Prepare for testing
IntelliJ IDEA works with multiple Java testing frameworks out of the box, for example, JUnit, Spock, or TestNG.
In the IDE, you can create a test class directly from the source code together with the necessary test methods. You can switch between test classes and source code with a shortcut, run multiple tests, view statistics for each test, and export test results to a file.
IntelliJ IDEA also features code coverage that allows you to analyze your code and understand which areas of your code are covered by tests and which areas require more testing.
For more information about testing your code in other languages, refer to:
Testing PHP (PhpStorm documentation)
IntelliJ IDEA allows you to add missing libraries as you code: once the IDE detects that you're using some code from the library that is not yet added to your project, it will prompt you to download and install it.
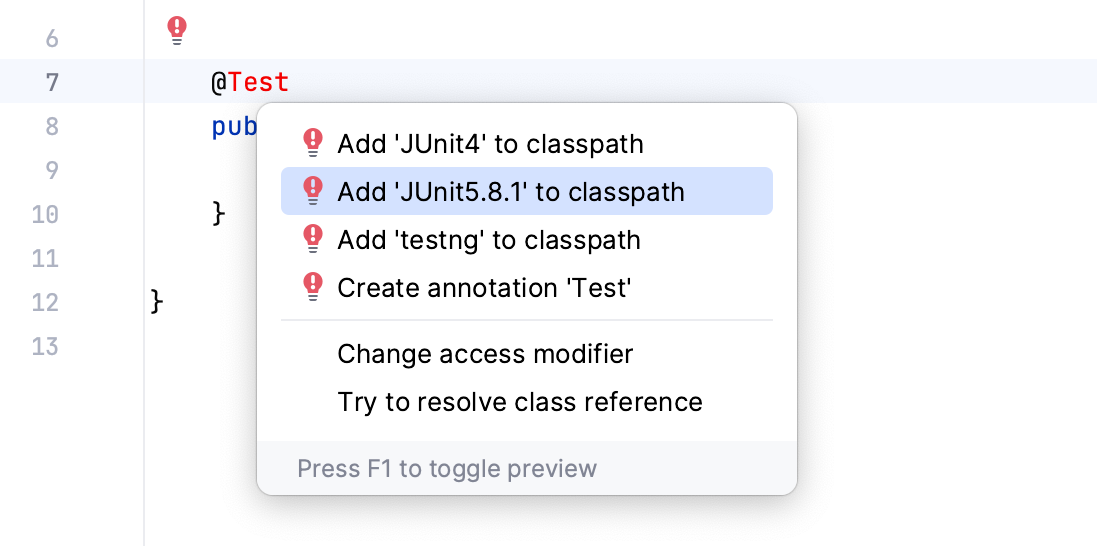
You can also add libraries to your project manually. For example, this can be helpful if you need a specific library version or distribution.
Follow these steps to add a library if you're building your project with the native IntelliJ IDEA builder:
In the main menu, go to File | Project Structure (CtrlAltShift0S).
Under Project Settings, select Libraries and click
| From Maven.
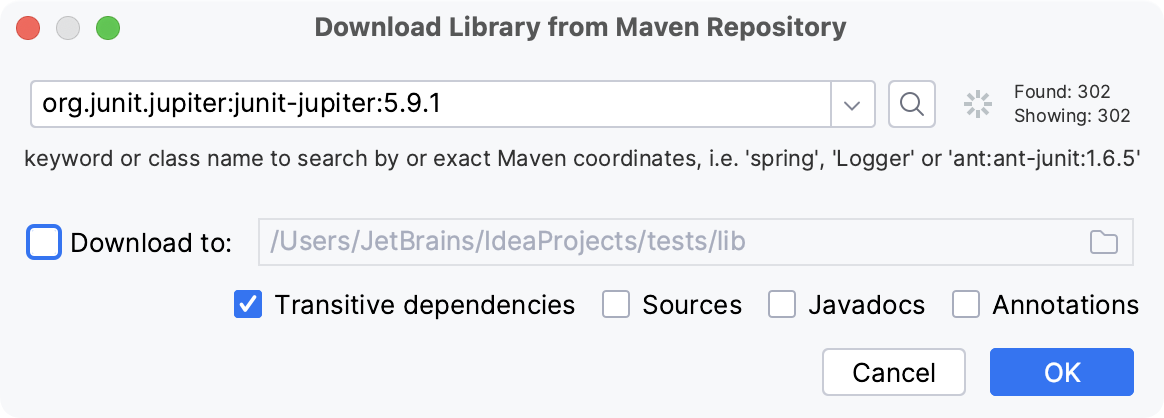
In the dialog that opens, specify the necessary library artifact, for example:
org.junit.jupiter:junit-jupiter:5.9.1.Apply the changes and close the dialog.
IntelliJ IDEA allows you to add missing libraries as you code: once the IDE detects that you're using some code from the library that is not added to your project yet, it will prompt you to download it. In this case, the IDE automatically adds the necessary dependencies to your pom.xml.

You can also add libraries to your project manually. For example, this can be helpful if you need a specific library version or distribution.
Follow these steps if you're using Maven in your project:
In your pom.xml, press AltInsert and select Dependency.
In the Maven Artifact Search tool window, type the name of the required dependency, for example:
org.junit.jupiter:junit-jupiter. In the list of results, select the one you need and click Add.
When the dependency is added to pom.xml, press CtrlShift0O or click
in the Maven tool window to import the changes.
For more information about working with Maven, refer to Maven dependencies.
In Gradle projects, add the necessary dependencies to your build file manually.
In your build.gradle, press AltInsert and select Add Maven artifact dependency.
In the Maven Artifact Search tool window, type the name of the required dependency, for example:
org.junit.jupiter:junit-jupiter. In the list of results, select the one you need and click Add.
When the dependency is added to build.gradle, press CtrlShift0O or click
in the Gradle tool window to import the changes.
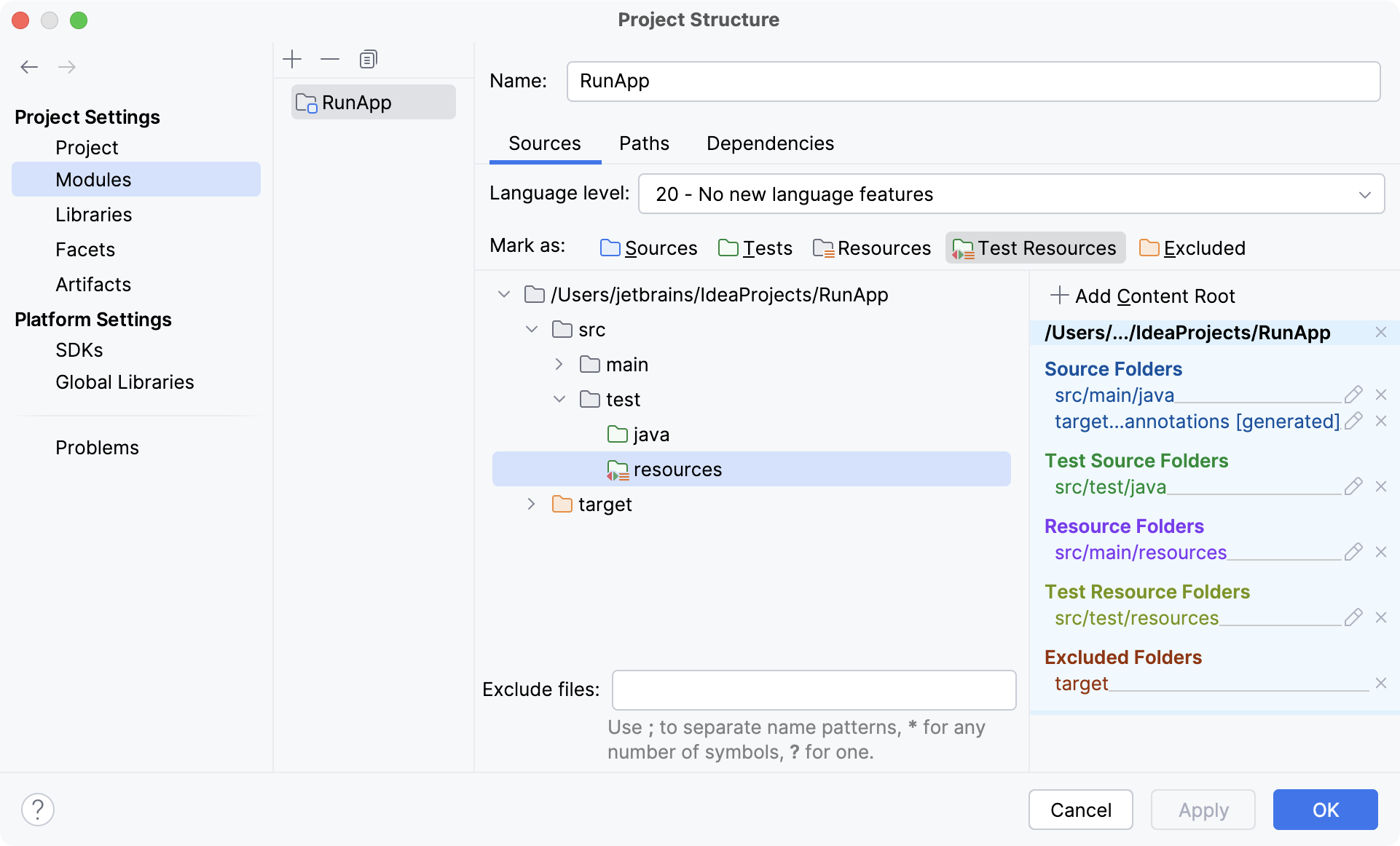
Before you start creating tests, make sure that the Test Sources Root is configured for your project. The Test Sources Root is a folder that stores your test code. In the Project tool window, this folder is marked with the Test Root icon .
The IDE processes the code from different sources differently. For example, compilation results for sources and test sources are normally placed into different folders. That is why, if the test sources root is missing, you need to create one. Otherwise, your code might be processed incorrectly.
Follow these steps if you're building your project with the native IntelliJ IDEA builder:
In the Project tool window (Alt01), create a new directory in which you will store your test code.
Right-click the new directory and select Mark Directory As | Test Sources Root.
The tests folder should be marked with the
icon.

Maven uses a standard directory layout for applications. Generally, it's recommended that you conform to this layout in your projects. For example, when you create a test folder in IntelliJ IDEA for a Maven project, the IDE suggests setting the standard name and location for such a folder. In this case, the IDE is also already aware that this test folder is your Test Sources Root.
However, you can override the standard directory layout by modifying the build file.
In the Project tool window (Alt01), create a new directory in which you will store your test code.
In your pom.xml, change the
testSourceDirectoryelement.Replace src
/new-test with the path to the new folder that you want to use as a test root./test <build> <testSourceDirectory>src/new-test/test</testSourceDirectory> </build>Press CtrlShift0O or click
in the Maven tool window to import the changes.
The new test root should be marked with the icon in the Project tool window.
Just like Maven, Gradle also has a strict project directory layout. When you create a test folder in IntelliJ IDEA for a Gradle project, the IDE suggests setting the standard name and location for such a folder. In this case, the IDE is also already aware that this test folder is your Test Sources Root.
However, you can override the standard directory layout by modifying the build file.
In the Project tool window (Alt01), create a new directory in which you will store your test code.
Open your build.gradle and add the following code.
Replace src
/new-test with the path to the new folder that you want to use as a test root./test sourceSets { test { java { srcDirs = ['src/new-test/test'] } } }Press CtrlShift0O or click
in the Gradle tool window to import the changes.
In the Project tool window (Alt01), create a new directory in which you will store your test code.
Open your build.gradle and add the following code.
Replace src
/new-test with the path to the new folder that you want to use as a test root./test sourceSets { test { java { srcDir 'src/new-test/test' } } }Press CtrlShift0O or click
in the Gradle tool window to import the changes.
The new test root should be marked with the icon in the Project tool window.
For more information about different types of folders, refer to Folder categories.
Test Resources Root is a folder that stores files associated with your test sources. In the Project tool window, this folder is located in the test root and is marked with .
For Maven and Gradle projects, the test resources folder is usually created automatically. If you're building your project with the native IntelliJ IDEA builder, you might need to create the resource root manually.
In the main menu, go to File | Project Structure (CtrlAltShift0S).
Under Project Settings, click Modules and then open the Sources tab on the right.
Right-click the test folder and select New Folder. Name the folder
resources.Right-click the new folder and select Test Resources. The folder will be marked with the
icon.
Apply the changes and close the dialog.