Quick start
The current version of Qodana (2025.3) provides the linters that let you analyze Java, Kotlin, Groovy, PHP, JavaScript, TypeScript, C#, Visual Basic, C, C++, Python, and Golang projects. You can also extend the default linter configuration using various features.
As an example, this section explains how you can quickly start working with Qodana using:
Prerequisites
Depending on your Qodana license, you probably need to obtain a trial license and complete the project setup stage in Qodana Cloud.
To run Qodana in the CLI and GitHub, you will be using a project token available after creating a Qodana Cloud project. To learn more about it, see the Project tokens section.
Run Qodana in JetBrains IDEs
Qodana is available in IntelliJ IDEA, PyCharm (both the Professional and Community editions), PhpStorm, WebStorm, GoLand, and Rider.
Here is a short animation showing how you can run Qodana in your IDE.
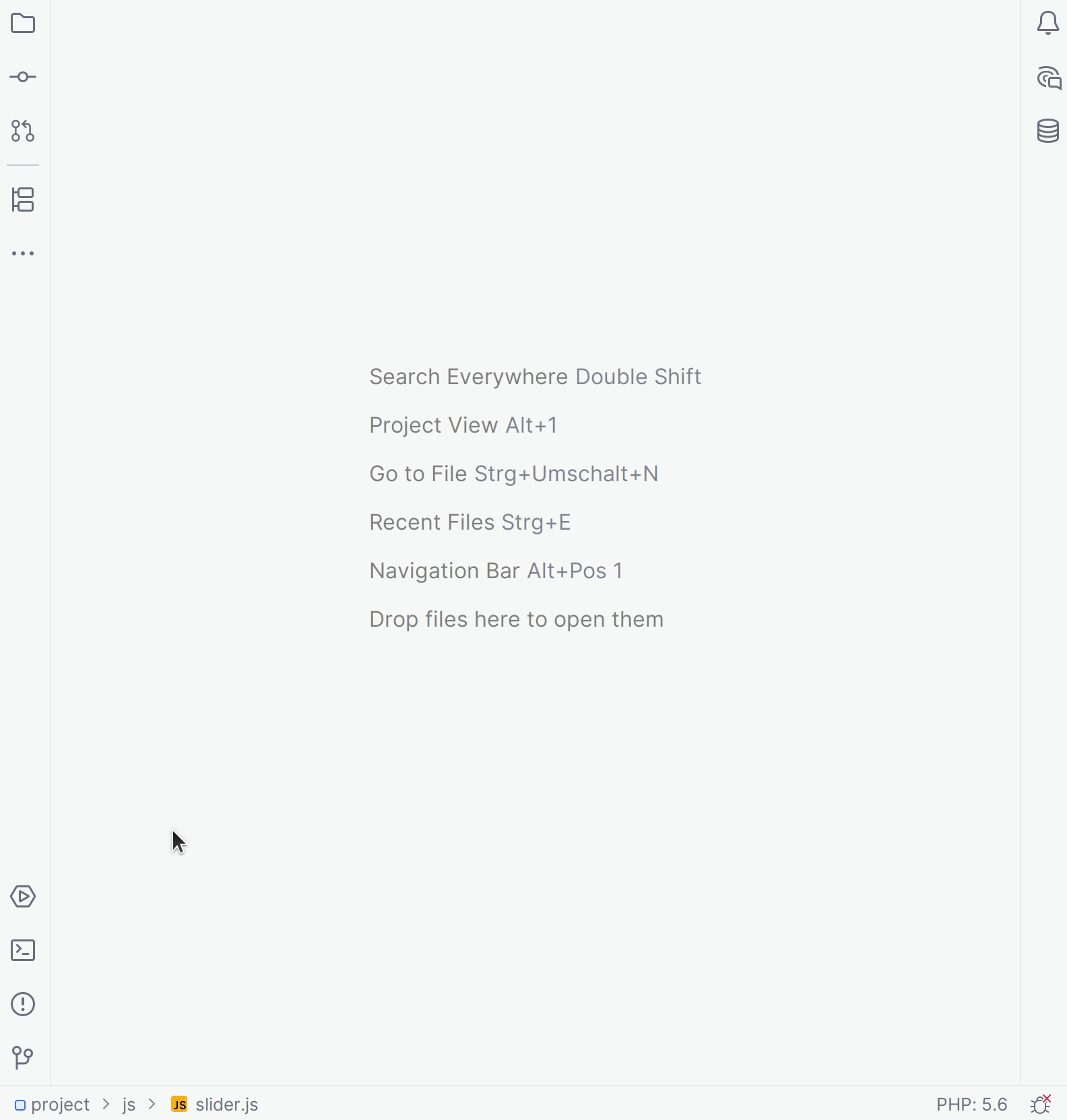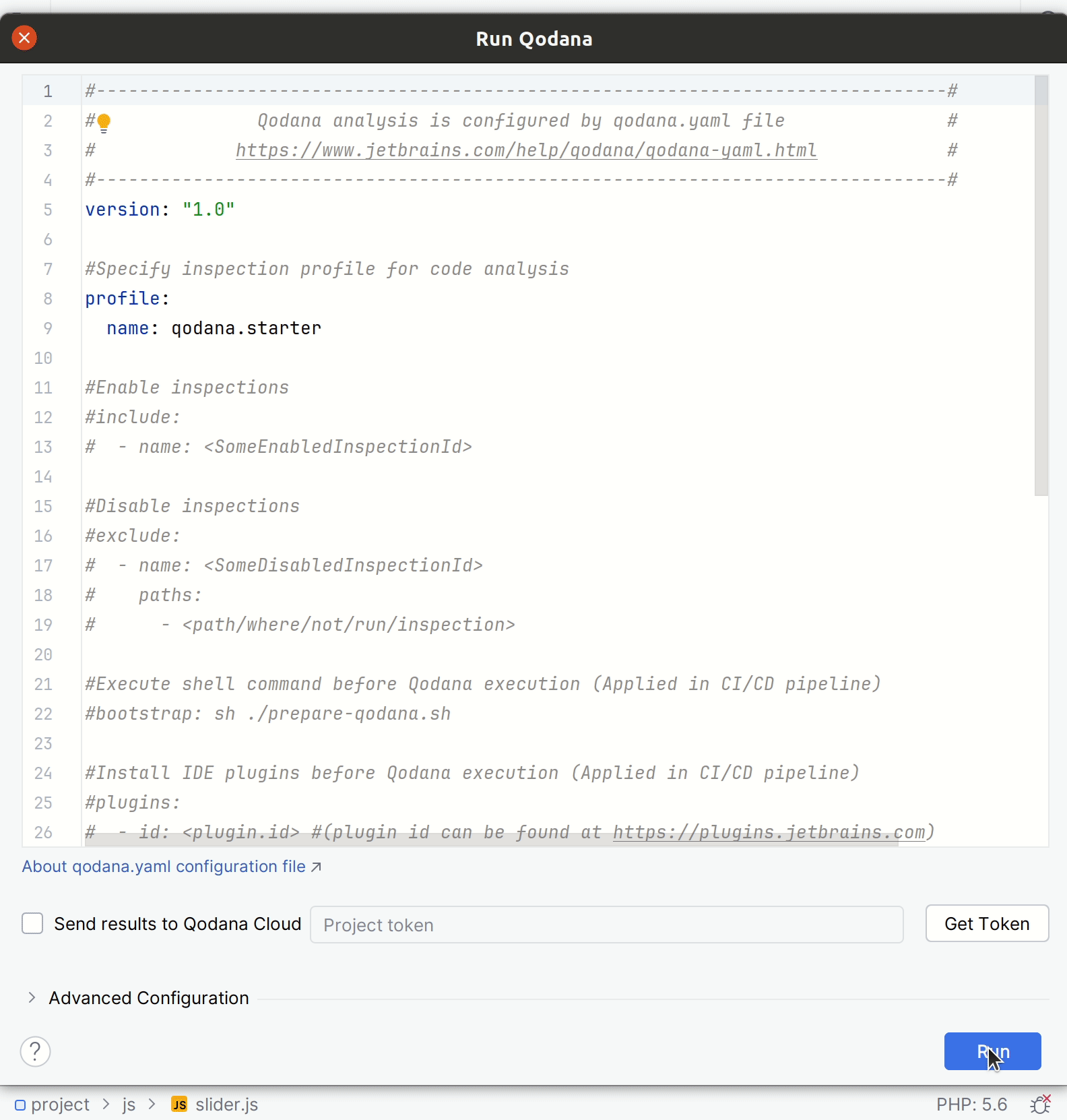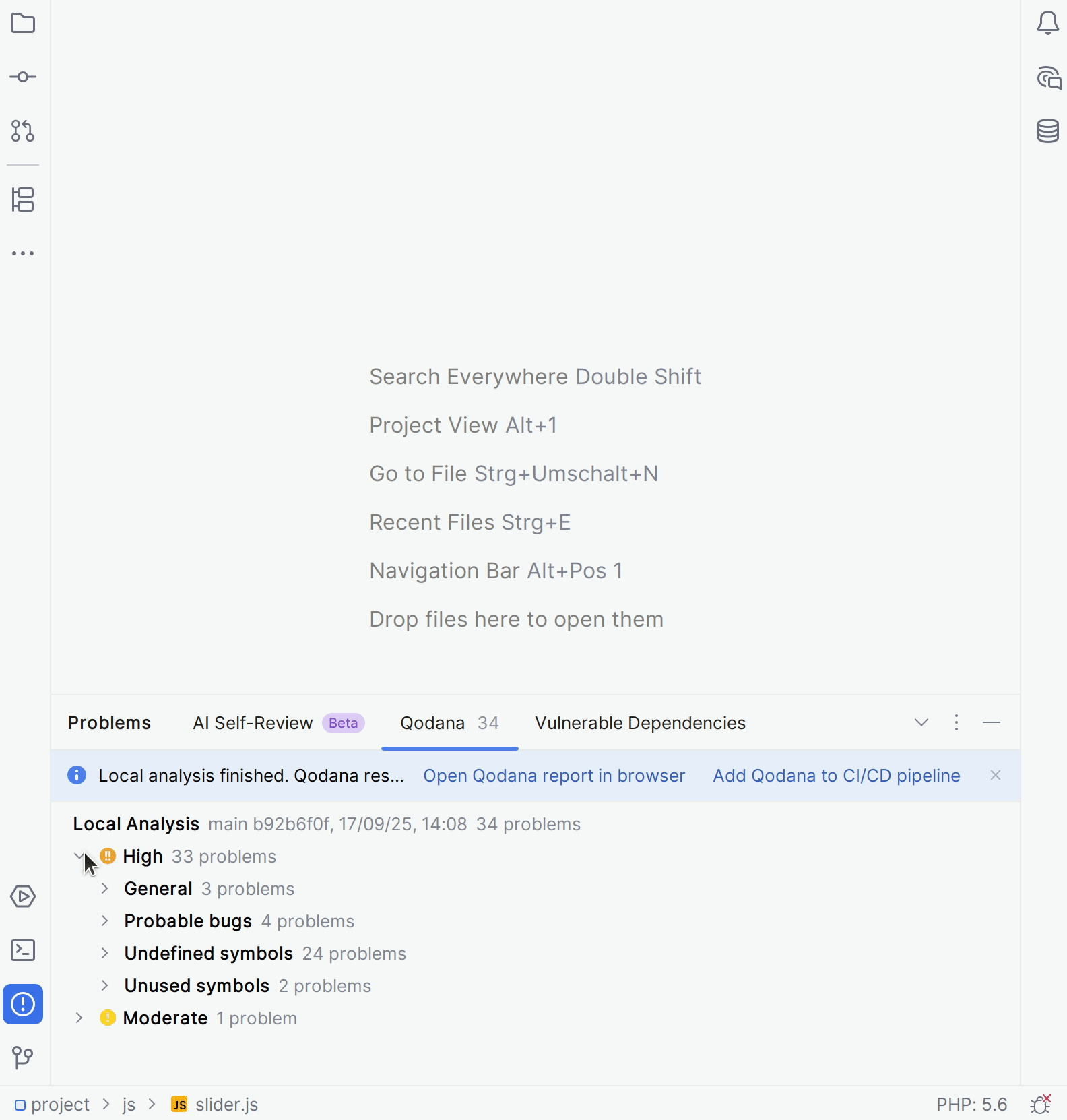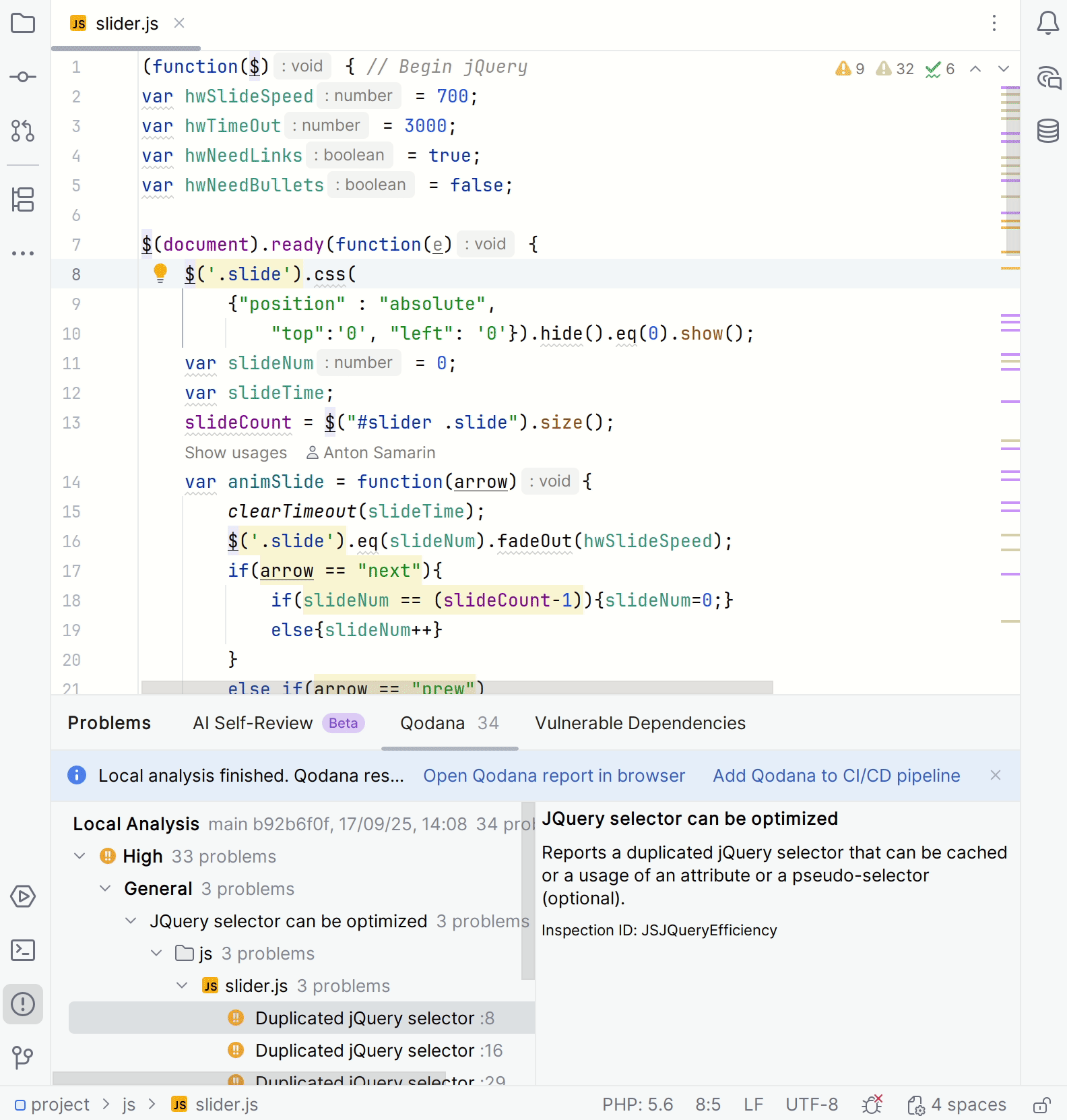
Here is the description of all steps shown in this animation:
In your IDE, navigate to the tool window.
In the tool window, click the tab.
On the tab, click the button to start Qodana.
On the tab, you can view analysis results. It also contains two links in the upper part of the tab.

Open the analysis report in your browser.

Open the configuration wizard to use Qodana in CI/CD pipelines.
To learn more about Qodana and CI/CD pipelines, see the Overview of CI integration section.
Run Qodana using CLI
Qodana provides two options for local analysis of your code. Qodana CLI is the easiest option to start. Alternatively, you can use the Docker command from the tab.
To run Qodana CLI in the default mode, you must have Docker or Podman installed and running locally. If you are using Linux, you should be able to run Docker under your current non-root user.
Install Qodana CLI on your machine using available options:
Install with Homebrew (recommended):
brew install jetbrains/utils/qodanaAlternatively, you can install Qodana CLI using our installer:
curl -fsSL https://jb.gg/qodana-cli/install | bashYou can install a
nightlyor any other version the following way:curl -fsSL https://jb.gg/qodana-cli/install | bash -s -- nightlyOn Linux, you can also install Qodana using Go:
go install github.com/JetBrains/qodana-cli@latestInstall with Windows Package Manager (recommended):
winget install -e --id JetBrains.QodanaCLIInstall with Chocolatey:
choco install qodanaInstall with Scoop:
scoop bucket add jetbrains https://github.com/JetBrains/scoop-utils scoop install qodanaIn the project root directory, declare the
QODANA_TOKENvariable containing the project token described in the prerequisites:QODANA_TOKEN=<cloud-project-token>set QODANA_TOKEN=<cloud-project-token>Run Qodana:
qodana scanqodana scan
This section assumes that you have the Docker application deployed on your machine.
Pull the image from Docker Hub (only necessary to get the latest version):
docker pull <image>Here,
imagedenotes the Docker image name of a Qodana linter from this table:Image name
Application
jetbrains/qodana-jvm2025.3
Java and Kotlin for Server Side projects, based on IntelliJ IDEA Ultimate.
jetbrains/qodana-jvm-community2025.3
Java and Kotlin for Server Side projects, based on IntelliJ IDEA Community.
jetbrains/qodana-jvm-android2025.3
Java and Kotlin for Server Side projects, based on IntelliJ IDEA with Android support.
jetbrains/qodana-php2025.3
PHP projects, based on PhpStorm.
jetbrains/qodana-python2025.3
Python projects, based on PyCharm Professional.
jetbrains/qodana-python-community2025.3
Python projects, based on PyCharm Community.
jetbrains/qodana-js2025.3
JavaScript and TypeScript projects, based on WebStorm.
jetbrains/qodana-go2025.3
Golang projects, based on Goland.
jetbrains/qodana-dotnet2025.3
.NET projects, based on Rider.
jetbrains/qodana-cdnet2025.3-eap
.NET projects, based on ReSharper.
jetbrains/qodana-clang2025.3-eap
C and C++ projects containing compilation databases.
Run this command to analyze your codebase:
docker run \ -v <source-directory>/:/data/project/ \ -e QODANA_TOKEN="<cloud-project-token>" \ jetbrains/qodana-<image>Here,
<source-directory>points to the root of your project, and theQODANA_TOKENvariable contains the project token described in the prerequisites.Navigate to your Qodana Cloud account to see analysis results.
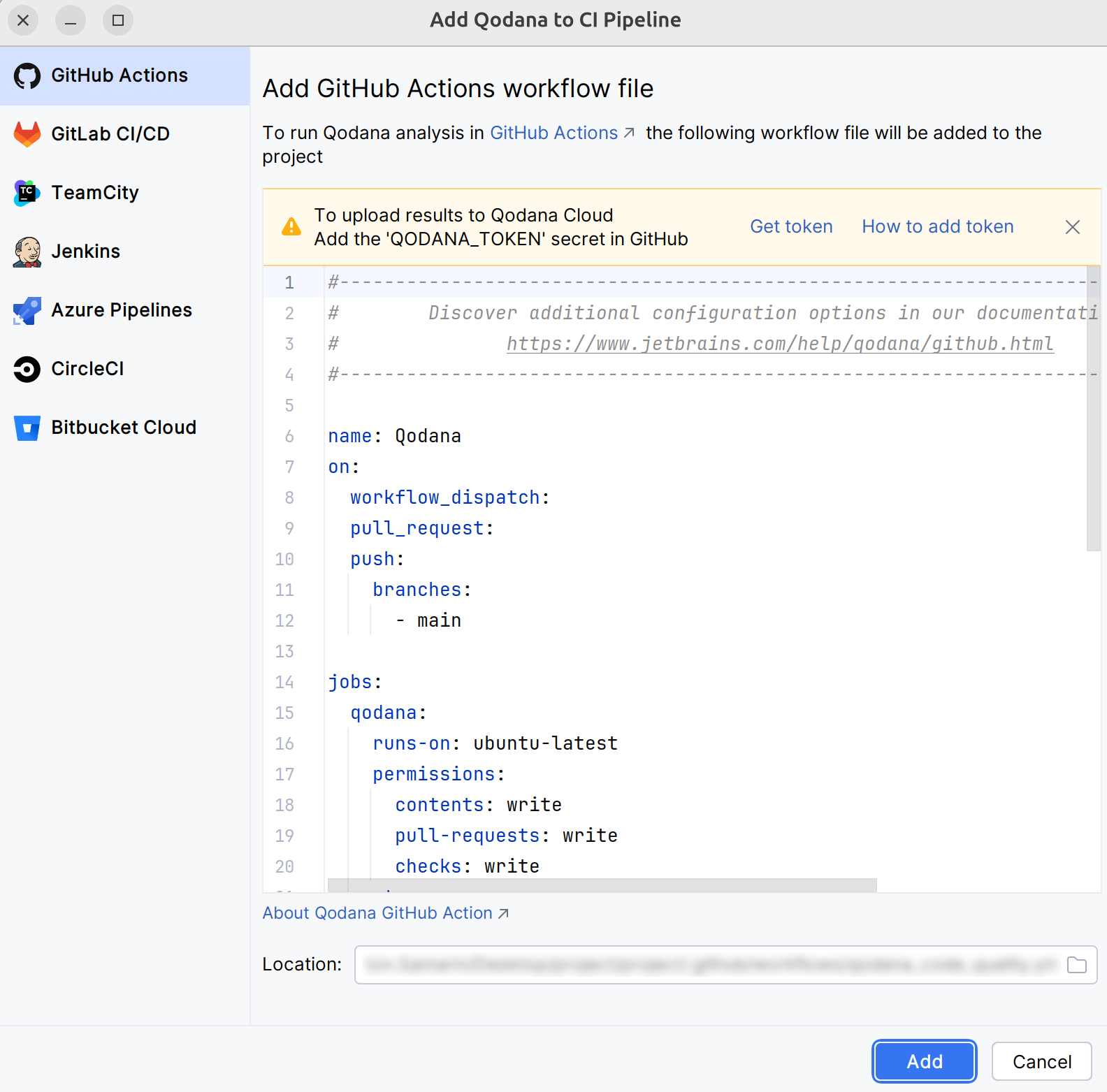
Run Qodana on GitHub
Here is the short video showing how you can configure and run Qodana in GitHub.

Assuming that you already generated a project token as described in the Prerequisites chapter, follow these steps to configure Qodana in GitHub:
On the tab of the GitHub UI, create the
QODANA_TOKENencrypted secret and save the project token as its value. If you are using a Qodana Cloud instance other thanhttps://qodana.cloud/, override it by declaring theQODANA_ENDPOINTenvironment variable.On the tab of the GitHub UI, set up a new workflow and create the
.github/workflows/code_quality.ymlfile.To analyze the
mainandmasterbranches, as well as release branches and the pull requests coming to your repository, save this workflow configuration to the.github/workflows/code_quality.ymlfile:name: Qodana on: workflow_dispatch: pull_request: push: branches: # Specify your branches here - main # The 'main' branch - master # The 'master' branch - 'releases/*' # The release branches jobs: qodana: runs-on: ubuntu-latest permissions: contents: write pull-requests: write checks: write steps: - uses: actions/checkout@v3 with: ref: ${{ github.event.pull_request.head.sha }} # to check out the actual pull request commit, not the merge commit fetch-depth: 0 # a full history is required for pull request analysis - name: 'Qodana Scan' uses: JetBrains/qodana-action@v2025.2 env: QODANA_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.QODANA_TOKEN }}