GitLab CI/CD
GitLab CI/CD is a tool for software development that uses various CI/CD methodologies. This section explains how you can run the Qodana Scan GitLab Pipeline component.
Before you start
Qodana Cloud
All configuration examples in this section use a project token generated by Qodana Cloud. This token is required for the paid Qodana linters and optional for use with the Community linters. You can see these sections to learn how to generate the project token in the Qodana Cloud UI:
The project setup section explains how to generate a project token when first working with Qodana Cloud.
The Manage a project section explains how to create a project token within an existing Qodana Cloud organization.
Once you obtain the project token, you can use the QODANA_TOKEN variable for identifying in a pipeline or workflow.
If you are using a Qodana Cloud instance other than https://qodana.cloud/, override it by setting the QODANA_ENDPOINT environment variable.
Prepare your project
Make sure that your project repository is accessible to GitLab CI/CD.
In GitLab CI/CD UI, create the following environment variables:
Variable name | Description |
|---|---|
| Generated project token. Save it in the GitLab CI/CD UI as described on the GitLab CI/CD website. |
| A personal access token or a project access token required for Quick-Fixes and summary reports as comments in merge requests. The holder of a personal access token will be shown as an author for all Qodana actions, so it is advised to use a project access token. For Quick-Fixes, enable the |
In the root directory of your project, save the .gitlab-ci.yml file. This file will contain a pipeline configuration that will be used by GitLab CI/CD.
Basic configuration
For the cloud-based version of GitLab CI/CD, in the .gitlab-ci.yml file save the following configuration to include the Qodana Scan GitLab Pipeline component:
This configuration already enables caches, Code Quality report generation, merge request analysis, and comments to merge requests. You can override these settings using descriptions from the sections below and the Configuration chapter. The --image argument specifies a Qodana image that you would like to employ.
The included component creates the qodana job that can be configured as any other job in GitLab CI/CD. You can view the predefined configuration of this job using our template.
For example, this code snippet lets you change the image used for running the qodana job, define before_script, change job execution rules, and add an environmental variable.
For the on-premise version of GitLab CI/CD, in the .gitlab-ci.yml file save the following configuration:
In this snippet, qodana-gitlab-ci is the GitLab CI/CD component described on the GitLab CI/CD website.
Configure cache
By default, caching is enabled in Qodana with the following keys:
If you wish to override the default cache settings, use this configuration:
Override an operating system
By default, Qodana is configured for Linux. You can override an operating system using the os keyword. For example, you can use the following configuration for Microsoft Windows:
Specific branches
By default, Qodana is configured for analyzing the master and main branches, release branches and merge requests meaning that you do not have to provide any additional configurations and use the basic configuration.
If you wish to override this behavior, you can modify the following configuration:
The rules block of this configuration tells Qodana what branches to inspect.
Quick-Fixes
Choose the Quick-Fix strategy using either of two configuration methods:
# Possible values: apply | cleanup fixesStrategy: apply# Possible values: --apply-fixes | --cleanup args: --apply-fixesDepending on your needs, in the pipeline configuration define the
push-fixesproperty:Save this configuration to create a new branch with fixes and a merge request to the original branch:
push-fixes: merge-requestSave this configuration to push fixes to the original branch:
push-fixes: branch
Here is an example configuration that uses the inputs block for configuring the pipeline:
Expose Qodana reports
To make a report available in any given merge request without using Qodana Cloud, you can use the upload-result keyword and specify the artifact name using the artifact-name keyword, for example:
Assuming that you have configured your pipeline similarly, this is what it may look like:
Qodana report affiliated with a pipeline in a merge request
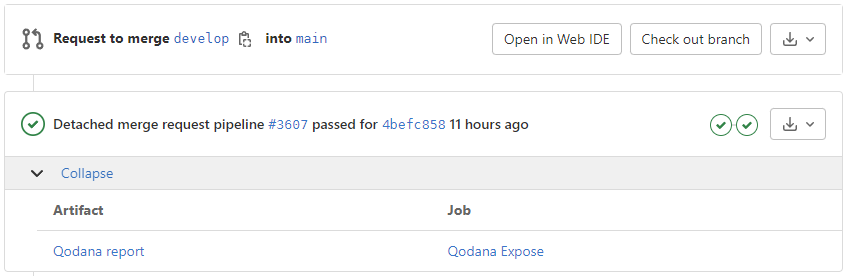
Available actions for a given exposed Qodana artifact
Quality gate and baseline
You can employ the --fail-threshold <number> and --baseline <path/to/qodana.sarif.json> lines in the inputs:args block to run the quality gate and baseline features.
Code Quality reports
Starting from version 2024.1 of Qodana, you can use the merge request UI of GitLab CI/CD to view specific lines of code that contain problems along with their description and recommendations for improvement.
To implement this feature, Qodana generates JSON-formatted analysis reports supported by Code Quality and contained in the gl-code-quality-report.json file.
By default, this feature is configured to true, so you do not need to make any additional settings. If necessary, you can override a path to reports using the codequality option:
Qodana logs
Use the following configuration to get log data from Qodana on GitLab CI/CD:
This configuration uses the .qodana/results directory for generating logs and then exposes this directory as an artifact.
To upload logs from a Qodana job that fails with a timeout, add the RUNNER_SCRIPT_TIMEOUT variable with a value less than a pipeline timeout:
The details are available on the GitLab CI/CD website.
Configuration
This table contains the list of options that can be configured using the inputs block:
Name | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
| CI stage for Qodana execution |
|
| A Qodana job name. Could be used to customize the order of running several Qodana jobs within the same pipeline |
|
| Additional Qodana CLI | - |
| Directory to store the analysis results relative to the project root. Optional. |
|
| Upload Qodana results (SARIF, other artifacts, logs) as an artifact to the job. Optional. |
|
| Specify Qodana results artifact name, used for result uploading. Optional. |
|
| Directory to store Qodana cache relative to the project root. Optional. |
|
| Utilize GitHub caches for Qodana runs. Optional. |
|
| Use Code Quality report produced by Qodana |
|
| Analyze ONLY changed files in a merge request. Optional. |
|
| Post a comment with a Qodana results summary to a merge request. Optional. |
|
| Push Qodana fixes to the repository, can be |
|
| Commit message used when Quick-Fixes are applied |
|
| Operating system used for running pipelines, required for pre-configuration. Could accept the |
|