Export
You can use a variety of methods to export data and object structures from your databases. These methods include usage of various generators, data extractors, and shortcuts. Also, you can export data in TXT, CSV, JSON, XML, Markdown, Excel, and other formats. You can select a predefined data extractor or create your own.
In DataGrip, you export object structures and data separately. It means that you can export a structure of a table or a view and then export data from these objects.
The full data dump is available for PostgreSQL and MySQL with the help of mysqldump and pg_dump. The full data dump includes structures of all database objects and data of these objects in a single file. For more information, see Create a full data dump for MySQL and PostgreSQL.
Data definition language (DDL) defines the structure of a database, including rows, columns, tables, indexes, and other elements. In DataGrip, you can generate data definition structures by using shortcuts with predefined settings or by using the SQL Generator and customize the export settings.
The following video shows how you can generate SQL for existing objects.
In the Database Explorer ( View | Tool Windows | Database Explorer) , right-click a database object and select SQL Scripts | SQL Generator… CtrlAlt0G.
On the right toolbar, you can find the following controls:
: copy output to the clipboard.
: save output to a file.
: open output in a query console.

note
The DEFINER clause specifies the security context (access privileges) for the routine execution. In MySQL and MariaDB, select Skip DEFINER clause to skip this clause when you generate DDL for a procedure or a function.
In the Database Explorer ( View | Tool Windows | Database Explorer) , right-click a database object (for example, a table) and select SQL Scripts | SQL Generator CtrlAlt0G.
In the SQL Generator tool window, click the File Output Options icon (
).
From the Layout list, select a method that you want to use:
File per object by schema: generates a set of SQL files sorted in folders by schemas.
File per object by schema and database: generates a set of SQL files sorted in folders by schemas and databases.
File per object: generates a set of SQL files.
File per object with order: generates a numbered set of SQL files.

In the Database Explorer ( View | Tool Windows | Database Explorer) , right-click a database object and select SQL Scripts | Generate DDL to Query Console.
In the Database Explorer ( View | Tool Windows | Database Explorer) , right-click a database object and select SQL Scripts | Generate DDL to Clipboard.
If your database stores DDL of the object, you can retrieve DDL from the database by selecting the Request and Copy Original DDL.
DataGrip uses data extractors to export data in various formats to a file or the clipboard. Each time you export or copy data, the copied data format is defined by the selected data extractor.
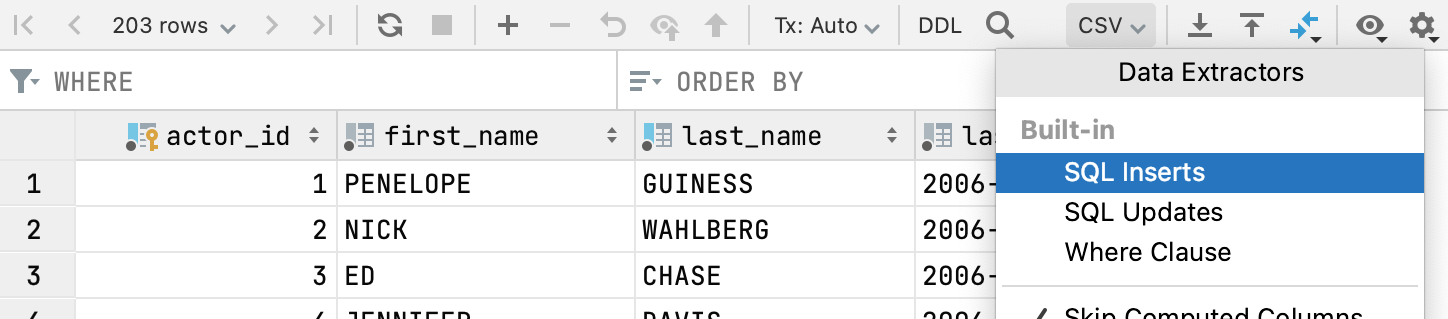
You can use a built-in data extractor, configure a custom extractor that is based on CSV or DSV format, and create a custom data extractor using a provided API.
The last selected extractor becomes the default one for newly opened editor tabs. For MongoDB, the default extractor is always JSON.
For more information about data extractors, refer to the corresponding page.
In the Database Explorer ( View | Tool Windows | Database Explorer) , right-click a database object and navigate to Import/Export | Export Data to File.
To export data from multiple database objects to files, select and right-click the objects, then navigate to Import/Export | Export Data to Files.
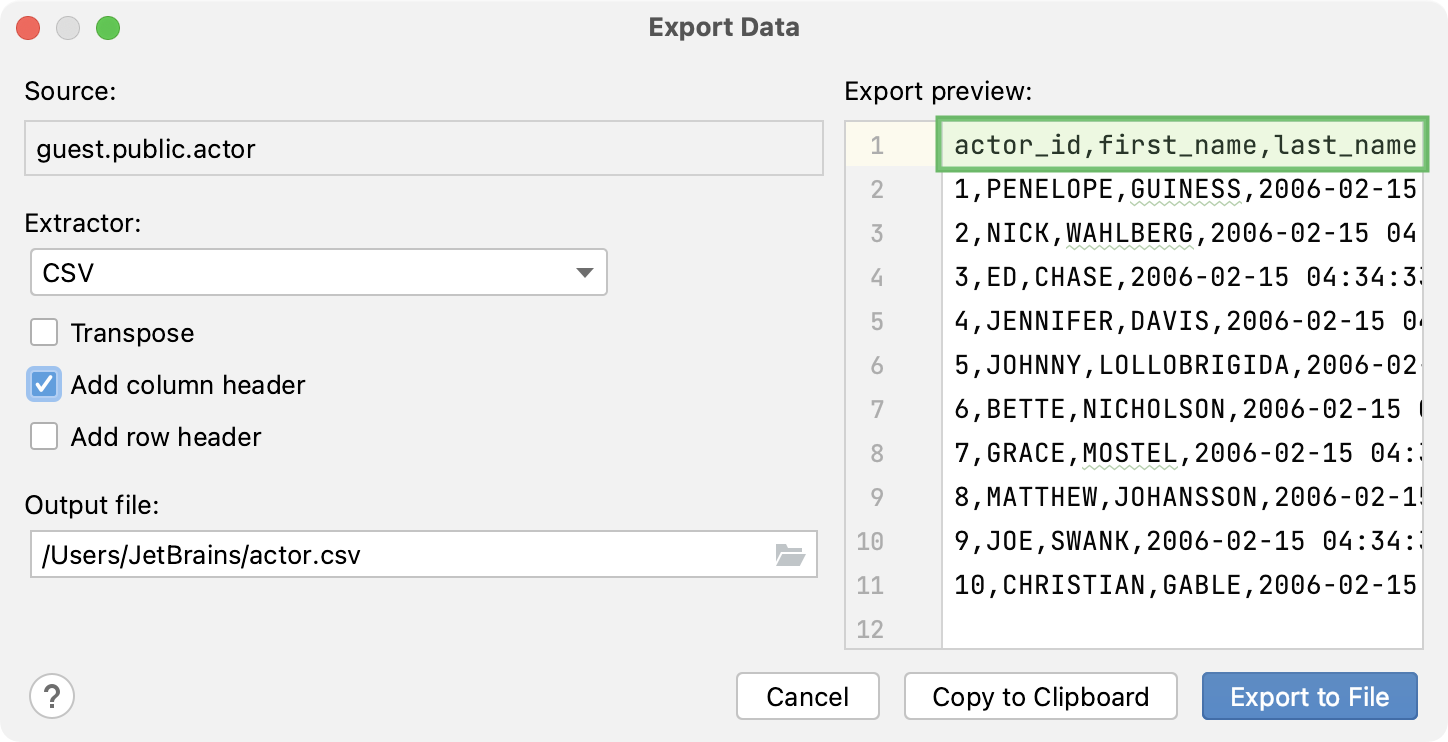
In the Export Data dialog, customize the following settings:
Extractor: select the export format (for example, Excel (xlsx)).
Transpose: select to export data in the transposed view. In this view, the rows and columns are interchanged.
Add column header: adds a row with column names at the beginning of the CSV list.
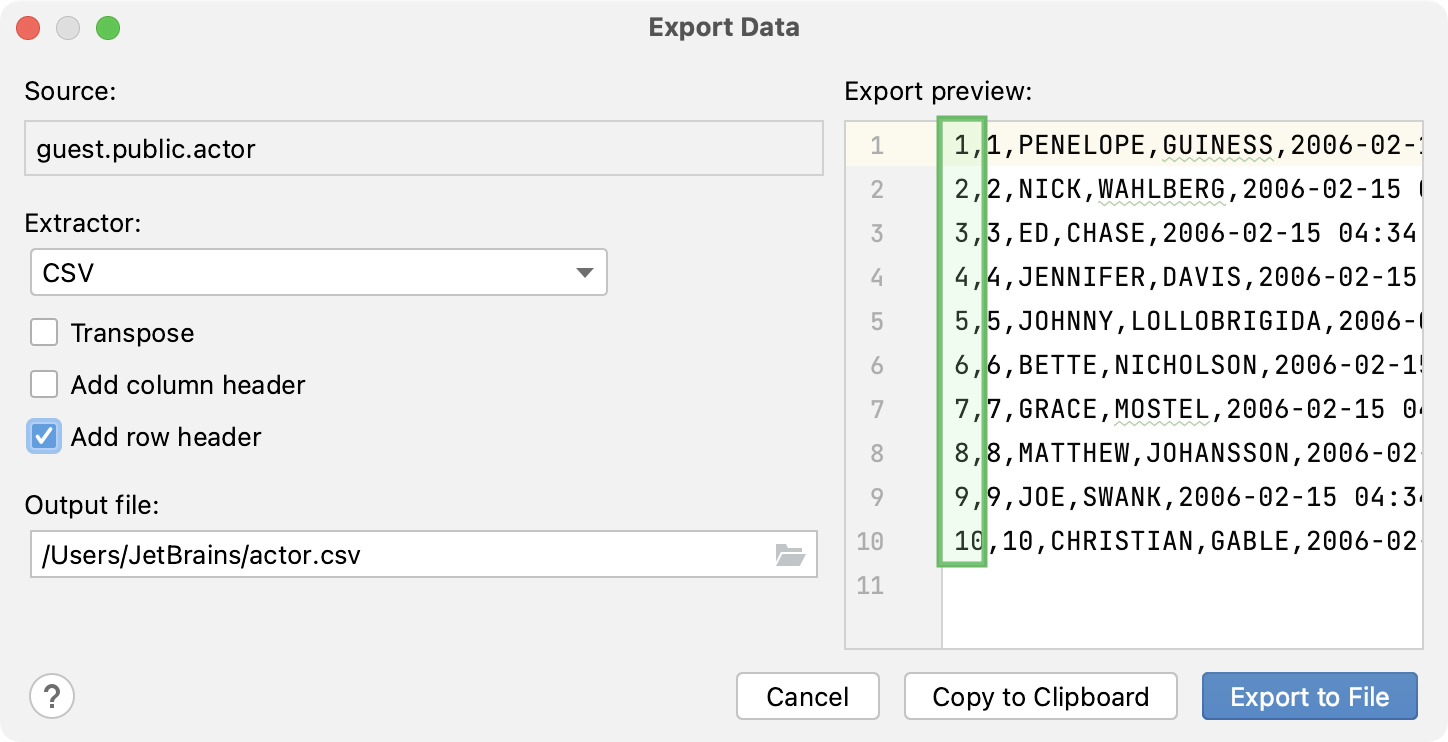
Add row header: adds a column with enumeration of rows.
Output file: select a file that will store the data.
To copy the generated script to the clipboard, click Copy to Clipboard. To save the script to a file, click Export to File.
Tables, views, and virtual views open in the data editor. Query result sets appear in the result tabs of Services tool window and in the In-Editor Results of query console.
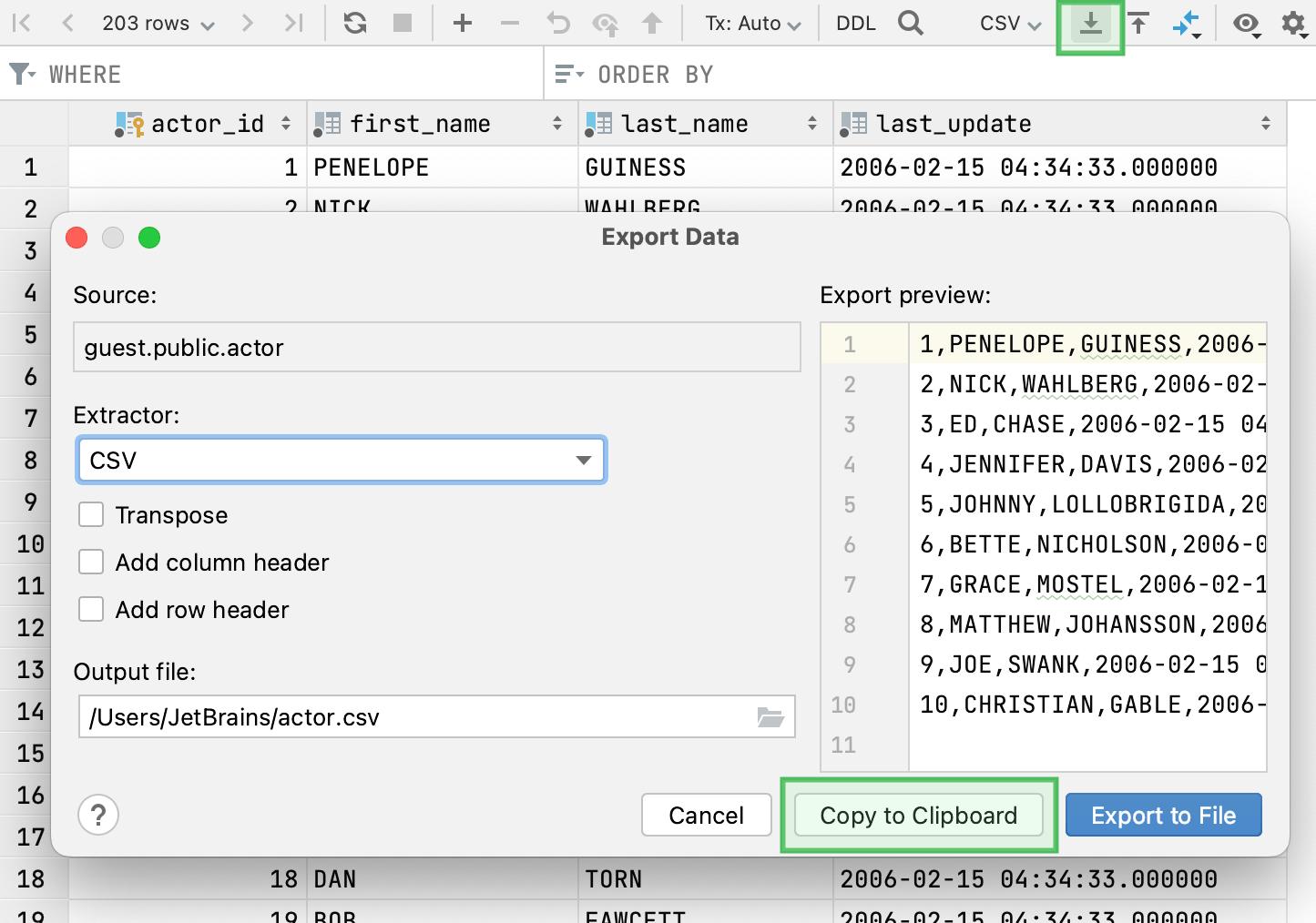
To export data to a file, open a table or a result set, click the Export Data icon (
). Configure the export settings and click Export to File.

To export the whole result or the whole table to the clipboard, open a table or a result set, right-click a cell and select Export Table to Clipboard.
In contrast to the Export Table to Clipboard action, the Copy action Ctrl0C only copies the selection of rows on the current page. To copy all the rows on the current page, click a cell, press Ctrl0A and then Ctrl0C. To configure a number of rows on a page, see Set a number of rows in the result set.
To copy the selection of rows from the result set or the data editor, press Ctrl0C.
To copy the whole result or the whole table to the clipboard, do one of the following:
Click a cell, press Ctrl0A and then Ctrl0C.
Click the Select All button.

On the data editor toolbar:
Click the Export Data icon (
).
Select the export format from the Extractor list and configure the export settings.
Click Copy To Clipboard.
To export the whole result or the whole table to the clipboard, open a table or a result set, right-click a cell and select Export Table to Clipboard.
To configure a number of rows on a page, see Set a number of rows in the result set.
Right-click the collection that you want to export and select Export Data to File.
In the Export Data dialog, click the Extractor list and select JSON.
The output of this operation is MongoDB Extended JSON. Read about MongoDB Extended JSON in MongoDB Extended JSON (v2) at docs.mongodb.com.

You can create backups for database objects (for example a schema, a table, or a view) by running mysqldump for MySQL or pg_dump for PostgreSQL. mysqldump and pg_dump are native MySQL and PostgreSQL tools. They are not integrated into DataGrip. You can read about them at dev.mysql.com and postgresql.org.
In the Database Explorer ( View | Tool Windows | Database Explorer) , right-click a database object and navigate to:
Export with "mysqldump": for MySQL data sources. The mysqldump tool is located in the root/bin directory of the MySQL installation directory.
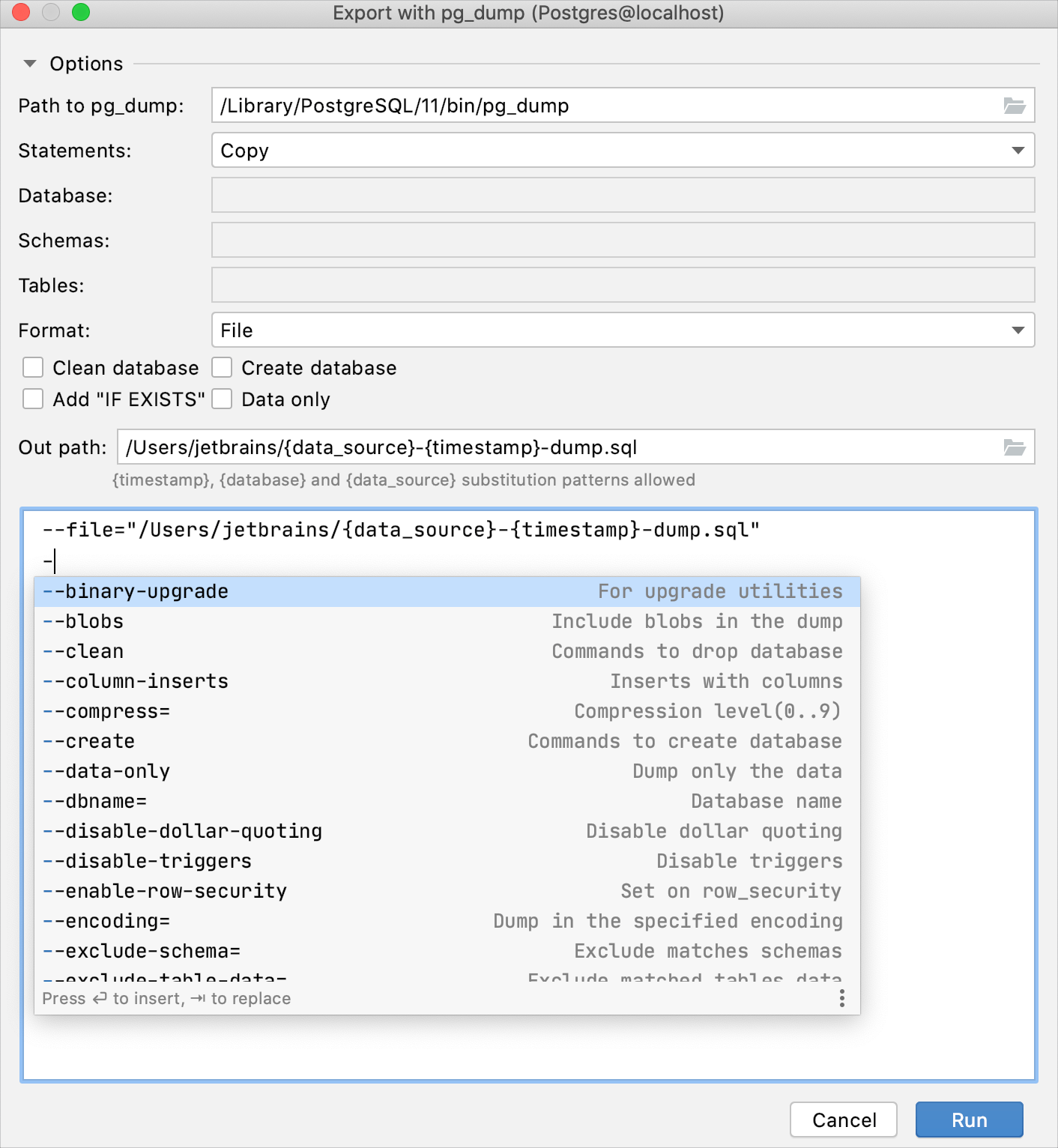
Export with "pg_dump": for PostgreSQL data sources. pg_dump, pg_dump_all, pg_restore tools are all located in the bin folder of the PostgreSQL.
note
To use mysqldump and pg_dump in DataGrip, you must install DataGrip on the same workstation.
In the Export with <dump_tool> dialog, specify the path to the dump tool executable in the Path to <dump_tool> field.
note
Specify the full explicit path to the dump tool executable.
(Optional) Edit the command-line options in the lower part of the dialog.
Click Run.
Thanks for your feedback!