Code inspections
ReSharper provides over 2500 code inspections in all supported languages. These inspections are applied to detect and highlight code issues in design time in all opened files , and/or to find all code issues in specific scope, which can be as large as the entire solution .
To find out what kind of code inspections ReSharper provides, check out the full list of ReSharper code inspections in different languages.
tip
The easiest way to deal with code issues highlighted in the editor is to place the caret at the highlighted code item and press or click the action indicator that appears to the left of the code issue . The action list will pop up where ReSharper suggests one or more quick-fixes for most issues.
Code inspections can be divided into the following groups:
ReSharper's own code inspections that include:
Inspections with the fixed severity level 'Error'. These inspections detect compiler errors and there is no way to disable or configure them.
Inspections with configurable severity levels, which detect the rest of code issues (for example, compiler warnings, runtime and logical errors, code smells, redundancies, improvement suggestions, and so on). You can find these configurable inspections on the Code Inspection | Inspection Severity page of ReSharper options Alt+R, O. These inspections can be configured in several ways — you can suppress the detected issues with comments and attributes, disable them or change their severity level in settings or .editorconfig files.
Custom code inspections defined as structural search and replace patterns, which also have configurable severity levels.
tip
You can get more inspections for specific purposes with ReSharper extensions.
Each ReSharper code inspection as well as structural search and replace pattern has one of the following severity levels:
tip
You can find default severity levels and other properties for each configurable inspection in the Code inspection index — just choose a language page and then use the browser search to find the details of the desired inspection.
Code inspections with this severity level are aimed at code issues that either prevent your code from compiling or result in runtime errors. Most of these inspections are not configurable, that is you cannot disable them or change their severity level.
In design-time inspection, ReSharper displays unresolved symbols in red:
![]()
and highlights erroneous statements or part of them with a red curly underline:

If there is at least one error in the current file, the status indicator displays the Error ![]() icon, and red markers are shown for each error on the marker bar.
icon, and red markers are shown for each error on the marker bar.
Code issues that are found with inspections having the 'Error' severity level, appear in the Errors/Warnings in Solution window if the solution-wide analysis is enabled.
This severity level corresponds to compiler warnings and to other issues that do not prevent your code from compiling but may nevertheless represent serious coding inefficiencies. For example, ReSharper informs you about redundant type casts or namespace import directives, incorrect format strings, declared but never used local variables or private fields, unused private methods, and so on.
In design-time inspection, ReSharper displays redundant symbols with greyed text:

and highlights statements or part of them with a blue curly underline:

If there is at least one warning in the current file, the status indicator displays the Warning ![]() icon, and yellow markers are shown for each warning on the marker bar.
icon, and yellow markers are shown for each warning on the marker bar.
Warnings also appear in the Errors/Warnings in Solution window if the solution-wide analysis with warnings is enabled
Code issues with this severity level provide insights into code structure, drawing your attention to things that aren't necessarily bad or wrong, but probably useful to know.
In design-time inspection, ReSharper highlights suggestions with a green curly underline:
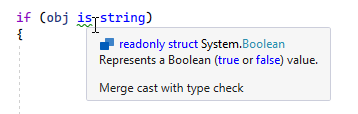
and adds green markers for each warning on the marker bar.
This is the lowest severity level. Code issues with this severity bring your attention to a particular code detail and/or recommends a way of improvement.
In design-time inspection, ReSharper highlights hints by adding a dashed green underline to the initial two letters of the corresponding symbol:

Unlike errors, warnings and suggestions, hints are not taken into account when you navigate between code issues in the editor, and not shown in the marker bar.
Note that when you place the caret over a highlighted hint, no popup is shown, the corresponding message only appears in the status bar.
note
In Visual Studio project settings, you can choose to treat warnings as errors. ReSharper is aware of this option and highlights warnings accordingly: if this setting is on, then issues that correspond to compiler warnings will be highlighted as errors. This setting is configurable in the project properties: Project | [Project Name] Properties | Treat warnings as errors and can be applied to all warnings if All is selected or to the specified warnings only.
When you inspect code in specific scope, ReSharper adds corresponding icons to the detected issues and allows sorting issues by the severity level in the Inspection Results window.
ReSharper groups configurable code inspections by several categories. These categories roughly define purposes of inspections and kinds of code issues that they detect. The categories are used to group code inspections on the Code Inspection | Inspection Severity page of ReSharper options Alt+R, O, and to group code issues found in specific scope and displayed in the Inspection Results window.
- Potential Code Quality Issues
This category includes inspections that detect critical issues (code smells), mostly with Error or Warning level. This category also includes inspections that ensure localization assistance.
- Common Practices and Code Improvements
This category groups inspections that hunt for medium severity issues that mainly affect code readability.
- Redundancies in Code
Code inspections in this category look for redundancies and dead code, which affect code readability and style, and could be safely removed. Some code redundancies cannot be fixed automatically, and quick-fixes for them are performed in the interactive mode, requiring the user input. But the majority of the redundancies can be fixed without user interaction, using either fix in scope or code cleanup.
- Language Usage Opportunities
This category includes code inspections, mostly with the suggestion severity level, which notify you when more advanced language constructs can be used. These inspections detect syntax of outdated language versions and suggest using features from more modern language versions. For most of the supported languages, language version can be detected automatically or set manually.
- Code Style
Inspections in this category detect violations of code syntax styles. In contrast to most code inspections, these inspections can either detect the same code construct as a code issue or not depending on the corresponding code style rule configured on the Code Editing | [Language] | Syntax Style page of ReSharper options Alt+R, O. You can also fix issues that these inspection detect using code cleanup.
- Constraints Violations
This category includes code inspections, mostly with the warning severity level, which detect violations related to symbol attributes, including ReSharper's code annotations, and other similar issues.
- Redundancies in Symbol Declaration
This category includes code inspections, mostly with the warning severity level, which detect empty and unused symbol declarations.
- Spelling Issues
These inspections detect typos in various contexts.
- Formatting
Inspections in this category detect code formatting problems.
- Clang-Tidy Checks
Inspections in this category are provided by Clang-Tidy — a powerful open-source code analysis tool integrated with ReSharper.
- Clang
Inspections in this category correspond to Clang compiler warnings integrated with ReSharper.
- Clang Static Analyzer Checks
Inspections in this category are diagnostics from Clang Static Analyzer integrated with ReSharper.
All static analyzer checks are disabled by default, since enabling them significantly slows down Clang-Tidy.
- Unreal Engine
Inspections in this category are specific to Unreal Engine projects.
- Unreal Build System
Inspections in this category are specific to Unreal Engine projects.
- Unity
Inspections in this category report code issues specific to Unity projects.
note
Unity features in ReSharper rely on the Unity Support plugin. The plugin is free and authored by JetBrains.
To install the plugin, select ReSharper | Extension Manager… from the main menu, find Unity Support plugin and click Install.
- Unity Burst Compiler Warnings
Inspections in this category report warnings of the Unity Burst Compiler before the code is actually compiled.
- Unity Performance Inspections
Inspections in this category report computationally inefficient patterns Unity projects.
Each configurable code inspection has two unique identifiers that you can use to configure it. Let's take the Possible 'System.NullReferenceException' inspection as an example:
- Inspection ID
is used to suppress the inspection with a comment for a single issue:
// ReSharper disable once PossibleNullReferenceExceptionor from the comment to the end of the file:
// ReSharper disable PossibleNullReferenceExceptionor, alternatively with an attribute for a type or a method:
[SuppressMessage("ReSharper", "PossibleNullReferenceException")].
- Inspection EditorConfig property
can be used to configure the inspection from .editorconfig files. For example, you can change the inspection's severity level to Error with the following line:
resharper_possible_null_reference_exception_highlighting=error
You can find identifiers for each configurable inspection in the Code inspection index — just choose a language page and then use the browser search to find the details of the desired inspection.
- Code Inspections in C#
- Code Inspections in VB.NET
- Code Inspections in JavaScript
- Code Inspections in TypeScript
- Code Inspections in C++
- Code Inspections in XAML
- Code Inspections in HTML
- Code Inspections in CSS
- Code Inspections in ASP.NET
- Code Inspections in HttpHandler or WebService
- Code Inspections in Razor
- Code Inspections in Regular expressions
- Code Inspections in Resource files
- Code Inspections in Web.config
- Code Inspections in MSBuild
- Code Inspections in NAnt
- Code Inspections in XML
- Code Inspections in Route templates
- Code Inspections in Blazor