Rename refactorings
Last modified: 18 March 2021
Shortcut for the action: Shift+F6
General refactoring settings:
In-place refactoring is available
tip
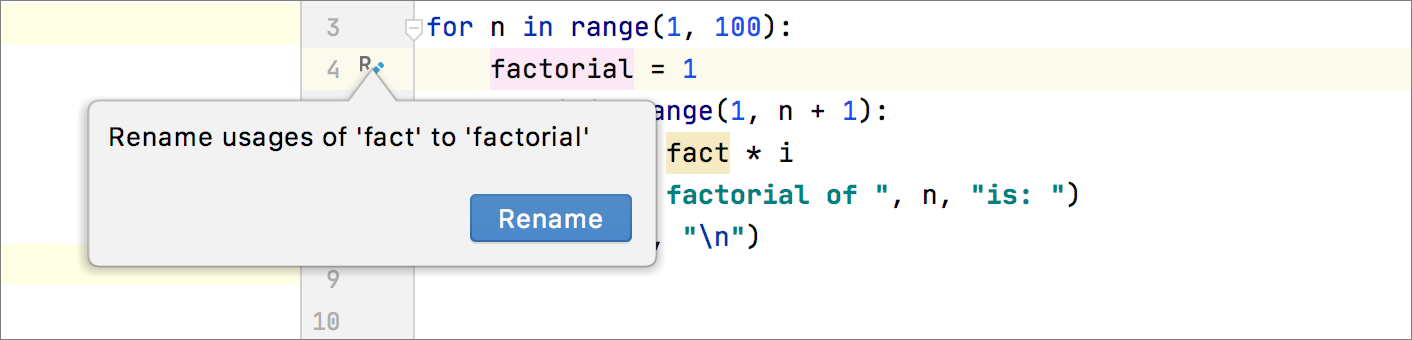
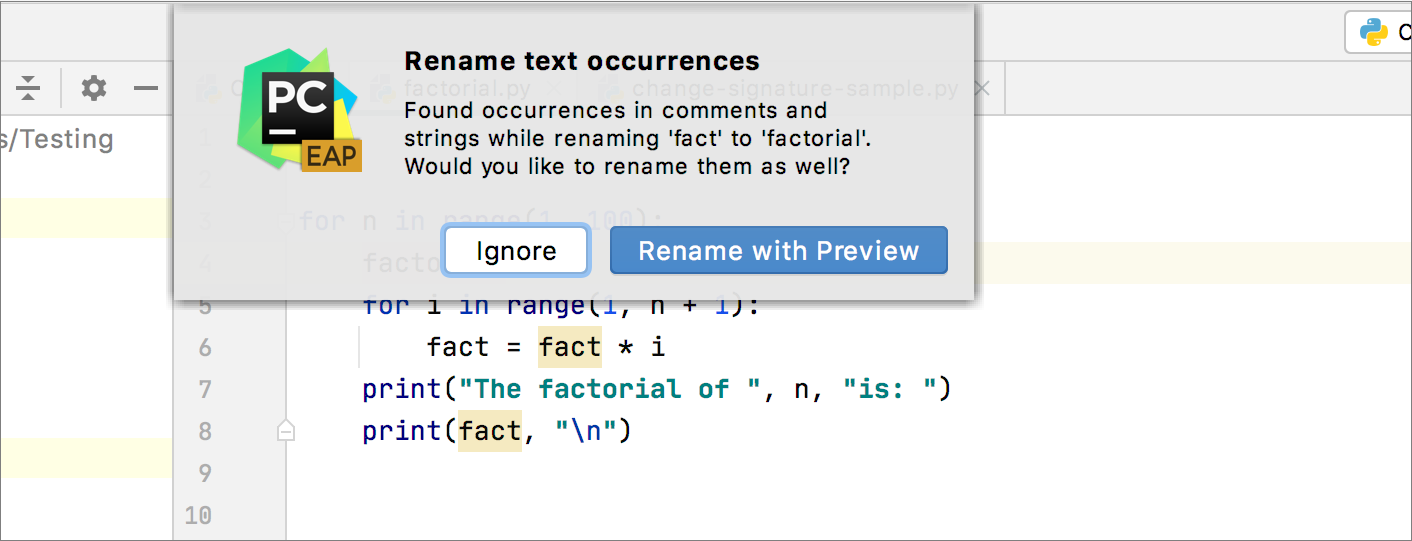
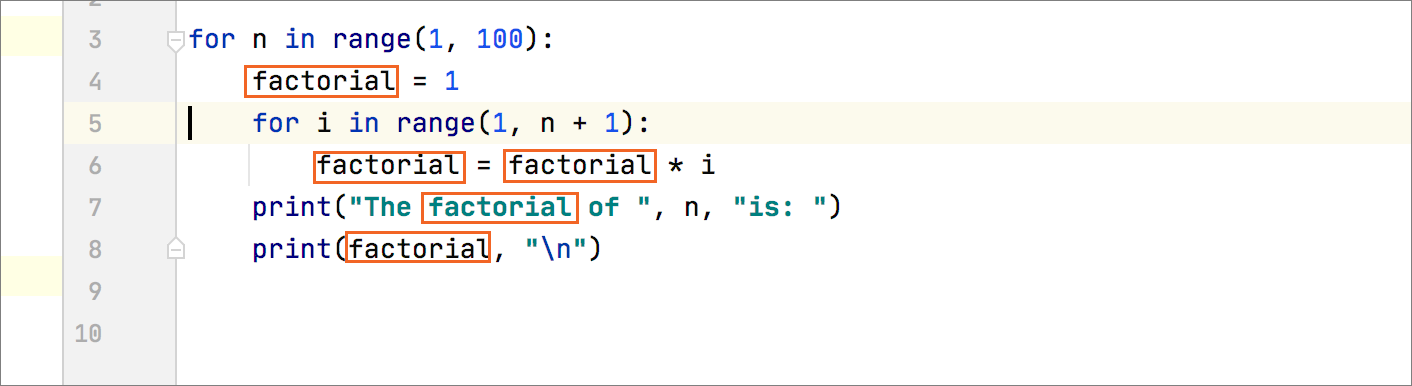
When you rename methods that are declared in interfaces, you can also review and rename their implementations as well. The refactoring changes are displayed on the Refactoring Preview tab in the Find tool window.
note
You cannot rename the .idea project directory since PyCharm always reads the project files from the directory with that exact name. Also you cannot rename any element that is defined outside of the project, for example, in an imported package.
tip
To rename just a part of variable and not the whole thing, clear the Preselect old name option located in in the Refactorings section.