Start, pause, resume, and stop
To debug a process — your application, a unit test, a static method, or anything that has an executable configuration, you need to have this process running with the attached debugger.
Start debugging session
There are several options for starting a debugging session:
If the source code can be started from the IDE, press Shift+F9 or click
Debug on the toolbar. This way you will start the currently selected run/debug configuration with the attached debugger (in the debug mode).
If the application is already running, attach the debugger to it. This way of debugging is convenient if you develop the application but are unable to launch it directly from the IDE.
In Windows, you can set JetBrains Rider as the default just-in-time (JIT) debugger and start it each time a process calls for the JIT debugger.
Launch a run configuration in debug mode
To use the currently selected configuration, do one of the following:
Press Shift+F9.
Click
Debug on the toolbar.
Choose from the main menu.
To debug another configuration, press Alt+Shift+F9 or select from the main menu, pick the desired configuration, and then press Enter.
If the currently selected configuration is .NET Project, .NET Static Method, .NET Executable, or .NET Launch Settings Profile, you can start debugging and then suspend the program in one go using the following actions:
Start Debugging and Step Over F8 or Start Debugging and Step Into F7 — starts the debugging and then breaks the execution at the entry point of the selected run configuration.
Start Debugging and Run to Cursor Alt+F9 — starts the debugging and then breaks the execution at the line where your caret is. If the execution encounters a breakpoint before the current line, it will break at the breakpoint.
Start Debugging and Run to Cursor Non-Stop Ctrl+Alt+F9 — starts the debugging and then breaks the execution at the line where your caret is. If there are breakpoints on the execution path, they will be ignored.
You can also invoke these actions on the toolbar of the Debug window or from the main menu, under .
Use JetBrains Rider as the default JIT debugger
Press Ctrl+Alt+S or alternatively go to in the main menu, then choose on the left.
Click Set rider as default debugger.
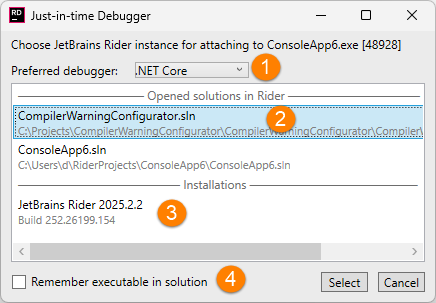
When JetBrains Rider is set as the default JIT debugger and a process calls
Debugger.Launch, you will see a dialog that helps you choose how to start the debugger:Select the debugger you want to use (.NET Core, .NET Framework, or Native)
If the solution with the application source code is open, you can pick it from the list of opened solutions.
Alternatively, you can choose a JetBrains Rider installation. In this case, the debugger will start in an empty solution, and you will be able to debug decompiled code of the process.
An additional checkbox allows you to remember the selected option, in which case for every future attempt, the debugger will be attached automatically.
Pause (suspend or break) execution
The main difference of running a program and debugging it is that the debugger can freeze the execution (it is also called 'pause', 'suspend', or 'break') so that you can examine the program in this frozen state.
When the code is running in debug mode, there are two ways to suspend it:
Set breakpoints in the code that you want to examine and wait until one of them is hit.
Break program execution with Ctrl+D, P. The debugger will finish the statement that is executing at the moment you pause, and then stop at the statement that should be executed next.
In the suspended state, the current execution point — the next statement to be executed — is marked with a yellow execution pointer ![]() in the left-hand gutter of the editor. To quickly find the current execution point, press Alt+F10 or click Show Execution Point
in the left-hand gutter of the editor. To quickly find the current execution point, press Alt+F10 or click Show Execution Point ![]() in the Debug window.
in the Debug window.
Resume execution
To resume the execution of a suspended process, press F9 or click Resume Program in the Debug window. The process will continue running until it hits a breakpoint, until it exits, until you stop the execution or detach the debugger.
If you debug a process that has its own window, the operating system focus will be switched to that window. If you want the focus to stay in JetBrains Rider after resuming the debugged process, clear the Focus target process after resume on the Build, Execution, Deployment | Debugger settings page Ctrl+Alt+S.
Stop execution
To finish the debugging session, press Ctrl+F2, select in the menu, or click Stop in the Debug window.
This will detach the debugger from the application and make the application exit (in case you have run it from JetBrains Rider).