Commit and push changes to Git repository
After you've added new files to the local Git repository, or modified files that are already under Git version control and you are happy with their current state, you can share the results of your work. This involves committing them locally to record the snapshot of your repository to the project history, and then pushing them to the remote repository so that they become available to others.
Generating a GitHub token in Fleet
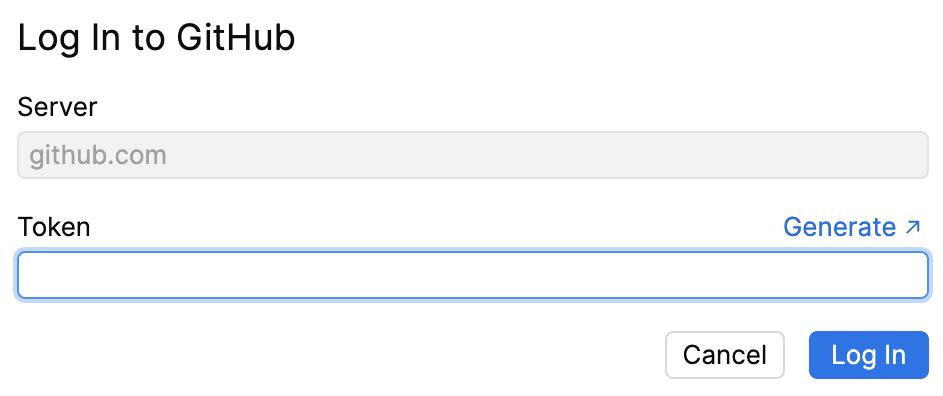
When a user attempts to perform an operation with a GitHub repository, such as push, pull, or fetch. The token input field appears, the user needs to click the provided link to generate a GitHub token. Fleet pre-fills suggested scopes for the token.
Work with commits
Commit changes locally
Open the Git tool or press ⌃ G,⌃ C.
If you want to group the list of changed files by directory, click the Settings icon and select .
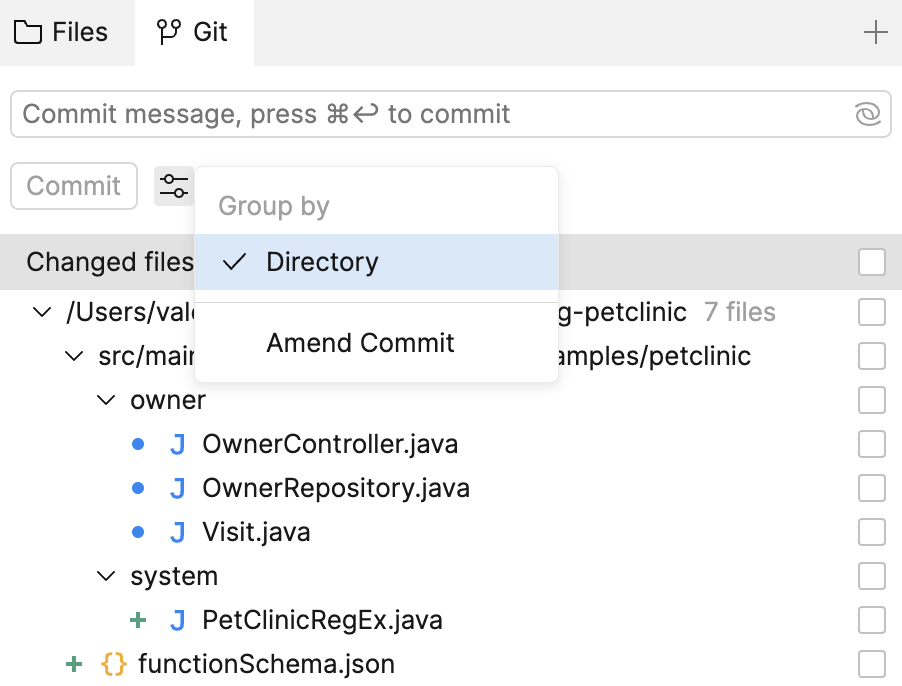
In the Changed files list, select the files you want to commit.
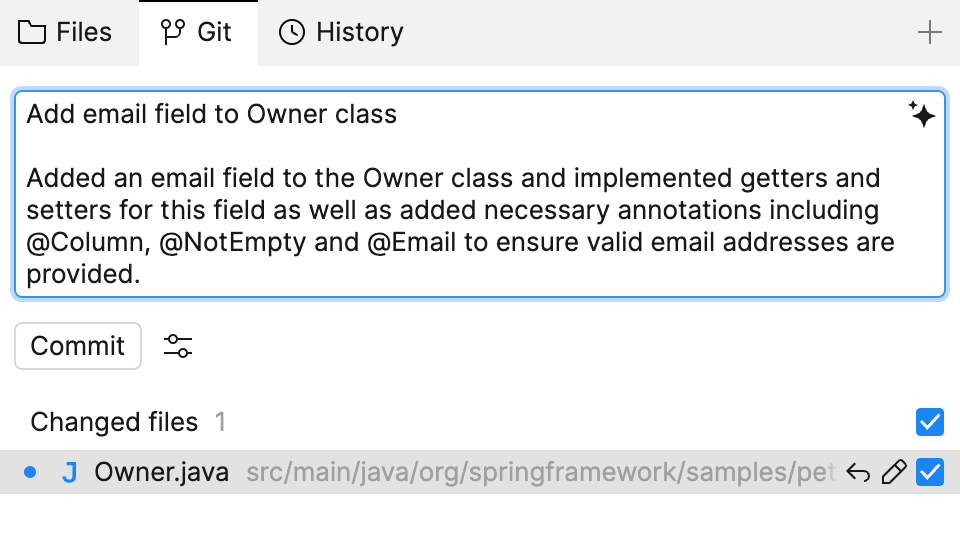
Enter the commit message and click Commit.
You can use AI Assistant to help you generate commit messages.
Generate commit message
To generate a commit message for pending changes, select the changes to stage, then click the AI icon in the commit message field.
AI Assistant can also help you understand the changes within a commit.
Explain commit
To explain the changes within a commit, right-click it in the Git History tool, then select Explain commit.

Amend commits
If you want to modify the latest commit, use the Amend Commit option.
In the Git tool, select the modified files containing the changes you want to add to the previous commit.
Click the Settings icon and select the Amend Commit option.
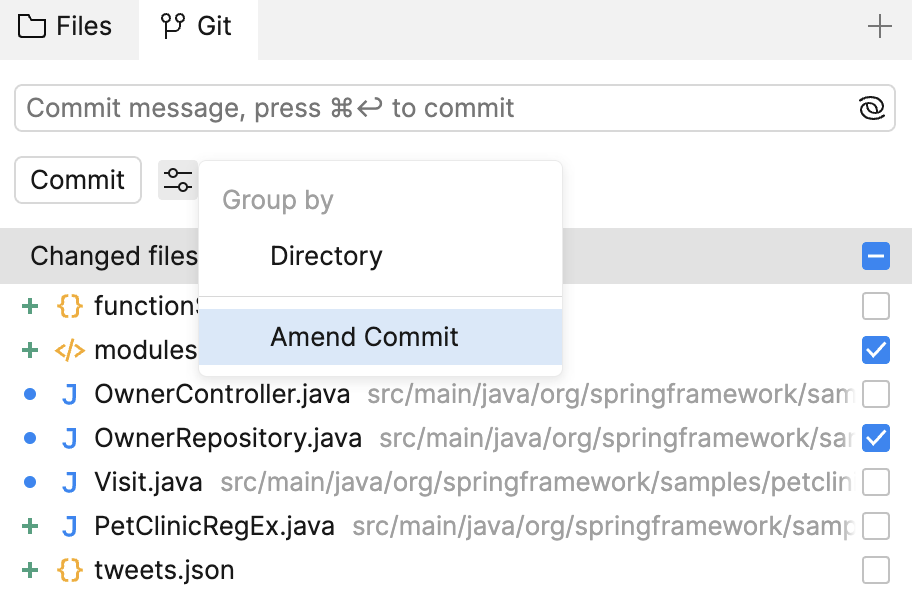
Modify the pre-filled commit message of the previous commit if necessary.
Click the Amend commit button.
Push changes to a remote repository
Before pushing your changes, sync with the remote and make sure your local copy of the repository is up to date to avoid conflicts.
Push your changes
From the main menu, choose Git | Push or press ⌃ G,⌃ P.
In the Git Push dialog that opens, click Push.
To push the changes to the remote branch, you now need to log in to your GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket account.
For GitLab and Bitbucket, enter your credentials and click Log in.
For GitHub, enter your personal access token and click Log in. If you do not have a token, follow the Generate link to generate a new personal access token in your GitHub settings.
After the successful login JetBrains Fleet pushes the local changes to the remote branch.