Databases
note
This topic describes displaying and working with databases in the Database tool window.
For information about connection configurations, refer to Data sources.
PyCharm displays databases that you select to be displayed. It can be useful if you have many databases. Also, by using this approach, you define which databases you want to introspect. During introspection, PyCharm loads the metadata from the database and uses this data later.
Databases () can be found in the Database tool window.
For the reference on other node and object icons, refer to the Data sources and their elements chapter of Database tool window topic.
Hide, sort, filter, and group tree objects using the tree objects view options in the View Options menu.
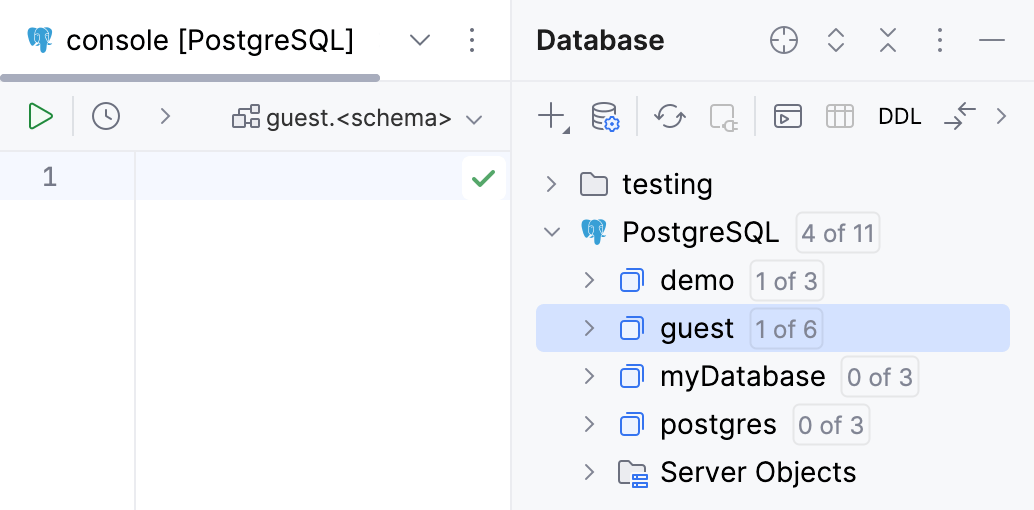
In the Database tool window (View | Tool Windows | Database) , expand the data source tree until the nodes of databases.
Right-click the data source or database node and select New | Database.
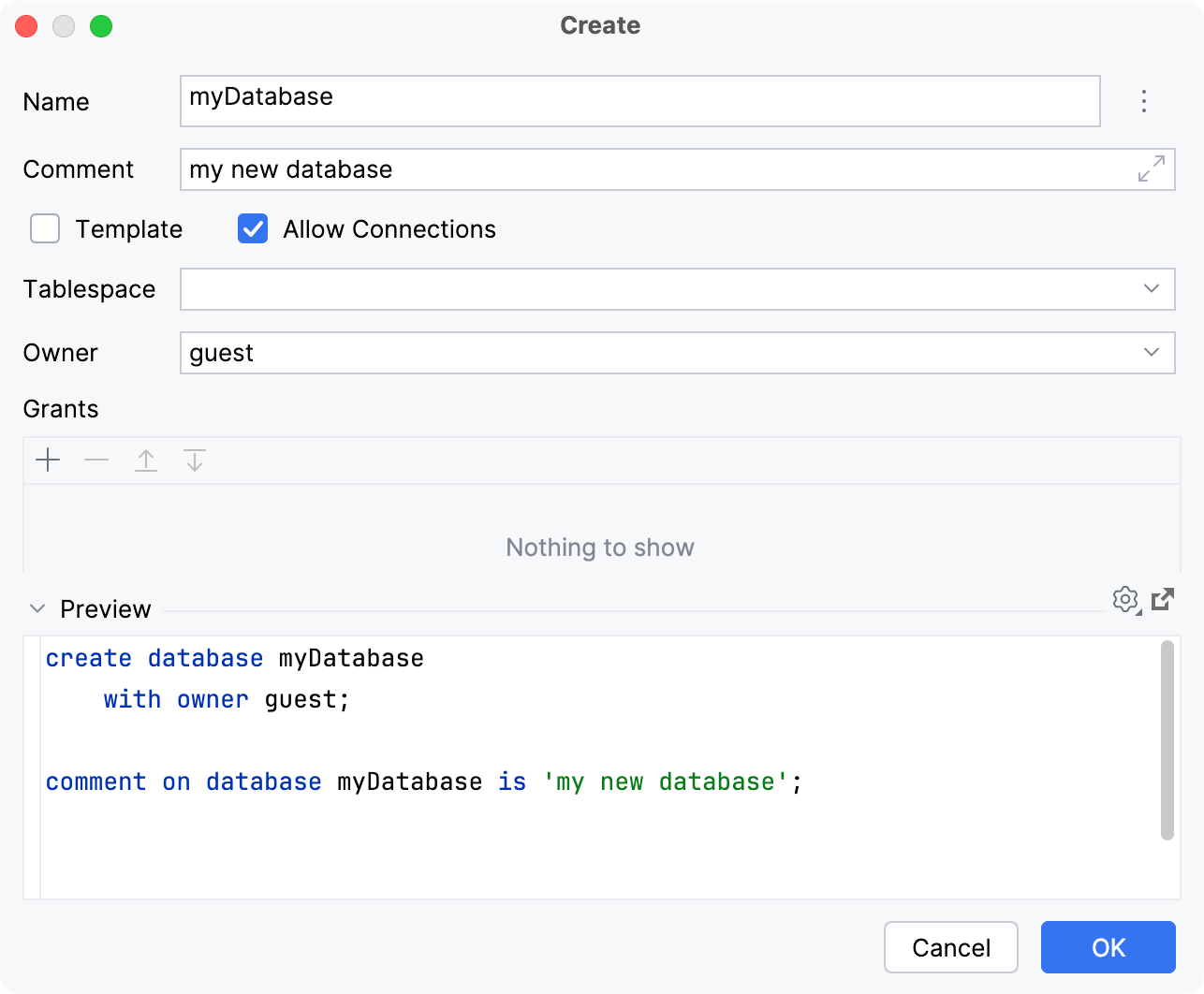
In the Create dialog that opens, enter the name of your database in the Name field.
In the Preview pane, you can view and change the generated SQL code.
Click OK to add your database.
note
When you create a data source, the data source is created with no databases or schemas selected to display. You need to select the ones you plan to work with yourself.
In the Database tool window (View | Tool Windows | Database) , right-click a data source and navigate to Tools | Manage Shown Schemas. Select or clear checkboxes of databases that you want to display or hide. Press Enter.
Click the N of M link near the data source name. In the database and schema selection window, select or clear checkboxes of databases that you want to display or hide. Press Enter.

To display and introspect all the databases with names that match a regular expression pattern, do the following:
In the Database tool window (View | Tool Windows | Database) , click the N of M link near the data source name.
In the databases and schemas selector, click the add pattern button near All databases.
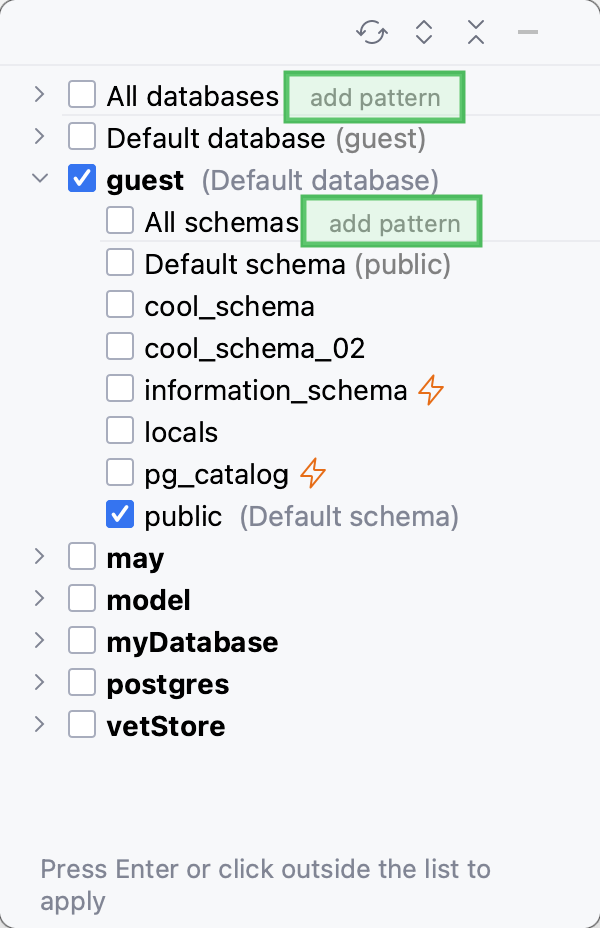
In the new filtering node, define the regular expression. For the syntax, click regex for databases near the input field. For more information about the syntax, refer to Summary of regular-expression constructs.
Press Enter to apply the filter in the selector.
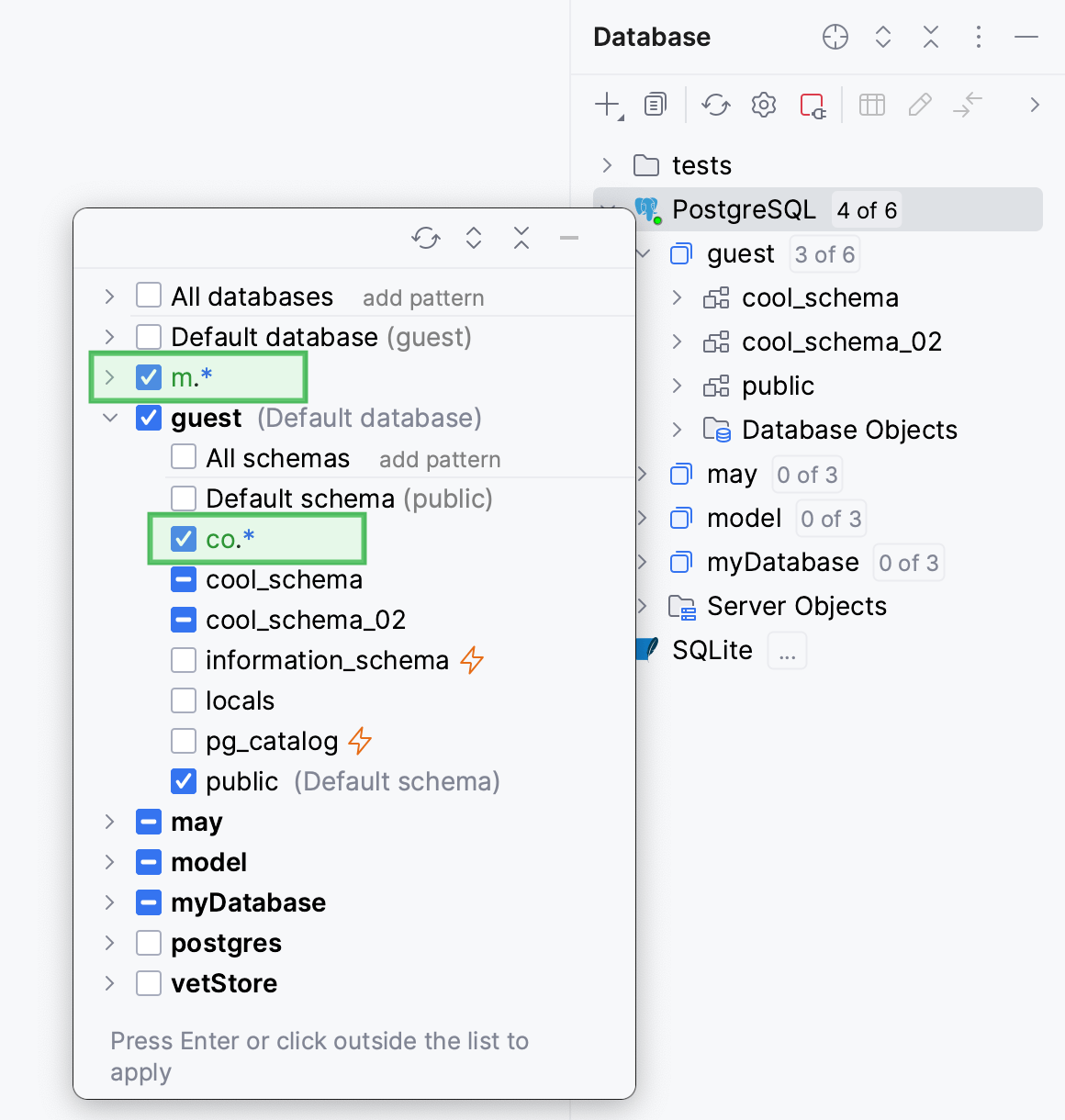
Press Enter to apply the filter in Database tool window.
The filtering node with filter can be added under any node, including another filtering node.
note
Multiple patterns combine multiplicities, not intersect them.
note
The All schemas node behaves differently now: it doesn't select the default schema automatically. You need to select between All schemas, Default schema, or a filtering node.
To display all the available databases in the Database tool window (View | Tool Windows | Database), click the Show Options Menu button and select the All Namespaces option.
Enabled

Disabled

The Force Refresh action clears the data source information from cache and loads it again from scratch.
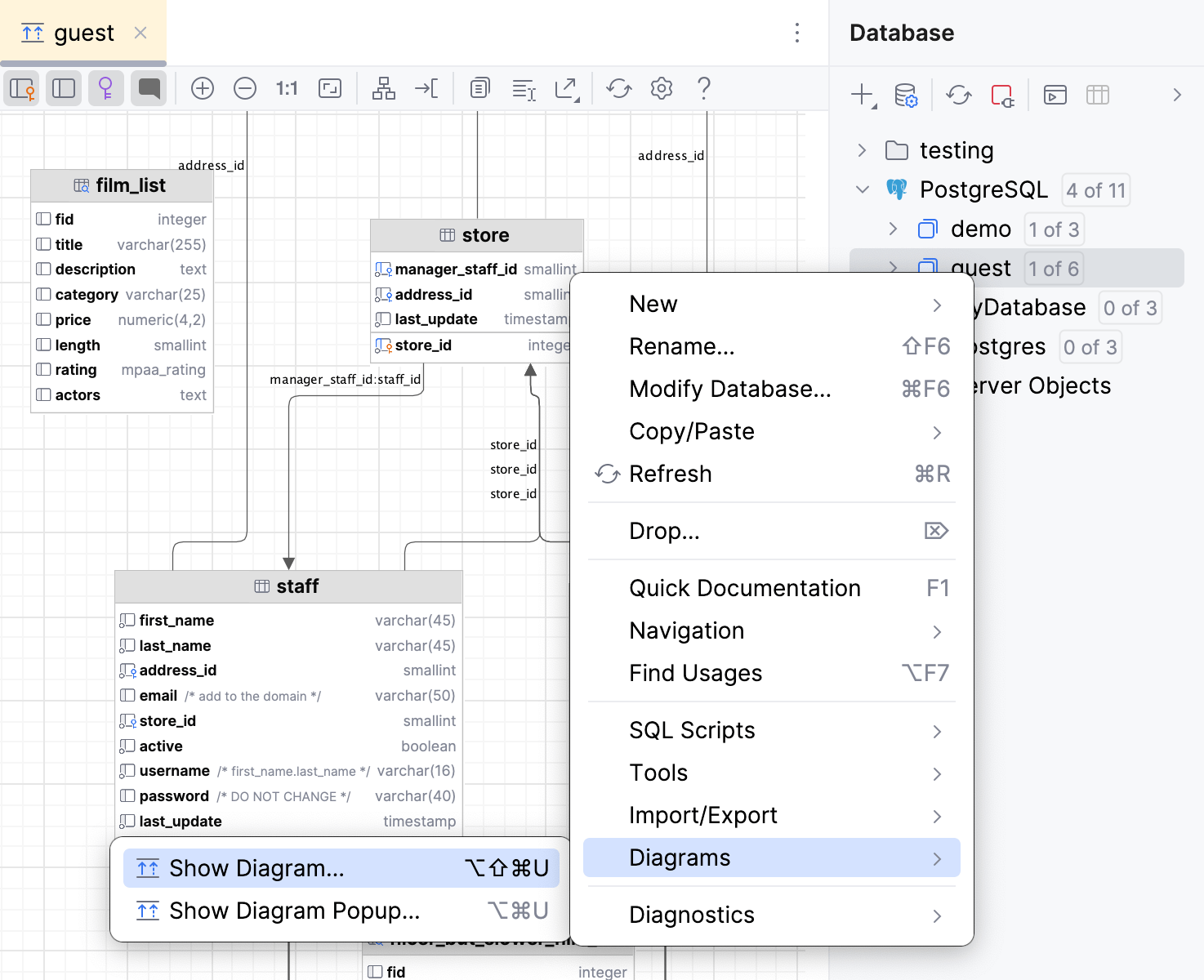
In the Database tool window (View | Tool Windows | Database) , right-click a data source and select Diagnostics | Force Refresh.
In the Database tool window (View | Tool Windows | Database) , right-click a database and select Diagrams | Show Diagram.
For full information, refer to Full Java Regular Expressions syntax description and Using Regular Expressions in Java.
Construct | Matches |
|---|---|
Characters | |
| The character x |
| The backslash character |
| The character with octal value 0n (0 <= n <= 7) |
| The character with octal value 0nn (0 <= n <= 7) |
| The character with octal value 0mnn (0 <= m <= 3, 0 <= n <= 7) |
| The character with hexadecimal value 0xhh |
| The character with hexadecimal value 0xhhhh |
| The tab character ('\u0009') |
| The newline (line feed) character ('\u000A') |
| The carriage-return character ('\u000D') |
| The form-feed character ('\u000C') |
| The alert (bell) character ('\u0007') |
| The escape character ('\u001B') |
| The control character corresponding to x |
Character classes | |
| a, b, or c (simple class) |
| Any character except a, b, or c (negation) |
| a through z or A through Z, inclusive (range) |
| a through d, or m through p: [a-dm-p] (union) |
| d, e, or f (intersection) |
| a through z, except for b and c: [ad-z] (subtraction) |
| a through z, and not m through p: [a-lq-z](subtraction) |
Predefined character classes | |
| Any character (may or may not match line terminators) |
| A digit: [0-9] |
| A non-digit: [^0-9] |
| A whitespace character: [ \t\n\x0B\f\r] |
| A non-whitespace character: [^\s] |
| A word character: [a-zA-Z_0-9] |
| A non-word character: [^\w] |
POSIX character classes (US-ASCII only) | |
| A lower-case alphabetic character: [a-z] |
| An upper-case alphabetic character:[A-Z] |
| All ASCII:[\x00-\x7F] |
| An alphabetic character:[\p{Lower}\p{Upper}] |
| A decimal digit: [0-9] |
| An alphanumeric character:[\p{Alpha}\p{Digit}] |
| Punctuation: One of !"#$%&'()*+,-./:;=>?@[\]^_`{|}~ |
| A visible character: [\p{Alnum}\p{Punct}] |
| A printable character: [\p{Graph}\x20] |
| A space or a tab: [ \t] |
| A control character: [\x00-\x1F\x7F] |
| A hexadecimal digit: [0-9a-fA-F] |
| A whitespace character: [ \t\n\x0B\f\r] |
java.lang.Character classes (simple java character type) | |
| Equivalent to java.lang.Character.isLowerCase() |
| Equivalent to java.lang.Character.isUpperCase() |
| Equivalent to java.lang.Character.isWhitespace() |
| Equivalent to java.lang.Character.isMirrored() |
Classes for Unicode blocks and categories | |
| A character in the Greek block (simple block) |
| An uppercase letter (simple category) |
| A currency symbol |
| Any character except one in the Greek block (negation) |
| Any letter except an uppercase letter (subtraction) |
Boundary matchers | |
| The beginning of a line |
| The end of a line |
| A word boundary |
| A non-word boundary |
| The beginning of the input |
| The end of the previous match |
| The end of the input but for the final terminator, if any |
| The end of the input |
Greedy quantifiers | |
| X, once or not at all |
| X, zero or more times |
| X, one or more times |
| X, exactly n times |
| X, at least n times |
| X, at least n but not more than m times |
Reluctant quantifiers | |
| X, once or not at all |
| X, zero or more times |
| X, one or more times |
| X, exactly n times |
| X, at least n times |
| X, at least n but not more than m times |
Possessive quantifiers | |
| X, once or not at all |
| X, zero or more times |
| X, one or more times |
| X, exactly n times |
| X, at least n times |
| X, at least n but not more than m times |
Logical operators | |
| X followed by Y |
| Either X or Y |
| X, as a capturing group |
Back references | |
| Whatever the nth capturing group matched |
Quotation | |
| Nothing, but quotes the following character |
| Nothing, but quotes all characters until \E |
| Nothing, but ends quoting started by \Q |
Special constructs (non-capturing) | |
| X, as a non-capturing group |
| Nothing, but turns match flags on - off |
| X, as a non-capturing group with the given flags on - off |
| X, via zero-width positive lookahead |
| X, via zero-width negative lookahead |
| X, via zero-width positive lookbehind |
| X, via zero-width negative lookbehind |
| X, as an independent, non-capturing group |
Thanks for your feedback!