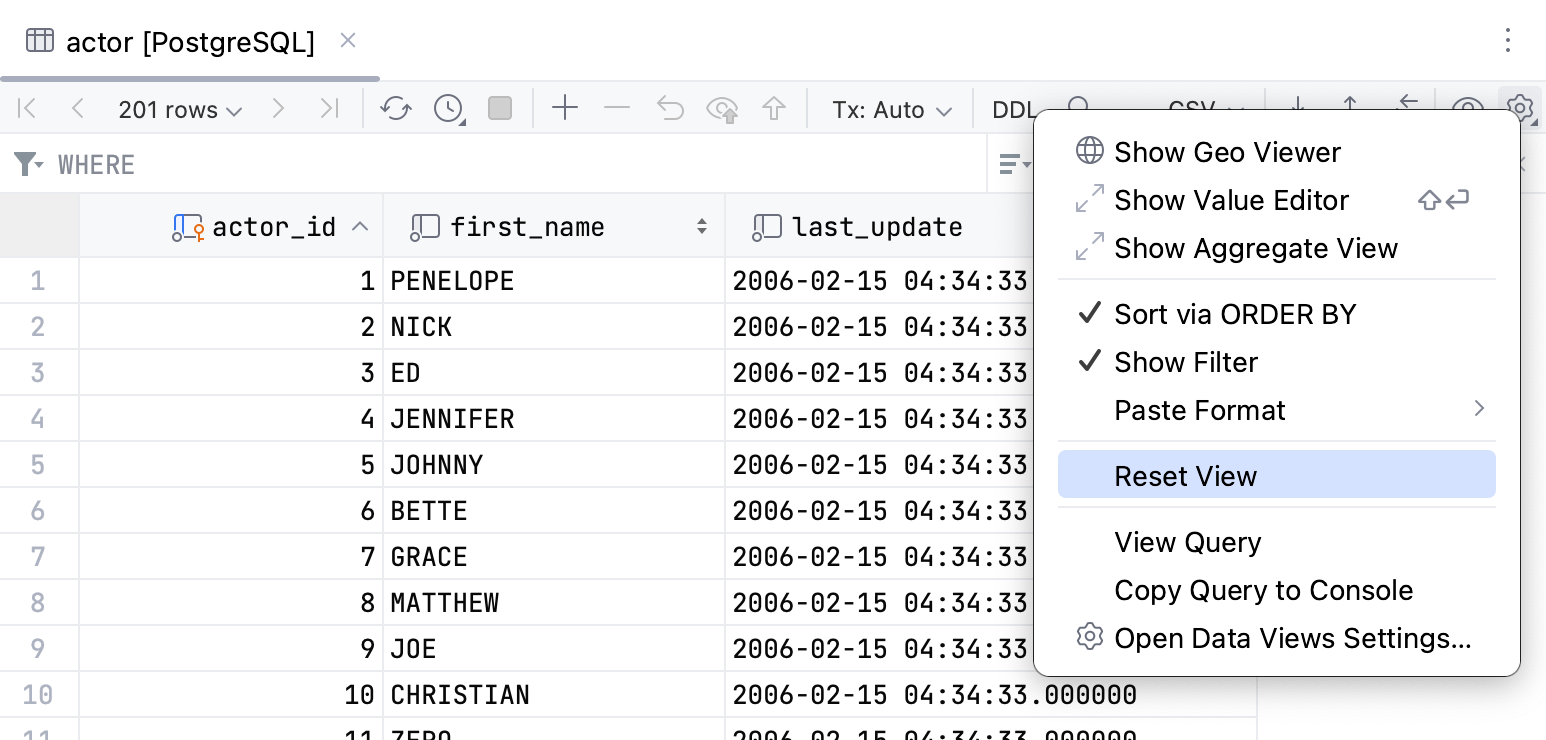
Reset the table view to the initial state
Click the settings icon (
) and select Reset View. As a result, the data becomes unsorted, the columns appear in the order they were defined initially, and all the columns are shown.
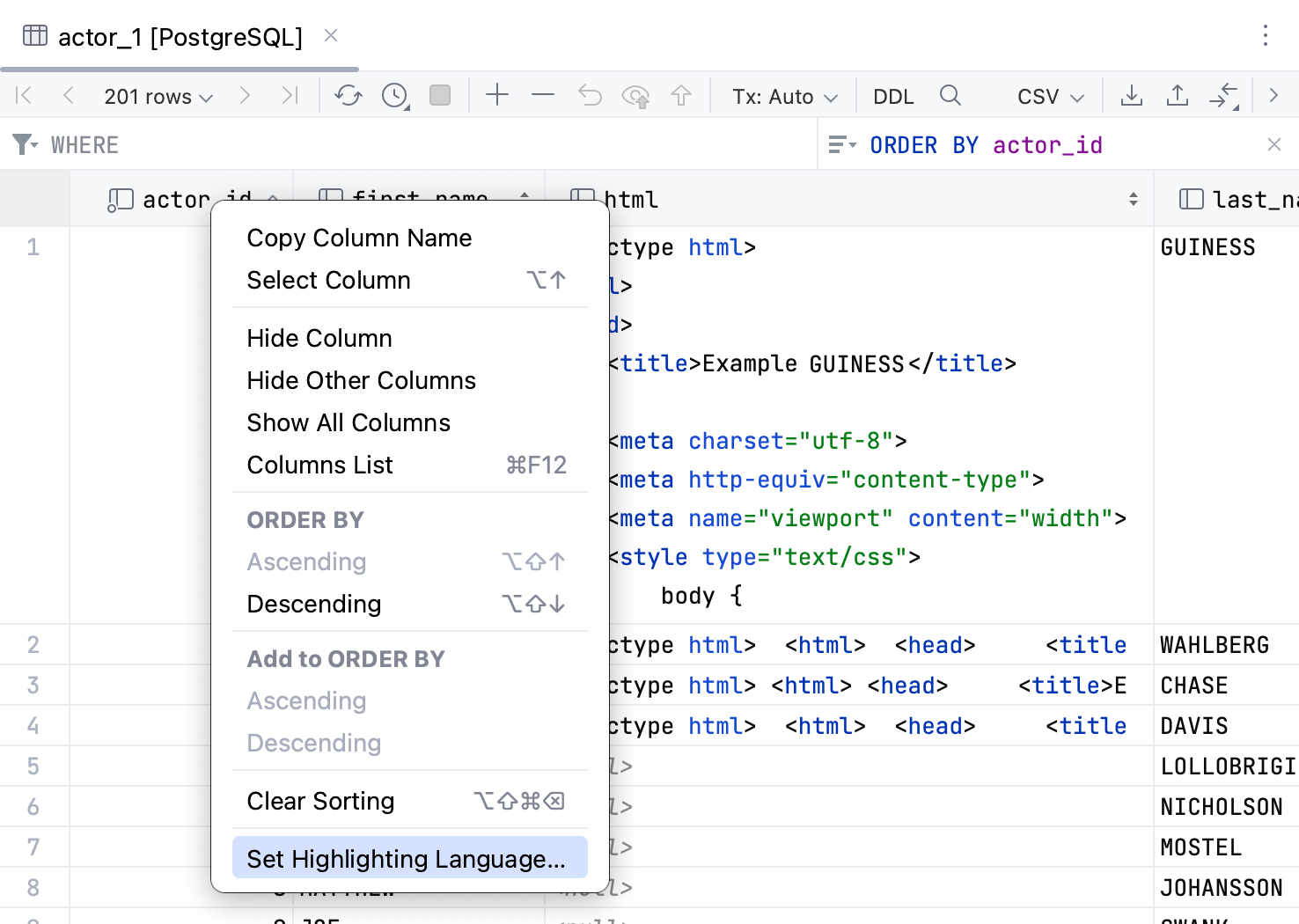
Inject a language for a column
You can assign HTML, CSS, XML, RegExp, or any other formal language for the whole column. So, when you have a piece of code inside the cell that belongs to the column, you can use code generation, code completion, and other IDE features.
To inject a language for the whole column, right-click the corresponding header cell, and select Set Highlighting Language. In the list of supported languages, select the language that you want to inject.
Change the column width
Place the caret between two columns, so it changes to the resize mode. Drag it to the preferred position.
Work with data
To learn how to work with column data, refer to the topics of Data editor and viewer section:
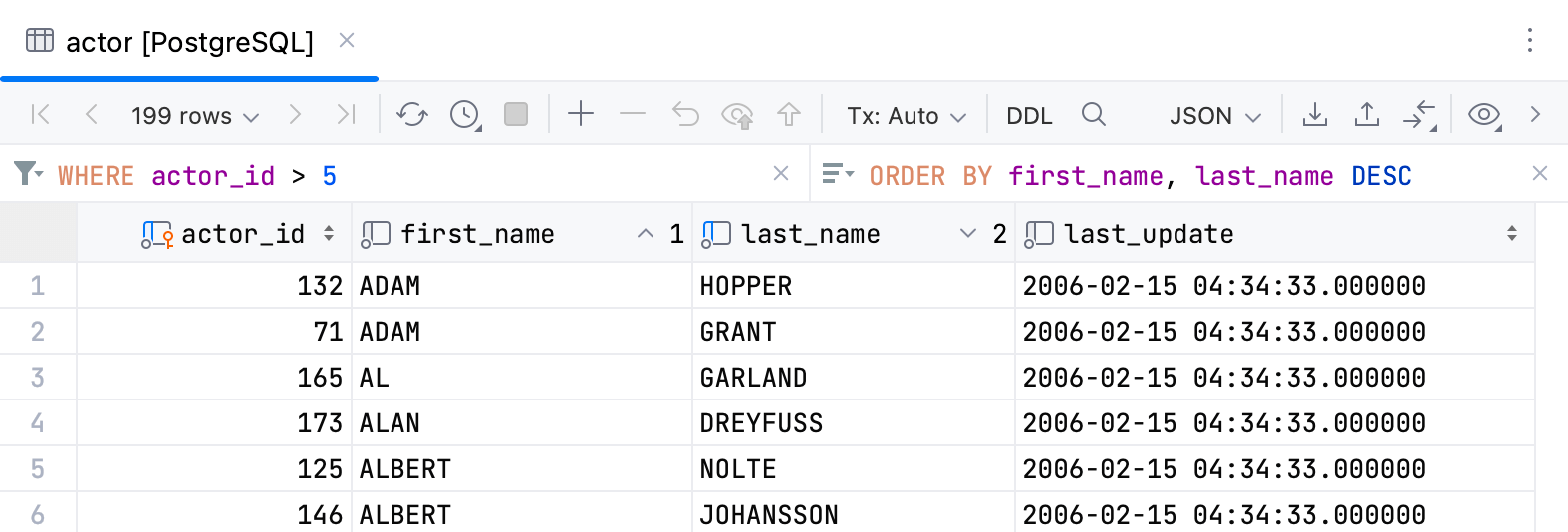
You can sort data by clicking a column's header, or by entering a sorting query into the corresponding field. By default, each time you sort data, PyCharm sends a new
ORDER BYquery to the database. You can also change the setting and sort data on the client side.Use one of the following ways to filter data:
Specify filtering conditions.
Run a search on the table.
Enter a filtering query into the corresponding field.
Productivity tips
Drag column names to your code
In the Database tool window, select any database objects and drag them to your code.