Use EditorConfig
tip
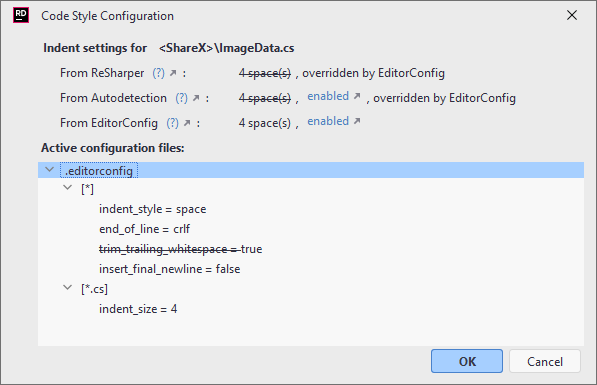
You can study all formatting style settings that affect the current file in the Code Style Configuration dialog ( Help | Find Action | Show Code Style Configuration).
JetBrains Rider supports code formatting styles, code syntax styles, C# naming styles, and code inspection severity levels defined in the EditorConfig format.
EditorConfig is a configuration file convention that is used to define and maintain consistent code styles between team members working on the same code as well as between different editors and IDEs that they might use. The styles are saved in INI-like files named .editorconfig, where section names are file masks and properties inside a section define code styles for files matching that masks.
tip
To create an .editorconfig file in Windows Explorer, create a file named .editorconfig., which will be automatically renamed to .editorconfig.
As EditorConfig convention suggests, JetBrains Rider will apply code styles defined in files named .editorconfig in the directory of the current file and in all its parent directories until it reaches the root filepath or finds an EditorConfig file with root=true. File masks specified in .editorconfig files, for example *Test.cs are also taken into account.
JetBrains Rider understands standard EditorConfig properties, most frequently used .NET-coding-convention EditorConfig properties, and provides a set of custom EditorConfig properties, which allow for much more granular configuration of formatting, syntax, and code inspection rules — in fact, each code style preference that you can configure in the JetBrains Rider settings dialog has its own EditorConfig property. This means that you can maintain the entire configuration of code style and inspection rules in EditorConfig files . Below is an example of EditorConfig properties supported by JetBrains Rider:
root = true
[*]
# Most of the standard properties are supported
indent_size=2
max_line_length=100
# Most frequently used .NET-coding-convention properties are supported
csharp_space_between_parentheses=expressions, type_casts, control_flow_statements
csharp_style_var_for_built_in_types=true
# dotnet_diagnostic rules are supported
dotnet_diagnostic.CS1058.severity = hint
# JetBrains Rider custom properties for code formatting styles
resharper_csharp_brace_style=next_line
resharper_csharp_blank_lines_around_invocable=2
# JetBrains Rider custom properties for code syntax styles
csharp_default_private_modifier=explicit
braces_for_ifelse=not_required
# JetBrains Rider custom properties for code inspections
resharper_possible_null_reference_exception_highlighting=error
resharper_replace_with_string_is_null_or_empty_highlighting=noneBy default, JetBrains Rider takes into account EditorConfig properties and they will override preferences defined in JetBrains Rider settings . If you want JetBrains Rider to ignore EditorConfig styles for code formatting and code syntax , clear the corresponding checkbox on the Editor | Code Style | C++ | General page of JetBrains Rider settings .
To configure code inspections and naming styles from EditorConfig, you have to select the Read settings from editorconfig, project settings and rule sets checkbox on the Editor | Inspection Settings page of JetBrains Rider settings .
When EditorConfig support is enabled and there are .editorconfig files that affect the current file, JetBrains Rider will help you understand which EditorConfig styles are applied and where these settings come from:
On JetBrains Rider code style and formatting options pages , you will see a yellow warning if at least one preference on the page is overridden by EditorConfig styles for the current file, each overridden preference will also be highlighted with yellow. For example:
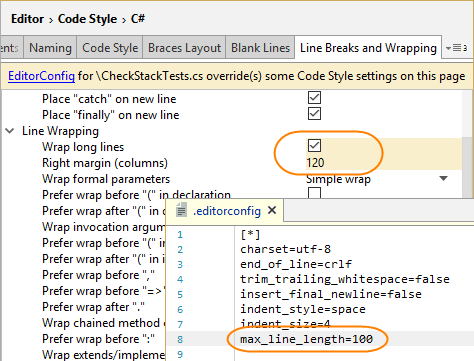
In the Code Style Configuration dialog, you can see and study all .editorconfig files that affect the current file:
note
JetBrains Rider also supports .NET code analysis rules and (unlike Visual Studio) standard EditorConfig properties if they are defined in a .globalconfig file which is referenced from your project file.
If you are going to share code style settings via EditorConfig, you may want to export the styles already configured in JetBrains Rider to the .editorconfig file.
Press CtrlAlt0S or choose File | Settings (Windows and Linux) or JetBrains Rider | Preferences (macOS) from the menu , then choose Editor | Code Style on the left.
Click Export next to Enable EditorConfig support. This will open the Export to .editorconfig dialog.
By default, JetBrains Rider writes the settings to a new .editorconfig file in the root directory of the current solution. If one or more .editorconfig files exist, JetBrains Rider will use the closest file in the directory hierarchy to save the settings. If necessary, you can change the destination file using the path selector at the top of the dialog.
In the Section (file mask) field, you can specify a wildcard pattern to use for the section with generated properties. Note that if you choose to export standard EditorConfig properties, they will be placed in other sections according to language conventions.
If there is an existing .editorconfig file in the specified location, there could be conflicts between values of properties that exist there and the ones that JetBrains Rider is about to save. Such properties will be shown in red and if you proceed with saving, the conflicts will be resolved in favor of the newly generated ones.
Click Export. JetBrains Rider will create or update the .editorconfig file in the specified location.
You can also save formatting styles to EditorConfig after contextual configuration of formatting rules.
In C#, you can disable the JetBrains Rider formatter using EditorConfig masks that have disable_formatter=true.
JetBrains Rider will apply the following standard EditorConfig properties:
indent_sizeindent_styletab_widthmax_line_lengthinsert_final_newline
Note that among JetBrains Rider's custom EditorConfig properties, there are properties that will override the standard properties for specific languages. For example, you can set a default indent size for all languages with indent_size property, and at the same set a different indent size for C# files with csharp_indent_size property.
Custom EditorConfig properties that JetBrains Rider provides, allow configuring code style and code inspection settings. Properties for code inspections can be found in the Code Inspections in C#. Properties for code style and formatting settings are listed in the child pages of the EditorConfig properties by language and category topic.
As of version 2023.2, JetBrains Rider supports most frequently used EditorConfig properties for the .NET coding conventions:
csharp_space_between_method_call_empty_parameter_list_parentheses
csharp_space_between_method_call_name_and_opening_parenthesis
csharp_space_between_method_declaration_empty_parameter_list_parentheses
csharp_space_between_method_declaration_name_and_open_parenthesis
csharp_space_between_method_declaration_parameter_list_parentheses
dotnet_diagnostic.*— supported for all compiler warnings.dotnet_naming_rule.*,dotnet_naming_style.*,dotnet_naming_symbols.*— will work if the specified kinds of symbols can be matched by kinds of symbols available in JetBrains Rider naming settings.